Dromornithidae
Dromornithidae, also commonly referred to as mihirungs, thunder birds or demon ducks, were a clade of large, flightless Australian birds of the Oligocene through Pleistocene epochs. All are now extinct. They were long classified in Struthioniformes, but are now usually classified as galloanseres.[1][2][3]
| Dromornithids | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Dromornis stirtoni | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Clade: | Anserimorphae |
| Order: | †Gastornithiformes |
| Family: | †Dromornithidae Fürbringer, 1888 |
| Genera | |
Dromornithids were part of the Australian megafauna. One species, Dromornis stirtoni, was 3 m (9 ft 10 in) tall. The collective term Australian megafauna is used to describe a number of comparatively large species of animals that lived in Australia until 50,000 to 20,000 years ago. The causes for the disappearance of these animals are under dispute, though hunting by humans has been identified as a potential instigator.[4][5]
It is also not clear to what degree dromornithids were carnivores. The massive, crushing beaks of some species suggest that at least some members of the family were a combination of carnivorous predators and scavengers or omnivores. Other features, such as the "hoof-like" feet, stomach structure, and eye structure that resulted in a wide field of vision but likely also created a centre blind spot of about forty degrees (which would hinder hunting significantly) suggest a more herbivorous, migratory lifestyle. The consensus is that they were indeed herbivores.[6]
The scientific name Dromornithidae derives from Greek δρομαίος, dromaios ("swift-running") and ὀρνις, ornis ("bird"). Additionally, the family has been called thunder birds, giant emus, giant runners, demon ducks and mihirungs.[7]
Classification
What the nearest relatives of this group are is a controversial issue. For many years it was thought that dromornithids were related to ratites, such as emus, cassowaries and ostriches. It is now believed that the similarities between these groups are the result of similar responses to the loss of flight. The latest idea on dromornithid relationships, based on details of the skull, is that they evolved early in the lineage that includes waterfowl (Anseriformes). However, some phylogenetic studies have recovered them as closer to gamefowl (Galliformes).[8]
Below is the general consensus of the phylogeny under the hypothesis that they are members of Anserimorphae.[9][10][11][12][13]
| Odontoanserae |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
A 2017 paper concerning the evolution and phylogeny of giant fowl by Worthy and colleagues have found phylogenetic support in finding the mihirungs to be the sister taxon to Gastornithidae.[14] Worthy et al. (2017) incorporated several new taxa and character traits into existing matrices of Galloanserae resulted in several of their phylogenies to support this grouping.[14] The authors did note the bootstrap support is weakly supported and one of their phylogenies even found gastornithiforms to be stem galliforms instead.[14] These were also weakly supported.[14] Below is a simplified phylogeny showing their one phylogeny supporting gastornithiforms as anserimorphs.[14]
| Anserimorphae |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Species
There are 7 species in Dromornithidae,[15] the smallest species was Barawertornis tedfordi, a bird about the size of a modern cassowary, weighing 80 to 95 kg (176 to 209 lb). The two species of Ilbandornis (Ilbandornis lawsoni and Ilbandornis woodburnei) were larger birds, but had more slender legs than the other dromornithids and were similar to ostriches in their build and size. Bullockornis planei (the "demon duck of doom") and Genyornis newtoni (the "mihirung") were more heavily built, stood about 2 to 2.5 m (6.6 to 8.2 ft) tall and probably reached weights of 220 to 240 kg (490 to 530 lb). The largest dromornithids were Dromornis australis, from which the family gets its name,[16] and the massive Dromornis stirtoni ("Stirton's thunderbird"). Genyornis is the best known genus.
Description and biology

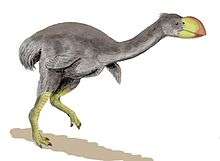
Dromornithids looked superficially like very large emus or moas. Most were heavy-bodied, with powerfully developed legs and greatly reduced wings. The last bones of the toes resembled small hooves, rather than claws as in most birds. Like emus and other flightless birds, dromornithids lost the keel on the breastbone (or sternum), that serves as the attachment for the large flight muscles in most bird skeletons. Their skull also was quite different from that of emus. These birds ranged from about the size of a modern cassowary 1.5 to 1.8 m (4 ft 11 in to 5 ft 11 in) up to 3 m (9 ft 10 in) in the case of Dromornis stirtoni, possibly the largest bird that ever lived after the elephant bird (Vorombe).
Diet
It has been generally thought that the dromornithids were plant eaters, a belief currently considered common scientific consensus.[17] This belief is based on:
- the lack of a hook at the end of the bill
- the lack of talons on the toes
- the association of gizzard stones (caveat: gastroliths are also found in the stomachs of some carnivores, such as modern crocodiles)
- the large number of individuals occurring together, suggesting flocking behaviour
The very large skull and deep bill of Bullockornis, however, are very unlike those found in large herbivorous birds such as moas. If this dromornithid ate plants, it was equipped to process very robust material that has thus far not been identified. Growing and maintaining such a large head would be detrimental and probably not occur unless it provided a substantial benefit of some sort, although it may have just been a social signal. However, it would require a highly developed or complex social structure to evolve.
It has been suggested that, despite the indications of herbivory in some dromornithids, Bullockornis may have been a carnivore or possibly a scavenger. However, most authorities consider it to be a herbivore.[17]
Locomotion
Because of their enormous size, dromornithids have been considered to have been slow lumbering creatures. Their legs are not long and slender like those of emus or ostriches, which are specialised for running. However, biomechanical analysis of the attachments and presumed sizes of the muscles suggest that dromornithids might have been able to run much faster than originally thought, making up for their less than ideal form with brute strength.
Sexual dimorphism
At least Dromornis shows evidence of sexual dimorphism. Males were more robust and heavier than females, though not necessarily taller.[18]
Distribution
Records of these birds are known only from Australia. Most of the records of dromornithids come from the eastern half of the continent, although fossil evidence has also been discovered in Tasmania and Western Australia. At some Northern Territory sites they are very common, sometimes comprising 60-70% of the fossil material. A fragment of a dromornithid-sized foot bone has been found in Antarctica, but whether it represents these birds is uncertain.
The earliest bones identified were found in Late Oligocene deposits at Riversleigh, northwest Queensland. There are foot impressions from the Early Eocene in southeast Queensland that may be referable to dromornithids. The most recent evidence, of Genyornis newtoni, has been found at Cuddie Springs, north central New South Wales and dated at 31,000 years old.[19]
Extinction
The reasons for the extinction of this entire family along with the rest of the Australian megafauna by the end of the Pleistocene are still debated. It is hypothesized that the arrival of the first humans in Australia (around 48-60 thousand years ago) and their hunting and landscape-changing use of fire may have contributed to the disappearance of the megafauna. However, drought conditions during peak glaciation (about 18,000 years ago) are a significantly confounding factor. Recent studies[20] appear to rule this out as the primary cause of extinction, but there is also some dispute about these studies.[21] It is likely that a combination of all of these factors contributed to the megafauna's demise. However, there is significant disagreement about the relative importance of each.
Discovery
The most recent species, Genyornis newtoni, was certainly known to Aborigines during the Late Pleistocene. Cave paintings thought to depict this bird are known, as are carved footprints larger than those considered to represent emus. At Cuddie Springs, Genyornis bones have been excavated in association with human artifacts. The issue of how much of an impact humans had on dromornithids and other large animals of the time is unresolved and much debated. Many scientists believe that human settlement and hunting were largely responsible for the extinction of many species of the Australian megafauna.
The first Europeans to encounter the bones of dromornithids may have been Thomas Mitchell and his team. While exploring the Wellington Caves, one of his men tied his rope to a projecting object which broke when he tried to descend the rope. After the man had climbed back up, it was found that the projecting object was the fossilised long bone of a large bird. The first species to be described was Dromornis australis. The specimen was found in a 55 metre deep well at Peak Downs, Queensland, and subsequently described by Richard Owen in 1872.
Extensive collections of any dromornithid fossils were first made at Lake Callabonna, South Australia.
In 1892, E. C. Stirling and A. H. C. Zietz of the South Australian Museum received reports of large bones in a dry lake bed in the northwest of the state. Over the several next years, they made several trips to the site, collecting nearly complete skeletons of several individuals. They named the newly found species Genyornis newtoni in 1896. Additional remains of Genyornis have been found in other parts of South Australia and in New South Wales and Victoria.
Other sites of importance were Bullock Creek and Alcoota, both in the Northern Territory. The specimen recovered there remained unstudied and unnamed until 1979, when Patricia Rich described five new species and four new genera.[15]
The best represented bones of dromornithids are vertebrae, long bones of the hindlimb and toe bones. Ribs and wing bones are uncommonly preserved. The rarest part of the skeleton is the skull. For many years, the only skull known was a damaged specimen of Genyornis. Early reconstructions of dromornithids made them appear like oversized emus. Peter Murray and Dirk Megirian of Australia's Northern Territory Museum recovered enough skull material of Bullockornis to give a good idea of what that bird's head looked like. It is now known that the Bullockornis skull was very large, with the enormous bill making up about two-thirds of it. The bill was deep, but rather narrow. The jaws had cutting edges at the front as well as crushing surfaces at the back. There were attachments for large muscles, indicating that Bullockornis had a powerful bite. More fragmentary remains of the skull of Dromornis suggest that it, too, had an oversized skull.
Bones are not the only remains of dromornithids that have been found:
- The polished stones that the birds kept in their gizzards (muscular stomachs) occur at a number of sites. These stones, called gastroliths, played an important role in their digestion by breaking up coarse food or matter that was swallowed in large chunks.
- Series of footprints, called trackways, have been found at several sites.[22][23][24]
- Impressions of the inside of the skull cavity (endocranial casts or endocasts) have been found. Endocasts are formed when sediments fill the empty skull, after which the skull is destroyed. These fossils give a fairly accurate picture of dromornithid brains.
See also
- Fossil birds
- Later Quaternary Prehistoric Birds
Notes
- Murray, P. F. & Megirian, D. (1998)
- Murray, P. F. & Vickers-Rich, P. (2004)
- Worthy, T.; Mitri, M.; Handley, W.; Lee, M.; Anderson, A.; Sand, C. (2016). "Osteology supports a steam-galliform affinity for the giant extinct flightless birds Sylviornis neocaledoniae (Sylviornithidae, Galloanseres)". PLOS ONE. 11 (3): e0150871. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1150871W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0150871. PMC 4814122. PMID 27027304.
- Miller, G. H. et al. (1999)
- Roberts, R. G. et al. (2001)
- Gerald Mayr, Paleogene Fossil Birds, 2009
- Mihirung paringmal is an Aboriginal word from the Tjapwuring people of western Victoria, that means 'giant bird'.
- Worthy, T. H.; Mitri, M.; Handley, W. D.; Lee, M. S. Y.; Anderson, A.; Sand, C. (2016-03-30). "Osteology Supports a Stem-Galliform Affinity for the Giant Extinct Flightless Bird Sylviornis neocaledoniae (Sylviornithidae, Galloanseres)". PLOS ONE. 11 (3): e0150871. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1150871W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0150871. PMC 4814122. PMID 27027304.
- Murrary, P.F; Vickers-Rich, P. (2004). Magnificent Mihirungs: The Colossal Flightless Birds of the Australian Dreamtime. Indiana University Press.
- Bourdon, E. (2005). "Osteological evidence for sister group relationship between pseudo-toothed birds (Aves: Odontopterygiformes) and waterfowls (Anseriformes)". Naturwissenschaften. 92 (12): 586–91. Bibcode:2005NW.....92..586B. doi:10.1007/s00114-005-0047-0. PMID 16240103.
- Agnolín, F. (2007). "Brontornis burmeisteri Moreno & Mercerat, un Anseriformes (Aves) gigante del Mioceno Medio de Patagonia, Argentina". Revista del Museo Argentino de Ciencias Naturales. 9: 15–25. doi:10.22179/revmacn.9.361.
- Livezey, B.C.; Zusi, R.L. (2007). "Higher-order phylogeny of modern birds (Theropoda, Aves: Neornithes) based on comparative anatomy. II. Analysis and discussion". The Science of Nature. 149 (1): 1–95. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2006.00293.x. PMC 2517308. PMID 18784798.
- Agnolín, F.L.; Egli, F.B.; Chatterjee, S.; Marsà, J.A.G (2017). "Vegaviidae, a new clade of southern diving birds that survived the K/T boundary". The Science of Nature. 104 (87): 87. Bibcode:2017SciNa.104...87A. doi:10.1007/s00114-017-1508-y. PMID 28988276.
- Worthy, T.H.; Degrange, F.J.; Handley, W.D.; Lee, M.S.Y. (2017). "The evolution of giant flightless birds and novel phylogenetic relationships for extinct fowl (Aves, Galloanseres)". Royal Society Open Science. 11 (10): 170975. Bibcode:2017RSOS....470975W. doi:10.1098/rsos.170975. PMC 5666277. PMID 29134094.
- Rich, P. (1979)
- Rich, Pat Vickers (1980). "The Australian Dromornithidae: a group of extinct large ratites". Contributions in Science. 330: 93––103.
- Peter F. Murray,Patricia Vickers-Rich, Magnificent Mihirungs: The Colossal Flightless Birds of the Australian Dreamtime
- Sexual dimorphism in the late Miocene mihirung Dromornis stirtoni (Aves: Dromornithidae) from the Alcoota Local Fauna of central Australia, DOI:10.1080/02724634.2016.1180298, Received: 9 Jul 2015 Accepted: 20 Feb 2015 Published online: 07 Jun 2016
- Field, J. H. & Boles, W. E. (1998)
- Roberts et al. 2001
- Wroe et al. 2002
- Vickers-Rich, P. & Molnar, R. E. (1996)
- Rich, P. & Gill, E. (1976)
- Rich, P. & Green, R. H. (1974)
References
- Field, J. H.; Boles, W. E. (1998). "Genyornis newtoni and Dromaius novaehollandiae at 30,000 b.p. in central northern New South Wales". Alcheringa. 22 (2): 177–188. doi:10.1080/03115519808619199.
- Murray, P. F.; Megirian, D. (1998). "The skull of dromornithid birds: anatomical evidence for their relationship to Anseriformes (Dromornithidae, Anseriformes)". Records of the South Australian Museum. 31: 51–97.
- Murray, P. F. & Vickers-Rich, P. (2004) Magnificent Mihirungs: The Colossal Flightless Birds of the Australian Dreamtime. Indiana University Press.
- Miller, G. H.; Magee, J. W.; Johnson, B. J.; Fogel, M. L.; Spooner, N. A.; McCulloch, M. T.; Ayliffe, L. K. (1999). "Pleistocene extinction of Genyornis newtoni: human impact on Australian megafauna". Science. 283 (5399): 205–208. doi:10.1126/science.283.5399.205. PMID 9880249.
- Rich, P (1979). "The Dromornithidae, an extinct family of large ground birds endemic to Australia". Bulletin of the Bureau of Mineral Resources, Geology and Geophysics. 184: 1–190.
- Rich, P.; Gill, E. (1976). "Possible dromornithid footprints from Pleistocene dune sands of southern Victoria, Australia". Emu. 76 (4): 221–223. doi:10.1071/mu9760221.
- Rich, P.; Green, R. H. (1974). "Footprints of birds at South Mt Cameron, Tasmania". Emu. 74 (4): 245–248. doi:10.1071/mu974245.
- Roberts, R. G.; Flannery, T. F.; Ayliffe, L. A.; Yoshida, H.; Olley, J. M.; Prideaux, G. J.; Laslett, G. M.; Baynes, A.; Smith, M. A.; Jones, R.; Smith, B. L. (2001). "New ages for the last Australian megafauna: continent-wide extinction about 46,000 years ago". Science. 292 (5523): 1888–1892. Bibcode:2001Sci...292.1888R. doi:10.1126/science.1060264. PMID 11397939.
- Vickers-Rich, P.; Molnar, R. E. (1996). "The foot of a bird from the Eocene Redbank Plains Formation of Queensland, Australia". Alcheringa. 20: 21–29. doi:10.1080/03115519608619220.
- Williams, D. L. G. (1981). "Genyornis eggshell (Dromornithidae; Aves) from the Late Pleistocene of South Australia". Alcheringa. 5 (2): 133–140. doi:10.1080/03115518108565426.
- Williams, D. L. G.; Vickers-Rich, P. (1992). "Giant fossil egg fragment from the Tertiary of Australia". Contributions in Science, Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. 36: 375–378.



