Dnieper River System of Dams
The Dnieper River system of dams (Ukrainian: Дніпровський каскад ГЕС) was created to prevent uncontrolled flooding[1] and improve water transportation infrastructure. Coordination and operation of all dams on Dnieper is conducted by government company Ukrhydroenerho.[2] The system of dams is also known as Dnieper Cascade of HES. In 1970, the Kyiv dam partially prevented flooding in comparison with the 1931 Kiev flooding.[3]
As with any dam, the water reservoirs of the Dnieper River in Ukraine pose a significant threat of a large-scale, human-made disaster if their dams fail. Such a threat is typical for reservoir dams; however, the Dnieper system of dams is especially dangerous due to its proximity to the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone. Those concerns were raised in particular in connection with the 2009 Sayano–Shushenskaya Dam disaster.[4]
To combat uncontrolled flooding, the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine had developed a program of flooding forecasting; however, as of 2012, the Government of Ukraine refused to adopt it.[5]
Infrastructure of "Dnieper Cascade"
Power stations and dams
- Dnieper Hydroelectric Station
- Middle Dnieper Hydroelectric Power Plant
- Kiev Hydroelectric Station
- Kaniv Hydroelectric Station
- Kremenchuk Hydroelectric Station
- Kakhovka Hydroelectric Station
- Kiev Hydro-Accumulating Power Station
On the Dnieper tributary Pripyat River, not far from Dnieper main course, is located nuclear station in Chornobyl (Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant).
Water reservoirs
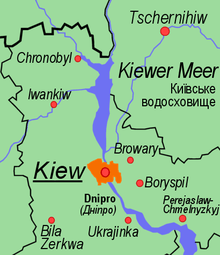
On the Prypiat river near its confluence with the Dnieper, there used to be a Chernobyl Reservoir to provide coolant to the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant.
Concerns
Like other reservoirs, Dnieper reservoirs pose a potential threat of causing major flooding if their dams fail. Such damage may be inflicted by a powerful natural disaster (e.g., an earthquake), a human-made disaster, or a deliberate attack by terrorists or enemy forces at war.
The Dnieper reservoirs contain an additional major threat—after the Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster in 1986, radionuclides washed away by rains badly contaminated the bottom silt of the Kiev Reservoir and presumably the others. During the years following the disaster, there were suggestions to drain the Kiev Reservoir because it was too shallow. It appeared that, if done, this could have created the threat of the tremendous amounts of radioactive dust travelling by wind, possibly affecting Europe.
The dams are supposed to be strong enough to survive natural and terrorist threats. Both their construction schemes and government efforts work towards this goal. For instance, some engineers guarantee that every Dnieper dam will survive an earthquake (to its typical regional extent), meteorite or aircraft falling.[6] There are also countermeasures against overflooding and malfunction of dams. Authorities pay significant attention to safeguarding the dams and bridges by special units of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and other security agencies.[7]
A failure of the Kiev Reservoir would cause a flooding of the low-lying areas of Kiev, mainly densely populated residential neighborhoods.[8] The aftermath of a possible complex flooding also include the spread of radioactive material from the Chernobyl disaster contained in the reservoirs, the widespread contamination by industrial and urban wastes and creation of swamps on bottoms of emptied reservoirs.
In 2001–03 the Security Service of Ukraine organized exercises on the Kiev Hydroelectric station, simulating a possible terrorist attack. The results of the exercises were considered satisfactory.[8]
Government position
New concerns arose in 2005 after a fake terrorist threat case. A police officer, dissatisfied with his commanders, anonymously called an emergency line stating that he had planted a bomb in a cargo train crossing the Kiev Reservoir's dam. An immediate check proved the threat to be fake and the alerter was arrested. But the incident caused another wave of public concern.[9]
In 2012, the former Kiev Hydroelectric Power Plant manager and veteran stated that its dam is guaranteed capable to withstand any physical threat except large space object impact or deliberate military attack of significant scale. However, an emergency plan exists to safely minimize consequences of a space impact if there would be an early warning on it.[10]
News media
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hydroelectric power plants in Ukraine. |
References
- Notes
- Tsalyk, S. Almost-Venice: Millennium history of flooding in Kiev (Майже Венеція: тисячолітня історія потопів у Києві). BBC in Ukrainian. 26 August 2018
- Yatsyk, A., Voshchynskyi, K. Dnieper Cascade of HES (ДНІПРО́ВСЬКИЙ КАСКА́Д ГЕС). Encyclopedia of Modern Ukraine. 2008
- Andriy Manchuk. The Great Kiev flooding. How it was (Велика київська повінь. Як це було). Istorychna Pravda (Ukrayinska Pravda). 4 April 2013
- Everything what need to be aware of the Ukrainian HES. The Ukrainian Week. 28 August 2009
- Anna Poludenko. How to dodge natural disaster? (Як уникнути природної катастрофи?). Den. 21 August 2012
- "The dam of the Kiev's power plant will be around for a thousand of years", - the chief engineer of the "Skhema Dnepra" [the "Pattern of the Dnieper river"] institution Yefim Bakshayev seems to be tired of repeating those words. "The catastrophe is possible if it is directly hit by the nuclear bomb. I think that no one would then be around to be saved from flooding. Yes, the accidents are possible at peace time if the metallic structures of the dam are not replaced on time. But this is taken care of for the Kiev dam. Besides, in the Netherlands, one third of the country spans across the territories gained from the sea. People build the reservoirs there for 400 years and no one is afraid of this proximity. Most important is to build the dam competently, provide it with modern equipment and follow on its operation [...] The capital is fully protected from flooding"
(in Russian) Lyudmila Kovalchuk, "Kiev Reservoir: where the radioactive silt is now there were 52 villages Archived 2007-03-27 at the Wayback Machine", Segodnya, March 23, 2005. - (in Ukrainian) Ю. П. Сурмін, Р. Н. Аврамчук, СТРУКТУРИ, ЗАСОБИ І СТРАТЕГІЯ РОЗВ'ЯЗАННЯ ПРОБЛЕМ НАЦІОНАЛЬНОЇ БЕЗПЕКИ Archived 2007-09-28 at the Wayback Machine (Framework, means and strategy of the state security.), by National Institute of State Security Archived 2006-07-04 at the Wayback Machine, Ukrainian governmental agency.
- (in Russian and Ukrainian) Zoya Vishnevskaya "Before the thunder Rolls".Zerkalo Nedeli (Mirror Weekly), March 13–19, 2004. Available online in Russian Archived 2005-11-01 at the Wayback Machine, in Ukrainian
- (in Russian and Ukrainian) "The caller is out of the calling area", Zerkalo Nedeli (Mirror Weekly), April 23 - May 6, 2005, available online in Russian Archived 2005-11-29 at the Wayback Machine, in Ukrainian
- Киевскую дамбу может разрушить только метеорит или война — Эксперт
- Bibliography
- (in Russian) "The strange initiative", Kievskiye Vedomosti, January 31, 2002
- (in Russian) Chernovetsky will check "the most dangerous place on the planet", Korrespondent.net, July 19, 2006
- “Комсомольская правда” об угрозах плотины Киевской ГЭС и водохранилища
- “Аргументы и факты” о реальных угрозах дамбы Киевского водохранилища и ГЭС
- “Известия” о проблематике плотины Киевского водохранилища и ГЭС
- Эксперт УНИАН об угрозах дамбы Киевского водохранилища
External links
- Battle of Chernobyl: The Consequences - details about the radioactive contamination
- Prymak, K. Dnieper Cascade of HES. Ukrainian Soviet Encyclopedia
- Chernousenko, O. HES Cascades (Каскади ГЕС). Power Generation: history, modernity, future.
- Dnipro Cascade of Hydroelectric Stations. Encyclopedia of Ukraine
- The 1970 flooding in Kiev. Istorychna Pravda (Ukrayinska Pravda).
- Parnikoza, I. History of formation and structure of Dnieper valley near Kiev (Історія формування та будова долини Дніпра у Києві). Kiev islands and river embankment of Dnieper, view through the ages.
- Tetiana Stetsenko. Is there threat to Cherkasy residents from the Dnieper Cascade (Чи загрожує черкащанам Дніпровський каскад?). Cherkasy 24. 30 November 2018.