Dehumidifier
A dehumidifier is an electrical appliance which reduces and maintains the level of humidity in the air, usually for health or comfort reasons, or to eliminate musty odor and to prevent the growth of mildew by extracting water from the air. It can be used for household, commercial, or industrial applications. Large dehumidifiers are used in commercial buildings such as indoor ice rinks and swimming pools, as well as manufacturing plants or storage warehouses.[1]

Overview
Dehumidifiers extract water from air that passes through the unit. There are two types of dehumidifiers - condensate dehumidifiers and desiccant dehumidifiers.
Condensate dehumidifiers use a refrigerator to collect water known as condensate, which is normally greywater but may at times be reused for industrial purposes. Some manufacturers offer reverse osmosis filters to turn the condensate into potable water.[2] Some designs, such as the ionic membrane dehumidifier, dispose of water as a vapour rather than liquid.
Desiccant dehumidifiers (known also as absorption dehumidifiers) bond moisture with hydrophilic materials such as silica gel. Cheap domestic units contain single-use hydrophilic substance cartridges, gel, and powder. Larger commercial units contain hot air recovery systems in order to remove humid air from outside the room.
The energy efficiency of dehumidifiers can vary widely.
History
The first dehumidifier was created by American inventor Willis Carrier in 1902 to dehumidify a Brooklyn printing plant.[3] Carrier cited the discovery as later motivating further discoveries in air conditioning.[4]
Thermal condensation dehumidification
These methods rely on drawing air across a cold surface. Since the saturation vapor pressure of water decreases with decreasing temperature, the water in the air condenses on the surface, separating the water from the air.
Refrigeration (electric)
Electric refrigeration dehumidifiers are the most common type of dehumidifiers. They work by drawing moist air over a refrigerated evaporator with a fan. There are 3 main types of evaporators. They are coiled tube, fin and tube, and microchannel technology.
The cold evaporator coil of the refrigeration device condenses the water, which is removed, and then the air is reheated by the condenser coil. The now dehumidified, re-warmed air is released into the room. This process works most effectively at higher ambient temperatures with a high dew point temperature. In cold climates, the process is less effective. Highest efficiency is reached above 20 °C (68 °F) and 45% relative humidity. This relative humidity value is higher if the temperature of the air is lower. .
This type of dehumidifier differs from a standard air conditioner in that both the evaporator and the condenser are placed in the same air path. A standard air conditioner transfers heat energy out of the room because its condenser coil releases heat outside. However, since all components of the dehumidifier are in the same room, no heat energy is removed. Instead, the electric power consumed by the dehumidifier remains in the room as heat, so the room is actually heated, just as by an electric heater that draws the same amount of power.
In addition, if water is condensed in the room, the amount of heat previously needed to evaporate that water also is re-released in the room (the latent heat of vaporization). The dehumidification process is the inverse of adding water to the room with an evaporative cooler, and instead releases heat. Therefore, an in-room dehumidifier will always warm the room and reduce the relative humidity indirectly, as well as reducing the humidity more directly, by condensing and removing water.
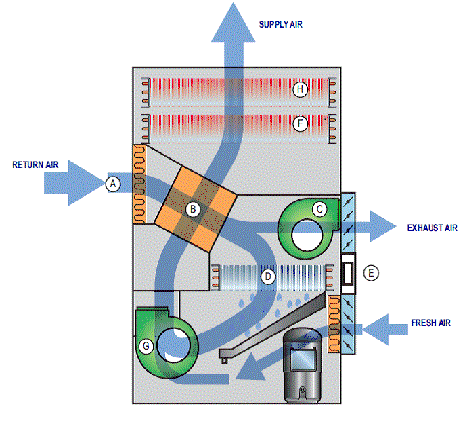
Warm, moist air is drawn into the unit at A in the diagram above. This air passes into a crossflow plate heat exchanger (B) where a substantial proportion of the sensible heat is transferred to a cool supply air stream. This process brings the extracted air close to saturation. The air then passes to the plenum chamber of the extract fan (C) where a portion of it may be rejected to outside. The amount that is rejected can be varied and is determined either by legislation on fresh air requirements, or by the requirement to maintain a fresh, odour free environment. The balance of the air then passes into the evaporator coil of the heat pump where it is cooled and the moisture is condensed. This process yields substantial amounts of latent energy to the refrigeration circuit. Fresh air is then introduced to replace the amount that was extracted and the mix is discharged by the supply fan (G) to the crossflow plate exchanger (B) where it is heated by the extract air from the pool. This pre-warmed air then passes through the heat pump condenser (F) where it is heated by the latent energy removed during the condensation process as well as the energy input to the compressor. The warm dry air is then discharged to the room.[5]
Conventional air conditioners
A conventional air conditioner is very similar to an electric dehumidifier and inherently acts as a dehumidifier when chilling the air.[6] In an air conditioner, however, the air passes over the cold evaporator coils and then directly into the room. It is not re-heated by passing over the condenser, as in a refrigeration dehumidifier. Instead, the refrigerant is pumped by the compressor to a condenser which is located outside the room to be conditioned, and the heat is then released to the outside air. Conventional air conditioners use additional energy exhausting air outside, and new air can have more moisture than the room needs, such as a pool room that already holds a high amount of moisture in the air.[7]
The water that condenses on the evaporator in an air conditioner is usually routed to remove extracted water from the conditioned space. Newer high-efficiency window units use the condensed water to help cool the condenser coil by evaporating the water into the outdoor air, while older units simply allowed the water to drip outside.
Spray dehumidifiers
When water is chilled below the atmospheric dewpoint, atmospheric water will condense onto it faster than water evaporates from it.[8] Spray dehumidifiers mix sprays of chilled water and air to capture atmospheric moisture. They also capture pollutants and contaminants like pollen, for which purpose they are sometimes called "air washers".
Makeshift dehumidifiers
Because window air conditioner units have condensers and expansion units, some of them can be used as makeshift dehumidifiers by sending their heat exhaust back into the same room as the cooled air, instead of the outside environment. If the condensate from the cooling coils is drained away from the room as it drips off the cooling coils, the result will be room air that is drier but slightly warmer.
However, many window air conditioners are designed to dispose of condensate water by re-evaporating it into the exhaust air stream, which cancels out the air humidity decrease caused by the condensation of moisture on the cooling coils. To be effective as a dehumidifier, an air conditioner must be designed or modified so that most or all of the water that condenses is drained away in liquid form, rather than re-evaporated. Even if condensate is drained, a modified air conditioner is still less efficient than a single-purpose appliance with a design optimized for dehumidification. Dehumidifiers are designed to pass air directly over the cooling coils and then the heating coils in a single efficient pass through the device.
In addition, most air conditioners are controlled by a thermostat which senses temperature, rather than a humidistat that senses humidity and is typically used to control a dehumidifier. A thermostat is not designed for the control of humidity, and controls it poorly if at all.
Ice buildup
Under certain conditions of temperature and humidity, ice can form on a refrigeration dehumidifier's evaporator coils. The ice buildup can impede airflow and eventually form a solid block encasing the coils. This buildup prevents the dehumidifier from operating effectively, and can cause water damage if condensed water drips off the accumulated ice and not into the collection tray. In extreme cases, the ice can deform or distort mechanical elements, causing permanent damage.
Better-quality dehumidifiers may have a frost or ice sensor. These will turn off the machine and allow the ice-covered coils to warm and defrost. Once defrosted, the machine will automatically restart. Most ice sensors are simple thermal switches and do not directly sense the presence or absence of ice buildup. An alternative design senses the impeded airflow and shuts off the cooling coils in a similar manner.
Thermoelectric dehumidifiers
Thermoelectric dehumidifiers use a Peltier heat pump to cool a surface and condense water vapor from the air. The design is simpler and has the benefit of being quieter compared to a dehumidifier with a mechanical compressor. However, because of its relatively poor Coefficient of Performance, this design is mainly used for small dehumidifiers. Ice buildup may be a problem, similar to problems with refrigeration dehumidifiers.
Absorption/desiccant dehumidification

This process uses a special humidity-absorbing material called a desiccant, which is exposed to the air to be conditioned. The humidity-saturated material is then moved to a different location, where it is "recharged" to drive off the humidity, typically by heating it. The desiccant can be mounted on a belt or other means of transporting it during a cycle of operation.
Dehumidifiers which work according to the absorption principle are especially suited for high humidity levels at low temperatures. They are often used in various sectors in industry so that humidity levels below 35% can be achieved.
Because of the lack of compressor parts desiccant dehumidifiers are often lighter and quieter than compressor dehumidifiers. Desiccant dehumidifiers can also operate at lower temperatures than compressor dehumidifiers as the unit does not rely on cooled coils for which the moisture condensing efficiency decreases at lower temperatures.
Ionic membrane dehumidification
An ionic membrane can be used to move humidity into or out of a sealed enclosure, operating at a molecular level without involving visible liquid water.
The solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) membrane is a low power, steady-state dehumidifier for enclosed areas where maintenance is difficult. The electrolytic process delivers dehumidifying capacities up to 0.2 grams/day from a 0.2 m³ (7 cu ft) space to 58 grams/day from an 8m³ (280 cu ft). SPE systems generally do not have high dehydration capacities, but because the water vapor is removed through electrolysis, the process is maintenance free. The process also requires very little electrical energy to operate, using no moving parts, making the ionic membranes silent in operation and very reliable over long periods of time. SPE dehumidifiers are typically used to protect sensitive electrical components, medical equipment, museum specimens, or scientific apparatus from humid environments.
The SPE consists of a proton-conductive solid polymer electrolyte and porous electrodes with a catalytic layer composed of noble metal particles.[9] When a voltage is applied to the porous electrode attached to the membrane, the moisture on the anode side (dehumidifying side) dissociates into hydrogen ions (H+) and oxygen. The hydrogen ions migrate through membrane to be discharged on the cathode (moisture discharging) side where they react with oxygen in the air, resulting in water molecules (vapor), being discharged.[10] Oxygen is released from the dehumidifying side and if a large amount of water is introduced to an airtight enclosure then oxygen can build up inside the enclosure.
Condensate

Disposal
Products using condensation technology has traditionally been using a cold surface where humidity in warm air is condensed. Today the warm condensation technology based on the concept of over-saturated steam inside a closed environment makes it possible to dehumidify air at sub-zero temperatures. This is a very energy efficient technology and equally efficient in all temperatures.
Most portable dehumidifiers are equipped with a condensate collection receptacle, typically with a float sensor that detects when the collection vessel is full, to shut off the dehumidifier and prevent an overflow of collected water. In a warm humid environment, these buckets will generally fill with water in 8–12 hours, and may need to be manually emptied and replaced several times per day to ensure continued operation.
Many portable dehumidifiers can also be adapted to connect the condensate drip output directly to a drain via a hose. Some dehumidifier models can tie into plumbing drains or use a built-in water pump to empty themselves as they collect moisture. Alternatively, a separate condensate pump may be used to move collected water to a disposal location when gravity drainage is not possible.
Central air conditioning units typically need to be connected to a drain, because manually removing the volume of condensate water extracted by such systems in containers is impractical. If the condensate water is directed into the sewer system, it should be suitably trapped to prevent septic odors and sewer gases from entering the building. The condensate should not be directed into a septic system of a house, because it doesn’t need to be treated as effluent. When the height of the air handler (containing the evaporator) is above the level of the surface drains used for rain water the condensate drain lines can often be routed into them. Air handlers located below grade level, e.g. the basement of a house, may need to use a condensate pump to lift the water to a surface drain.
Potability
Generally, dehumidifier water is considered a rather clean kind of greywater: not suitable for drinking, but acceptable for watering plants, though not garden vegetables.[11] The health concerns are:[11]
- The water contains trace metals from the heat exchanger, copper and aluminum, zinc from galvanized steel supporting frame and drain pan. Condensate would only be exposed to tin-lead solder in copper drain pipe, but lead is particularly dangerous. These trace metals may pose a danger if used on edible plants, as they can bioaccumulate. However, the water is usable for irrigation of ornamental plants and lawns.
- Various pathogens, including fungal spores, may accumulate in the water, particularly due to its stagnancy. Unlike in distilled water production, the water is not boiled, which would kill pathogens (including bacteria).
- As with distilled water, beneficial minerals are largely absent.
Food-grade dehumidifiers, also called atmospheric water generators, are designed to avoid toxic metal contamination and to keep all water contact surfaces clean. The devices are primarily intended to produce pure water, and the dehumidifying effect is viewed as secondary to their operation.
Maintenance
If condensate water is handled automatically, most dehumidifiers require very little maintenance. Because of the volume of airflow through the appliance, dust buildup needs to be removed so it does not impede airflow; many designs feature removable and washable air filters. Condensate collection trays and containers may need occasional cleaning to remove debris buildup and prevent clogging of drainage passages, which can cause water leakage and overflow, if large amounts of certain particulates or dust are collected then this may need to be performed more often to avoid microbial growth.
Applications

Relative humidity in dwellings should preferably range from 30 to 50%.[12]
Homes and offices
Dehumidification within buildings can control:
- excessive body perspiration buildup that cannot evaporate in moisture-saturated air
- condensation dripping from cold-water pipes
- warping and sticking of furniture and doors
- mold and mildew, which can cause fabrics, books, and furnishings to develop mustiness
- clothes moths, fleas, cockroaches, woodlice, millipedes, and dust mites, which thrive in damp conditions (basements, crawl spaces, kitchens, bedrooms, bathrooms, spas or indoor pool areas, warehouses, workshops)
Construction
Dehumidifiers are also used in construction areas and renovations of indoor space to remove excess humidity or mildew.
Industrial processes
Dehumidifiers are used in industrial climatic chambers, to reduce relative humidity and the dew point in many industrial applications from waste and fresh water treatment plants to indoor grow rooms where the control of moisture is essential.[13]
Some industries include:
- Printing
- Grinding and machining
- Food packaging and processing
Market size
According to a 2015 estimate, the projected annual global total addressable market of dehumidifiers was about $3.5 billion by 2022.[14] This includes various types and applications, encompassing different applications such as household and industrial and different technologies such as ventilating and desiccant.[14]
See also
- Air ionizer, a different device for conditioning air
- Atmospheric water generator, a machine that extracts pure drinking water from air
- Food dehydrator, device for decreasing moisture in food, to prevent spoilage
- Humidifier, an appliance that increases the humidity of air
- Thermoelectric cooling
References
- "3" (PDF). Technical Guidelines of an Ice Rink. International Ice Hockey Federation. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- Frigidaire (2009). All about the Use & Care of your Dehumidifier. Electrolux Home Products, Inc. p. 7.
- Harriman, L. G. Iii; Plager, D.; Kosar, D. (1 November 1997). "Dehumidification and cooling loads from ventilation air". ASHRAE Journal. 39 (11). OSTI 563883.
- Nagengast, Bernard. "100 Years of Air Conditioning". CiteSeerX 10.1.1.545.9425. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Warm & Dry dehumidifiers heat recovery in dehumidifiers". Archived from the original on 24 September 2016.
- KMC Controls. "How Hot Do You Feel?". Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- "Swimming Pool Room Dehumidifiers - Top Systems and Units". Dehumidifier Corporation of America. Dehumidifier Corporation of America. Retrieved 16 September 2019.
- "Dehumidifier". airconditioning-systems.com.
- "How Rosahl works". Rosahl (website). Ryosai Technica Company (Japan). Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- Sakuma, Shuichi; Yamauchi, Shiro; Takai, Osamu (2010). "Estimation of dehumidifying performance of solid polymer electrolytic dehumidifier for practical application". Journal of Applied Electrochemistry. Springerlink. 40 (12): 2153–2160. doi:10.1007/s10800-010-0197-4.
- Laumer, John (29 July 2005). "Can I Water My Plants With It?". TreeHugger.com. Retrieved 15 July 2011.
- Dehumidifier Basics. US EnergyStar Program. Retrieved 15 July 2011.
- "Best Dehumidifiers For Industrial Use". Dehumidifier Corporation of America.
- "Dehumidifier Market Size to Reach $3.54 Billion by 2022". Air Conditioning, Heating & Refrigeration News. San Francisco. 28 October 2015. Retrieved 16 September 2019.
Further reading
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dehumidifiers. |
- Energy Star Qualified Dehumidifiers table listing removal rates and efficiencies. Long Island Power Authority, January 2011.
- AHAM Dehumidifier Product Certification Program. Association of Home Appliance Manufacturers.