Church of the Redeemer, Sacrow
The Protestant Church of the Redeemer (German: Heilandskirche, Latin: S. Ecclesiae sanctissimi Salvatoris in portu sacro) is located to the south of the village of Sacrow, which since 1939 has been incorporated to Potsdam, the capital of the German Bundesland of Brandenburg. It is famous for its Italian Romanesque Revival architecture with a separate campanile (bell tower) and for its scenic location. It was built in 1844. The design was based on drawings by King Frederick William IV of Prussia, called the Romantic on the Throne. The building was realized by Ludwig Persius, the king's favorite architect.
| Church of the Redeemer | |
|---|---|
Heilandskirche | |
 Western front of the church with the entrance | |
 Church of the Redeemer Location of Church of the Redeemer in Germany | |
| 52°25′28.7″N 13°5′47.3″E | |
| Location | Sacrow, Potsdam, Brandenburg |
| Country | Germany |
| Denomination | Lutheran |
| Website | www |
| History | |
| Status | active |
| Founder(s) | King Frederick William IV of Prussia |
| Dedication | Salvator Mundi |
| Dedicated | 21 July 1844 |
| Architecture | |
| Architect(s) | Ludwig Persius |
| Style | Byzantine Revivalism |
| Years built | 1841-1844 |
| Groundbreaking | 1841 |
| Completed | 1844 |
| Construction cost | Thaler 45,234 and 27 silver grosch |
| Closed | 1961-1989 |
| Specifications | |
| Materials | brick |
| Administration | |
| Parish | Evangelische Pfingstgemeinde, Potsdam |
| Deanery | Kirchenkreis Potsdam |
| Synod | Evangelical Church of Berlin-Brandenburg-Silesian Upper Lusatia |
| Part of | Palaces and Parks of Potsdam and Berlin |
| Reference | 532ter |
| Inscription | 1990 (14th session) |
| Extensions | 1992, 1999 |
| Coordinates | 52°25'29"N, 13°5'47"E |

Location

The church is situated on the bank of lake Jungfernsee, a part of the river Havel, 300 metres south of Sacrow Manor at the edge of its park, designed and expanded in the 1840s by landscape architect Peter Joseph Lenné. Both church and manor were restored in the 1990s. They are part of Potsdam Havel Landscape. This area of lakes, forests, parks, and castles has been classified as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO. Though the direct distance from Potsdam City across the Jungfernsee is no more than 1.2 km (2/3 mile), the distance by road is more than 10 km (6.2 mi).
History
Earlier churches in Sacrow
Little is known about the first church at Sacrow. The first church stood in the middle of the village and was built of boulders. It probably collapsed during the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648). The first written description is found in a chronicle from 1661, when the priest of Fahrland became responsible for the parish.
In 1694, a half-timbered church was erected at the same location, above the arches of the previous building's crypt. Johann Andres Moritz, Pastor of Fahrland from 1774 to 1794, in his diary gave a detailed description of life in the village and of the changing owners of the manor house built in 1774. The writer Theodor Fontane integrated parts of these records into his travelogue Wanderungen durch die Mark Brandenburg (Hikes through the Mark Brandenburg). As quoted by Fontane, Father Moritz in 1790 expressed his aversion to caring for the remote parish: "Meine Pfarre ist eine beschwerliche Pfarre. Sakrow (nur Filial) liegt eine Meile ab...es ist in allem betrachtet ein verdrießlich Filial, und doch muß ich es alle 14 Tage bereisen. Gott! Du weißt es, wie ich dann...bis Abend fahren und reden muß, wie sauer es mir jetzt wird...." ("My parish is an exhausting parish. Sakrow (only a subsidiary) lies a league away... over all, it has to be regarded an irksome subsidiary, and nevertheless I must travel there every fortnight. God! You know it, how I then...must travel until evening and speak, how disgusted it makes me now ....") After Father Moritz had died, in 1794 Sacrow was transferred to the parish of St. Nicholas' Church, Potsdam. After 1808 it was returned to Fahrland.
The small half-timbered church was unusable after 1813 and had to be torn down in 1822 because it was at risk of collapsing. The congregation arranged to meet in a prayer room in a house near the manor. This state of affairs continued until the Church of the Redeemer was finished in 1844.
Construction of the present church

Over the centuries the village of Sacrow and its manor changed hands many times. In October 1840, Friedrich Wilhelm IV, King of Prussia, bought the estate for 60,000 thalers and added it to his lands in Potsdam a month later. Long before the purchase, the king had sketched out a church building for Sacrow. The new building was appropriate for a cove, a port where fishermen on the Havel could seek shelter with their boats during storms. For the king, the location quite symbolic: he saw the nave as a bulwark against the storms of life. The church seal alludes to this with its Latin inscription: S. Ecclesiae sanctissimi Salvatoris in portu sacro (Church of the Most Holy Redeemer in the Sacred Port).
Ludwig Persius, the court architect, turned the king's sketches into a building and put his colleague, Ferdinand von Arnim, in charge of the construction process. The church extends into the water and gives the impression of an actual ship anchored near the lakeshore. This design took up a third of the actual overall construction cost of 45,234 thalers and 27 silver grosch. Sacrow Manor was used as the church's parsonage. Construction began in 1841, and the church's festive dedication took place three years later on July 21, 1844.
Beginning in 1842, the landscape architect Peter Joseph Lenné designed the church grounds, the cove, the Sacrow Manor's park, and a rented house in the Italian style (1843/44) by Persius called Zum Doctor Faustus, which stood farther to the east. In his usual fashion, Lenné designed wide walking paths and a wide view of the Parks of Glienicke and Babelsberg, of the New Garden, Potsdam, and of the City of Potsdam itself. Through his transformation of the landscape, the over 24 hectare (c. 60 acre) Sacrow Park was incorporated into the Potsdamer Havellandschaft.
After the dedication on July 21, 1844, Sacrow remained an independent congregation for only four years. Then it became part of the parish of the Church of Peace (Friedenskirche) at Sanssouci, and after 1859, it was assigned to the parish of Bornstedt. The final change came in 1870, when the Church of the Redeemer congregation was merged with the parishes of Klein-Glienicke (later part of Neubabelsberg) and the District of Stolpe (now Berlin-Wannsee), and the Church of Ss. Peter and Paul on Nikolskoë, forming together the Evangelical Congregation of Neubabelsberg.
On December 22, 1941 the official German Evangelical Church called for appropriate action by all Protestant church bodies to exclude baptised non-Aryans from all spheres of Protestant church life.[1] Many German Christian-dominated congregations followed suit. However, the Evangelical Congregation of Neubabelsberg handed in a list of signatures in protest against the exclusion of the stigmatised Protestants of Jewish descent.[2]
Decay and restoration since 1961


The building of the Berlin Wall in August 1961 led over the following decades to heavy damage to the Church of the Redeemer. The barrier along the border between the East German Democratic Republic (GDR) and West Berlin was built straight across the lot of the church property and the campanile was used as part of the protective wall of concrete. The church nave stood in the foreland between wall and border. In spite of these circumstances, regular services were still held in the church until Christmas Eve 1961. A few days later, the church's interior, which stood in an area strictly controlled by the GDR border troops, was defiled – almost certainly by the troops. This way the church was made unserviceable. The border authority thus created a reason to seal off the church completely, in order to prevent any escape in that section of the border.
Out of reach of its parish, the church deteriorated year by year. By the end of the 1970s, it became obvious from the West Berlin side of the Havel that the building was in substantial danger. The tin surface of the roof had become fragmented. Some edges of the nave were settled by plants. Some people in West Berlin started a campaign to stop the decay of the church. A great deal of the merit for the preservation of the building is due to Richard von Weizsäcker, at that time Mayor of West Berlin. By protracted negotiations with the responsible Protestant church body, the Evangelical Church in Berlin-Brandenburg and the authorities of the GDR and through the promise of sharing the costs, he won the agreement of the East German section of Berlin-Brandenburg's Protestant church to organize the restoration of the exterior of the building. At the beginning of the works in 1984, the sculptures of the Twelve Apostles were saved and stored. Other wooden furnishings, such as the twelve corbels and the gallery, still in evidence in pictures taken in 1981, were lost.
In November 1989 the Iron Curtain fell, and on Christmas Eve 1989, a service was held once again in the Church of the Redeemer, after almost three decades. The interior was still in a wasted state.
In 1992, the church along with the park and Sacrow Manor was added by UNESCO to the World Heritage Site "Palaces and Parks of Potsdam and Berlin".[3]
From 1993 to 1995 the building was extensively restored. The preparatory investigation began in 1990. The architects assigned co-operated with the Monument Commission and the Church Building Authority. They used old drawings and black-and-white photos to reconstruct lost structures. However, the consoles for the apostle statuettes are freely modeled after historic originals from abroad. The statuettes were placed without knowledge of their original positions.
Eight hectares of the garden area designed by Lenné had been completely destroyed in the course of fortifying the border and the park of Sacrow Manor was damaged by the building of garages and kennels, as well as the typical border interface for the training of customs dogs. The park was reconstructed after 1994.
The parsonage had been dissolved in 1977. Hence Sacrow parish today is part of the Protestant Pfingstgemeinde parish in Potsdam. Since the restoration of the Sacrow building in 1995, it is the site of regular worships again. Regular concerts are held there as well.
Architecture
Nave
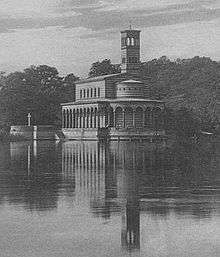
As with the later Church of Peace in Sanssouci Park, the Church of the Redeemer used early Christian buildings, as well as Roman markets and forums, as inspiration for the final design. The early-Christian style building was, for Frederick William IV, an architectural reminiscence of early Christianity, whose unified community of the faithful inspired him. Part of this Mediterranean style was the shallow roof – in contrast to the much steeper roofs of ordinary German village churches.
The over 9 meter high, 18 meter long, and 8 meter wide church building, with its eastern apse, is surrounded by a covered arcade. This gives the church the visual impression of a three-aisle basilica. Since the arcade protrudes onto a semi-circular platform in the Havel, to those in the river or in Wannsee-Berlin on its opposite shore, the church looks like it an old ship anchored near the bank. From a distance, the bell tower looks like the chimney of a Mississippi steamboat, an impression the reflection in the water only enhances.
The fluted columns have a palmette ring of cast zinc instead of capitals. At the front entrance the row of columns is broken by two wide pillars of sandstone. On them are Bible verses carved into the stone: the Gospel of John verses 1-16 and 1 Corinthians chapter 13. Light enters the church's interior through the round arched window in the clerestory and the rose window on the western gable. The outer walls, with their yellow-rose bricks, were striped with blue varnish broken by yellow tiles. The church resembles a Greek temple from pre-Christian times with its pitched roof and different devices. On the roof's peak is a pediment cross made of the same cast zinc as at the front.
Interior of the nave

The simple church hall is dominated by Byzantine-style frescoes in the apse. On it glazed gold underside is Christ enthroned holding the Book of Life, surrounded by the Four Evangelists, Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John with their symbols of the lion, eagle, man, and bull. Angels float in a half-circle above their heads. At the peak of the half-circle is the dove representing the Holy Ghost. Adolph Eybel undertook the painting in 1845, basing his work on a sketch by German romantic painter Carl Joseph Begas. In the half-circle of the bema, the color sequence of the church hall, gold stars on a blue background, returns.
The original free-standing, cedar altar table was wantonly destroyed in 1961. Since a reconstruction was not possible because of missing documentation, a stylistically similar one now stands in its place. The nave has a coffered ceiling with secure timber-frame construction. The unique fields are covered with blue cloth and painted light blue stars. Between the clerestory windows stand statues of the Twelve Apostles made of linden wood. They were carved from 1840 to 1844 by Jakob Alberty. He used the apostle statues made by Peter Vischer for Sebaldus' Grave at St. Sebald in Nuremberg (c. 1500) and Christian Daniel Rauch's finished models for the Berlin Cathedral as models.
The pews originally stood parallel to the long walls but are now arranged in blocks of four in the direction of the apse. The pews' very high backs and the similarly high doors between rows of benches prevent distraction and keep the parishioners' gaze raised to the three stages of worship: the altar, chancel, and lectern.
The only entrance to the church is on the western side. Above it, there is the organ gallery. The original organ of 1844 had only five registers with an attached pedal. It was expanded in 1907 with more pipes, which gave it six manual and one pedal registers. It was destroyed by vandals in 1961. At the time of the general restoration of the interior in 1990, the parish could not afford a new organ. The new instrument was installed in June 2009. It is equipped with two manuals, a pedal, and 14 registers on slider chests. In order to complete the general view of the gallery, at present the organ space is held by a deceitfully real looking paper mockup.
Campanile

On rectangular forecourt with its exedra on the narrow side, stands the over 20 meter high campanile (from Latin campana = bell). The tower has the same mixture of bricks and tiles as the rest of the church. The arched windows rise to the top and end in the last story with an open belvedere. The tower culminates in a shallow pavilion roof with a ball and cross atop it.
The Church of the Redeemer campanile contains a c. 600-year-old bronze bell. Its traditional casting date is 1406, although this is impossible to prove. It was first mentioned in 1661. The bell presumably comes from the old stone church. A second bell was confiscated for armament production in 1917 and its replacement suffered the same fate in 1944.
In the summer of 1897, the bell tower was used by the physicists Adolf Slaby and Georg Graf von Arco to try to perfect Marconi's radio technology. It was the site of the first German antenna for wireless telegraphs. On August 27, their signal transmission arrived at the imperial seaman station Kongsnaes on the opposite side of the Jungfernsee at Swan Alley in Potsdam 1.6 km away . A commemorative plaque that was put up in 1928 by Hermann Hosaeus over the entrance door to the Campanile alludes to this incident. In the middle of the plaque, which is made of green dolomite, is Atlas supporting the globe, surrounded by lightning and the commemoration: "An dieser Stätte errichteten 1897 Prof. Adolf Slaby und Graf von Arco die erste Deutsche Antennenanlage für drahtlosen Verkehr." (At this spot in 1897, Prof. Adolf Slaby and Graf von Arco erected the first German antenna for wireless communication.)
References
- The information in this article is based on that in its German equivalent.
- PEDA-Kunstführer: Potsdam-Sacrow. Heilandskirche. Ev. Kirchengemeinde Potsdam-Sacrow (Ed.). Kunstverlag PEDA, Passau 1998 ISBN 3-930102-33-1
- Theodor Fontane: Wanderungen durch die Mark Brandenburg . Part 3. Havelland. (1st edition 1873) Here, the version published in München, Frankfurt/M and Berlin: Nymphenburger Verlagshandlung, 1971, quote chapter Sacrow, pp. 223–234. ISBN 3-485-00293-3
Notes
- Circular (Rundschreiben) by the church chancery of the German Evangelical Church to all governing bodies of the Protestant church bodies (22 December 1941), published in Kurt Meier, Kirche und Judentum: Die Haltung der evangelischen Kirche zur Judenpolitik des Dritten Reiches, Halle upon Saale: Niemeyer, 1968, pp. 116seq. No ISBN.
- Cf. Evangelisches Zentralarchiv, Berlin: I/C3/172, vol. 3.
- "Palaces and Parks of Potsdam and Berlin". Whc.unesco.org. Retrieved 6 June 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Heilandskirche am Port von Sacrow. |
- (in German) Heilandskirche Sacrow (self-published source)
- (in German) Wandern in Brandenburg: Zur Havel bei Sacrow (photos of the damaged church from 1981 on a website about hiking)
- (in German) ars-sacrow.de