Havel
The Havel (German: [ˈhaːfl̩] (![]()
| Havel | |
|---|---|
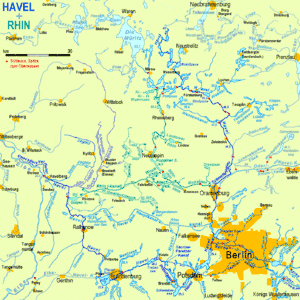 Rivers Havel (dark blue) and Rhin (turquoise) | |
| Location | |
| Country | Germany: Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Berlin, Saxony-Anhalt |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Ankershagen, Mecklenburg |
| • coordinates | 53.467778°N 12.935556°E |
| • elevation | 65 m (213 ft) |
| Mouth | |
• location | Rühstädt-Gnevsdorf |
• coordinates | 52.908333°N 11.877222°E |
• elevation | 22 m (72 ft) |
| Length | 325 km (202 miles) |
| Basin size | 23,858 km2 (9,212 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Havelberg |
| • average | 103 m3/s (3,600 cu ft/s) |
| • minimum | 18.8 m3/s (660 cu ft/s) |
| • maximum | 215 m3/s (7,600 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Elbe→ North Sea |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Woblitz, Briese, Tegeler Fließ, Spree, Nuthe, Plane, Buckau |
| • right | Rhin, Dosse |
For much of its length, the Havel is navigable, and it provides an important link in the waterway connections between the east and west of Germany, and beyond.
Course
The source of the Havel is located in the Mecklenburg Lake District, between Lake Müritz and the city of Neubrandenburg. There is no obvious visible source in the form of a spring, but the river originates in the lakes in the Diekenbruch near Ankershagen, close to and south-east of the watershed between the North and Baltic seas. From there the river initially flows southward, eventually joining the Elbe, which in turn flows into the North Sea. Every river north-east of it flows to the Baltic Sea. The river enters Brandenburg near the town of Fürstenberg. In its upper course and between Berlin and Brandenburg an der Havel the river forms several lakes.
The Havel's main tributary is the Spree, which joins the Havel in Spandau, a western borough of Berlin, and is longer and delivers more water than the Havel itself above the confluence. The second largest tributary is the Rhin, named in the Middle Ages by settlers from the lower Rhine. At the southern end of the Ruppiner See, weirs can distribute the waters of the Rhin either east- or westwards, rejoining the Havel in two places 67 kilometres (42 mi) apart along a straight line, and more than 160 kilometres (99 mi) apart along the course of the river.
The region around and north of the middle Havel is called the Havelland. It consists of sandy hills, often called Ländchen, and low marshes, called luche. A few kilometres of the river before its confluence with the Elbe near Havelberg are in the state of Saxony-Anhalt. Due to its minimal gradient it is susceptible to high waters in the Elbe.
Unless in extreme floods, if the dike of the Elbe is submerged, the discharge of the Havel is improved by the Gnevsdorfer Vorfluter (something like "Gnevsdorfer outfall"). By this canal, the mouth of the Havel, that naturally would be near Havelberg, is placed 11 km downstream. As the course of the Elbe has a higher gradient than the Havel, the water level of the Havel in Havelberg can be kept 1.4 meters below the Elbe (at the junction of the traverse communicating canal, protected by a lock).
Towns along the river include: Fürstenberg, Zehdenick, Oranienburg, Berlin, Potsdam, Werder, Ketzin, Brandenburg, Premnitz, Rathenow and Havelberg.
History
In earlier Greek or Latin sources, such as Tacitus' Germania, the name of the river was also written as Habola, Habula, Havela. The river name Havel is related to German Haff, habe, hafen, MHG Hafen meaning port, harbor).
The Slavic people who later moved into the Havel area were referred to in German sources as Heveller (occasionally as Havolane).
Navigation

The Havel is navigable from the Mecklenburg Lake District to its confluence with the Elbe. Whilst its upper reaches carry little other than leisure traffic, further downstream it provides an important link in the German commercial waterway network, carrying traffic from the Rhine and the North Sea to Berlin and Poland.[2]
From a navigation perspective, the Havel can be split into four sections with somewhat different characteristics and different administrative arrangements.
Head of navigation to Liebenwalde

The Havel is navigable to canoes and similar small craft from close to its source. Motor craft are prohibited above the first lock at Zwenzow, which links the Useriner See to the Großer Labussee. The stretch of the river between this lock and the junction with the Oder–Havel Canal is administered as part of the Obere–Havel–Wasserstraße, along with various connecting canals and waterways.[3][4]
From Zwenzow downstream to Liebenwalde is a distance of 92 kilometres (57 mi). In this distance the navigation passes through the lakes of Großer Labussee, Woblitzsee, Wangnitzsee, Großer Priepertsee, Ellbogensee, Ziernsee, Röblinsee, Baalensee, Schwedtsee and Stolpsee. It also descends through the locks at Wesenberg, Steinhavelmühle, Fürstenberg, Bredereiche, Regow, Zaaren, Schorfheide, Zehdenick, Bischofswerder and Liebenwalde.[3][4]
The Woblitzsee also gives access to the Kammer Canal, which allows vessels to reach Neustrelitz. The Ellbogensee links to the Müritz–Havel–Wasserstraße, which proceeds deeper into the Mecklenburg Lake District, eventually connecting with the Müritz–Elde–Wasserstraße. Other connected waterways are the Lychener Gewässer, the Templiner Gewässer and the Wentow Gewässer.[3]
Liebenwalde to Spandau

The stretch of the river between the junction with the Oder–Havel Canal near Liebenwalde and the confluence with the Spree at Spandau is administered as part of the Havel–Oder–Wasserstraße, which also includes the Oder-Havel Canal. This stretch of the river forms part of the main inland waterway route from Germany to Poland and carries significant commercial traffic. This stretch of the river is 40 kilometres (25 mi) long, and the river descends through two locks at Lehnitz and Spandau.[5]
At Hennigsdorf, 30 kilometres (19 mi) downstream of Liebenwalde, the Havel Canal joins the river on the west bank. This canal connects to Paretz, on the Havel downstream, and was built in the 1950s to allow East German vessels to avoid the stretch of the river under the political control of West Berlin. Some 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) further downstream, the Berlin-Spandau Ship Canal joins the river on the east bank, providing a connection to central Berlin without passing through the lock at Spandau.[5]
A car ferry crosses the river between Hakenfelde and Konradshöhe, in the Berlin boroughs of Spandau and Reinickendorf respectively.
The last 10 kilometres (6 mi) of this stretch of the river, from Hennigsdorf, passes through a series of interconnected lakes, including the large Tegeler See. The river enters Berlin 6 kilometres (4 mi) before Spandau, having formed the boundary for the previous 4 kilometres (2.5 mi). During the partition of Germany, this formed the border between East Germany and West Berlin, and border control points were established for vessels navigating the river.[5]
Spandau to Plaue
The stretch of the river between the confluence with the Spree at Spandau and the junction with the Elbe–Havel Canal at Plaue is administered as part of the Lower Havel–Waterway, which also includes the stretch of river downstream to the confluence with the Elbe. Between Spandau and Plaue, the river forms part of the main inland waterway route from the Rhine and the west of Germany, and from Hamburg and the North Sea ports, to both Berlin and Poland. It thus carries a considerable amount of commercial traffic.[2]
South of Spandau, the river widens into a wide lake, including a large arm known as the Großer Wannsee, which due to its proximity to Berlin can be very busy with leisure craft. The island of Pfaueninsel is also a feature of this stretch of the river. Several of Berlin's ferries cross these waters, carrying passengers and tourists.[2]
The Teltow Canal joins the river from the east via the Griebnitzsee just before the city reaches the city of Potsdam, providing an alternative route to the Oder–Spree Canal avoiding central Berlin. The Griebnitz Canal provides a short cut for smaller vessels from the Griebnitzsee to the Großer Wannsee.[2]
At Potsdam the navigation splits into two channels. The Havel, here known as the Potsdamer Havel, takes a route south-west through Potsdam and the Templiner See to the Schwielowsee, then north-west to Paretz, whilst the Sacrow–Paretz Canal takes a shorter route due east to Paretz, saving some 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) compared to the 29 kilometres (18 mi) Potsdamer Havel. The Potsdamer Havel is crossed by the Kiewitt Ferry in Potsdam itself, and by the Caputh Ferry at the entrance to the Schweilowsee.[2]
At Paretz the two channels join up again, as does the Havel Canal from further upstream. Just downstream of Paretz, the river is crossed by the Ketzin Cable Ferry. At Brandenburg an der Havel, the navigation again splits into two routes. Commercial shipping descends through a lock into the Silo Canal that passes to the north of the city centre. Leisure craft pass through the centre of the city, using the short Brandenburg City Canal, a smaller lock, and a stretch of the river. Both routes rejoin in the linked lakes of Breitling See and Plauer See, which leads up to Plaue.[2]
Plaue to Havelberg
Like the preceding stretch of the river, the stretch from Plaue to the confluence with the Elbe at Havelberg is administered as part of the Lower Havel–Waterway. Unlike the previous stretch, this stretch carries considerably less commercial traffic. Vessels heading to or from the Rhine and the west of Germany take the Elbe–Havel Canal at Plaue. Whilst the lower reaches of the Havel provide the most direct route to Hamburg and the North Sea ports, variable water levels in the Elbe affect those in the lower Havel, and together these can restrict navigation. A less direct, but more reliable route is available via the Elbe–Havel Canal, the Magdeburg Water Bridge, the Mittelland Canal and the Elbe Lateral Canal.[2]
This stretch of the river descends through locks at Bahnitz, Rathenow, Grütz, Garz and Havelberg. At Rathenow there are two channels, each with a lock. North of Plaue, the river is crossed by the Pritzerbe Ferry.[2]
References
- http://www.duden.de/rechtschreibung/Havel
- Sheffield, Barry (1995). Inland Waterways of Germany. St Ives: Imray Laurie Norie & Wilson. pp. 93–100. ISBN 0-85288-283-1.
- Sheffield, Barry (1995). Inland Waterways of Germany. St Ives: Imray Laurie Norie & Wilson. pp. 106–108. ISBN 0-85288-283-1.
- "Hauptstrecken Abkürzungen" [Main route abbreviations] (in German). Wasser- und Schifffahrtsverwaltung des Bundes. Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 6 February 2011.
- Sheffield, Barry (1995). Inland Waterways of Germany. St Ives: Imray Laurie Norie & Wilson. pp. 100–103. ISBN 0-85288-283-1.
Gallery
 Wentow channel in Zehdenick
Wentow channel in Zehdenick Weir of Voss Channel in Liebenwalde-Bischofswerder
Weir of Voss Channel in Liebenwalde-Bischofswerder Lehnitz lock in Oranienburg
Lehnitz lock in Oranienburg Alte Fahrt branch in Potsdam
Alte Fahrt branch in Potsdam

 Old harbour in Rathenow
Old harbour in Rathenow Gnevsdorf outfall
Gnevsdorf outfall
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Havel. |