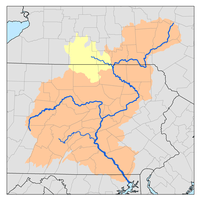
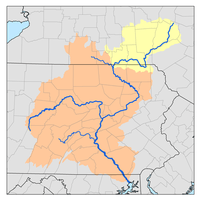
Chest Creek
Chest Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River in Cambria County and Clearfield County, in Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is approximately 40.4 miles (65.0 km) long and flows through Allegheny Township, East Carroll Township, Clearfield Township, Patton, Chest Township, and Elder Township in Cambria County and Westover Township, Chest Township, Newburg, Bell Township, and Mahaffey in Clearfield County.[1] Although it is considered by the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection to be impaired by situation, it is a coldwater fishery or a high-quality coldwater fishery throughout its length. The watershed of the creek has an area of 129.22 square miles (334.7 km2).
Course
Chest Creek begins in a valley in Allegheny Township, Cambria County. It flows north for several miles to Bradley Junction, where its valley widens and it turns northeast. The creek picks up the tributary Laurel Lick Run and eventually turns north again and flows along the border between East Caroroll Township and Clearfield Township. It eventually reaches the community of Patton, where it picks up the tributary Little Chest Creek and turns north-northwest, flowing along the border between Chest Township and Elder Township. After a number of miles, the creek receives the tributaries Rock Run and Brubaker Run. A short distance downstream, it leaves Cambria County.[1]
Upon leaving Cambria County, Chest Creek enters Westover Township, Clearfield County. In this township, the creek turns northeast, picking up Rougues Harbor Run and Ashcraft Run. It then passes by the community of Westover. The creek enters Chest Township, Clearfield County and starts meandering. It crosses once and flows parallel to Pennsylvania Route 36 for a number of miles and receives the tributaries Pine Run, Spring Run, Kings Run, Snyder Run, and North Camp Run. The creek eventually passes through the community of Newburg, where it receives Wilson Run and Rattling Run. It then enters Bell Township and turns northwest, flowing parallel to Pennsylvania Route 36. A few miles later, it passes through Mahaffey and reaches its confluence with the West Branch Susquehanna River.[1]
Tributaries
Tributaries of Chest Creek include Ashcraft Run, Brubaker Run, and Duclos Run.[2]
Hydrology
A total of 20.29 miles (32.65 km) of Chest Creek is considered by the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection to be impaired by siltation.[2]
The annual load of sediment in the main stem of Chest Creek is 12,340,075.6 pounds (5,597,364.1 kg). About 8,531,600.0 pounds (3,869,868.7 kg) per year comes from croplands and 2,707,800.0 pounds (1,228,237.4 kg) comes from stream banks. A total of 830,200.0 pounds (376,572.4 kg) of sediment per year comes from hay and pastures, and 106,000.0 pounds (48,080.8 kg) comes from land classified by the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection as "low-intensity development". About 91,400.0 pounds (41,458.3 kg) of sediment per year comes from forests and 41,200.0 pounds (18,688.0 kg) per year comes from turf grass. About 9,000.0 pounds (4,082.3 kg) per year comes from land classified by the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection as "transition", 4,200.0 pounds (1,905.1 kg) comes from coal mines, and 400.0 pounds (181.4 kg) comes from wetlands.[2]
Geography, geology, and climate
The elevation near the mouth of Chest Creek is 1,253 feet (382 m) above sea level.[3]
There are strainers throughout the length of Chest Creek. Additionally, there are two dams on the creek in its upper reaches. The creek flows through a canyon in its middle reaches.[4]
The main stem of Chest Creek is in the Appalachian Plateaus physiographic province.[2]
The average rate of rainfall in the watershed of Chest Creek is 46.12 inches (117.1 cm) per year. The average rate of runoff is 3.53 inches (9.0 cm) per year.[2]
Watershed
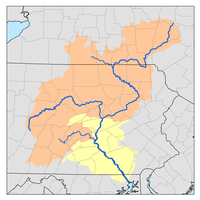
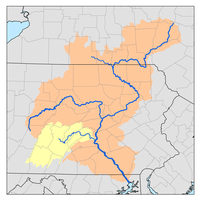
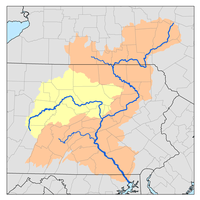
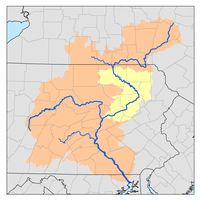
The watershed of Chest Creek has an area of 129.22 square miles (334.7 km2). There are approximately 264 miles (425 km) of streams in the watershed.[2]
Fifty-seven percent of the watershed of the main stem of Chest Creek is forested land. Thirty-seven percent of this part of the watershed is agricultural land, and 6 percent has other uses.[2]
Biology
Most of Chest Creek (the entire length of the creek between its mouth and Patton) is designated as a coldwater fishery. The creek's headwaters are designated as a high-quality coldwater fishery.[2]
Recreation
It is possible to canoe on 34.0 miles (54.7 km) of Chest Creek during snowmelt or within two days of heavy rain. The difficulty rating of the creek is between 1 and 3. Edward Gertler describes the scenery along it as between poor and good, depending on the location. The creek is the first major tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River that it is possible to canoe on.[4]
See also
References
- United States Geological Survey, The National Map Viewer, archived from the original on April 5, 2012, retrieved September 15, 2014
- Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (August 2011), Chest Creek Watershed Sediment TMDL West Branch Susquehanna River Cambria County, Pennsylvania (PDF), archived from the original (PDF) on March 4, 2016, retrieved September 15, 2014
- Topographic Map Stream Features in Clearfield County, Pennsylvania, retrieved September 15, 2014
- Edward Gertler (1984), Keystone Canoeing, Seneca Press, pp. 348–349