Senftenberg
Senftenberg (Sorbian languages: Zły Komorow) is a town in southern Brandenburg, Germany, capital of the Oberspreewald-Lausitz district.
Senftenberg | |
|---|---|
 Market Square | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Senftenberg within Oberspreewald-Lausitz district  | |
 Senftenberg  Senftenberg | |
| Coordinates: 51°31′N 14°01′E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Brandenburg |
| District | Oberspreewald-Lausitz |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Andreas Fredrich (SPD) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 127.56 km2 (49.25 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 102 m (335 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 24,275 |
| • Density | 190/km2 (490/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 01945 (Peickwitz), 01968 (Brieske, Großkoschen, Niemtsch, Sedlitz, Senftenberg), 01996 (Hosena) |
| Dialling codes | 03573, 035756 (Hosena, Peickwitz) |
| Vehicle registration | OSL, CA, SFB |
| Website | www.senftenberg.de |
Geography
Senftenberg is located in the southwest of the historic Lower Lusatia region at the border with Saxony. Its town centre is situated north of the river Black Elster and the artificial Senftenberger Lake, part of the Lusatian Lake District chain, approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) northwest of Hoyerswerda, and 35 kilometres (22 mi) southwest of Cottbus.
Senftenberg station is north of the centre and a major railway freight yard is located to its north-east, with a locomotive depot.
History
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Senftenberg was first mentioned in a 1279 deed issued by Henry III the Illustrious of Wettin, then margrave of Lusatia. With Lower Lusatia, the settlement was acquired by the Kingdom of Bohemia under Charles IV of Luxembourg in 1368. Elector Frederick II of Saxony acquired Senftenberg in 1448, whereafter the area as a border stronghold of the House of Wettin was separated from Bohemian Lusatia, until in 1635 all Lusatian territories fell to Saxony by the Peace of Prague. According to the 1815 Congress of Vienna, Lower Lusatia was annexed by Prussia and incorporated into the Province of Brandenburg.
Names
- Czech: Zlý Komorov
- German: Senftenberg
- Polish: Zły Komorów
- Upper Sorbian: Zły Komorow
- Lower Sorbian: Zły Komorow
International relations
Senftenberg is twinned with:
Tourism
Lake "Senftenberger See"
The Senftenberger See (Senftenberger Lake) is a popular destination for both day trips and holiday. In 1973, the former open cast mine, was officially opened to the public. Today, the lake is known for its excellent water quality. It is part of the so-called Lusatian Lakeland, a group of 23 artificial lakes.
On Senftenberger See one can stay at the Wellnesshotel Seeschlößchen - Privat-SPA & Naturresort. Here there are multiple saunas, fine dining restaurants, peaceful gardens, and services such as massage available.
Demography
After the second half of the 19th century the inhabitants increased because of workers coming to Senftenberg to work in the coal mines. After the German Reunion, many inhabitants moved to the western part of Germany.
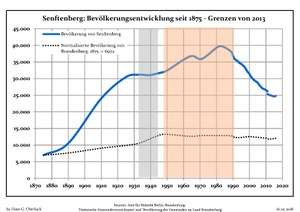 Development of Population since 1875 within the Current Boundaries (Blue Line: Population; Dotted Line: Comparison to Population Development of Brandenburg state; Grey Background: Time of Nazi rule; Red Background: Time of Communist rule)
Development of Population since 1875 within the Current Boundaries (Blue Line: Population; Dotted Line: Comparison to Population Development of Brandenburg state; Grey Background: Time of Nazi rule; Red Background: Time of Communist rule)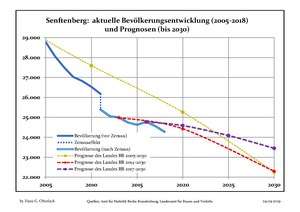 Recent Population Development and Projections (Population Development before Census 2011 (blue line); Recent Population Development according to the Census in Germany in 2011 (blue bordered line); Official projections for 2005-2030 (yellow line); for 2014-2030 (red line); for 2017-2030 (scarlet line)
Recent Population Development and Projections (Population Development before Census 2011 (blue line); Recent Population Development according to the Census in Germany in 2011 (blue bordered line); Official projections for 2005-2030 (yellow line); for 2014-2030 (red line); for 2017-2030 (scarlet line)
|
|
|
People
- Hermann Kuhnt (1850–1925)
- Herbert Windt (1894–1965)
- Joachim Sauer (born 1949)
Photogallery
- Senftenberg
(Old Town) - Estate housing
- Lutheran church
in "Jüttendorf"  Coats of Arms of Poland and Saxony on a postal milestone
Coats of Arms of Poland and Saxony on a postal milestone
See also
- Senftenberger See
References
- "Bevölkerung im Land Brandenburg nach amtsfreien Gemeinden, Ämtern und Gemeinden 31. Dezember 2018". Amt für Statistik Berlin-Brandenburg (in German). July 2019.
- Detailed data sources are to be found in the Wikimedia Commons.Population Projection Brandenburg at Wikimedia Commons