Braintree branch line
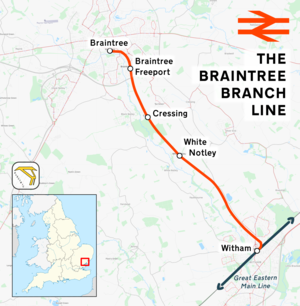
The Braintree branch line is a railway branch line in the East of England that diverges from the Great Eastern Main Line at Witham and runs north-west to Braintree. The route is 6 miles 30 chains (10.3 km) in length and there are five stations, including the two termini. The line is part of Network Rail Strategic Route 7, SRS 07.06, and is classified as a London and South-East commuter line.[1]
| Braintree branch line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Braintree is the western terminus of the line | |||
| Overview | |||
| Type | Regional rail | ||
| System | National Rail | ||
| Status | Operational | ||
| Locale | East of England | ||
| Termini | Witham Braintree | ||
| Stations | 5 | ||
| Services | 1 | ||
| Operation | |||
| Opened | 1848 | ||
| Owner | Network Rail | ||
| Operator(s) | Greater Anglia | ||
| Character | Branch line | ||
| Rolling stock | Class 321 | ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 6 miles 30 chains (10.3 km) | ||
| Number of tracks | 1 | ||
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge | ||
| Electrification | 25 kV AC OHLE | ||
| |||
Braintree branch line | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mileage from Liverpool Street | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The stations and all services are currently operated by Greater Anglia. As of 2019 the typical off-peak weekday service-frequency is one train per hour in each direction. The timetabled journey time between Witham and Braintree is 16 minutes.
History
Originally constructed from Maldon to Braintree via Witham, only the line from Braintree to Witham remains open. The line was proposed by the Maldon, Witham & Braintree Railway (MWBR) and given royal assent in June 1846. The MWBR was subsequently purchased by the Eastern Counties Railway (ECR), and the line opened in 1848.[2]
The section from Maldon to Witham was constructed as double-track, however one track was lifted during the period of the Crimean War (1854-56) and sold to the War Office.[2]
The Bishop's Stortford–Braintree branch line, built by the Great Eastern Railway (GER), was opened in 1869. This created a route from Maldon through to the West Anglia Main Line.
The line was extended from Maldon to Woodham Ferrers in 1889.[2]
In 1923, both lines became part of the London and North Eastern Railway (LNER).[2]
During the Second World War passenger services on the section between Maldon East and Heybridge and Woodham Ferrers were withdrawn and never reinstated.[2]
The Bishop's Stortford–Braintree branch closed to passenger traffic in 1952 and then to freight in 1971. The section from Maldon East and Heybridge to Witham was closed to passengers following the Beeching cuts to the railways in 1964, although goods services on that section continued until 1966.[2]
The franchise for the line is currently held by Greater Anglia.
Infrastructure
The line is single-track throughout and the route is electrified at 25 kV AC. It has a loading gauge of W6 and a maximum line speed of 50 mph.[1]
Services are usually formed of Class 321 units.
Most of the former railway alignment between just east of Bishops Stortford and Braintree has been preserved, and is managed by Essex County Council as the Flitch Way linear park. Two local groups volunteer to improve the site and campaign for improvements.
Stations
The following table summarises the line's five stations, their distance measured from London Liverpool Street, and estimated number of passenger entries/exits in 2018/19:
| Station | Location | Local authority | Mileage | Patronage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Witham | Witham | District of Braintree | 38½ | 2,349,496 |
| White Notley | White Notley | District of Braintree | 41¾ | 12,046 |
| Cressing | Cressing/Black Notley | District of Braintree | 43 | 39,010 |
| Braintree Freeport | Braintree | District of Braintree | 44¼ | 91,574 |
| Braintree | Braintree | District of Braintree | 45 | 727,982 |
References
- "Route 7 – Great Eastern" (PDF). Network Rail. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 22 May 2009.
- "The Old Railway Lines to Maldon". This is Malden. Retrieved 4 May 2009.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Braintree Branch Line. |