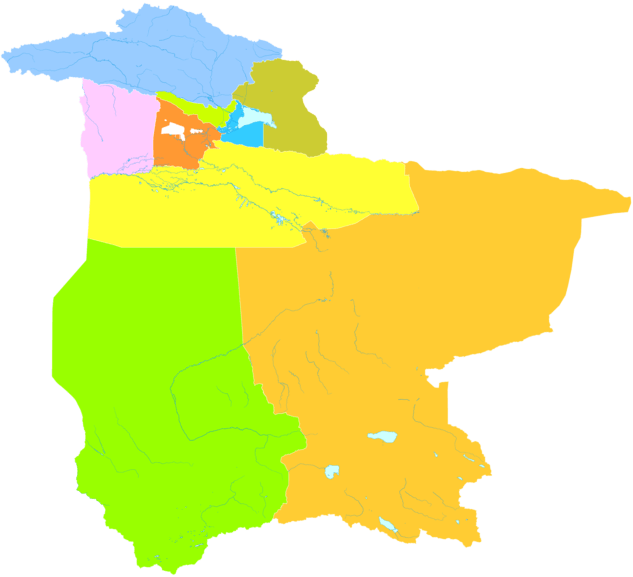
Bayingolin Mongol Autonomous Prefecture
Bayingolin (Chinese: 巴音郭楞蒙古族自治州; pinyin: Bāyīnguōléng Měnggǔzú Zìzhìzhōu; often abbreviated to Bayingol;[2] also as Bayinguoleng) is an autonomous prefecture for Mongol people in the southeast of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, Western China. It borders Gansu to the east, Qinghai to the southeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the south. It is the largest prefecture-level division nationally, with an area of 462,700 km2 (178,600 sq mi), which is even larger than its neighboring province of Gansu. The prefectural capital is Korla.
Bayingolin Prefecture 巴音郭楞州 · بايىنغولىن ئوبلاستى | |
|---|---|
| Bayingolin Mongol Autonomous Prefecture 巴音郭楞蒙古自治州 بايىنغولىن موڭغۇل ئاپتونوم ئوبلاستى | |
Bayanbulak grassland in Hejing County | |
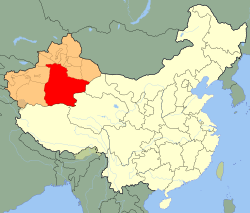 Bayingolin Mongol Prefecture (red) in Xinjiang (orange) | |
| Coordinates: | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Autonomous region | Xinjiang |
| Prefectural seat | Korla |
| Area | |
| • Total | 472,472.1 km2 (182,422.5 sq mi) |
| Population (2010)[1] | |
| • Total | 1,278,486 |
| • Density | 2.7/km2 (7.0/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-XJ-28 |
| Bayingolin Mongol Autonomous Prefecture | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||||
| Chinese | 巴音郭楞蒙古自治州 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Shorter name | |||||||||
| Chinese | 巴音郭楞州 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Bayingolin Prefecture | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Shortest name | |||||||||
| Chinese | 巴州 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Bā Prefecture | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||||
| Mongolian script | ᠪᠠᠶᠠᠨᠭᠣᠣᠯ ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ ᠥᠪᠡᠷᠲᠡᠭᠡᠨ ᠵᠠᠰᠠᠬᠤ ᠵᠧᠦ | ||||||||
| Uyghur name | |||||||||
| Uyghur | بايىنغولىن موڭغۇل ئاپتونوم ئوبلاستى | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Bayingolin | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||||
| Chinese | 巴音郭楞 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Rich river (from Mongolian) | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||||
| Mongolian script | ᠪᠠᠶᠠᠨᠭᠣᠣᠯ | ||||||||
| Uyghur name | |||||||||
| Uyghur | بايىنغولىن | ||||||||
| |||||||||
History
In a 2017 announcement from officials in Bayingolin Mongol Autonomous Prefecture, it was proclaimed that "there is a severe threat from international terrorism, and cars have been used as a key means of transport for terrorists as well as constantly serving as weapons. It is therefore necessary to monitor and track all vehicles in the prefecture."[3]
Demographics
According to the 2000 census, Bayingolin has 1,056,970 inhabitants (population density: 2.28 per km²).
As of 2015, 826,063 of the 1,393,812 residents of the county were Han Chinese, 440,283 were Uyghur, 64,979 were Hui and 50,091 were Mongol.[4]
Ethnic groups in Bayingolin
When Bayingolin was established in 1954, Mongols comprised 35% of the prefecture's population.[5] Due to development needs and migration, the Han population increased from 1,682 in the region of Bayingolin in 1947 to over 660,000 in 2004.[6][7]
- Population by ethnicity
| Nationality | 2000[8] | 2010[9] | 2015[4] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | % | Population | % | Population | % | |
| Han Chinese | 607,774 | 58.05% | 757,983 | 59.29% | 826,063 | 59.27% |
| Uyghur | 345,595 | 33.01% | 406,942 | 31.83% | 440,283 | 31.59% |
| Hui | 52,252 | 4.99% | 60,451 | 4.73% | 64,979 | 4.66% |
| Mongol | 43,544 | 4.16% | 43,484 | 3.40% | 50,091 | 3.59% |
| Tujia | 2,336 | 0.18% | ||||
| Miao | 1,362 | 0.11% | ||||
| Dongxiang | 1,148 | 0.09% | ||||
| Kazakhs | 1,091 | 0.09% | ||||
| Manchu | 888 | 0.07% | ||||
| Other | 7,805 | 0.74% | 2,801 | 0.22% | 12,396 | 0.89% |
| Total | 1,046,970 | 100% | 1,278,486 | 100% | 1,393,812 | 100% |
Subdivisions
Bayin'gholin directly controls one county-level city, seven counties and one Hui autonomous county.
| Name | Simplified Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Uyghur (UEY) | Uyghur Latin (ULY) | Mongolian | Population (2010 Census) | Area (km²) | Density (/km²) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Korla[10] | 库尔勒市 | Kù'ěrlè Shì | كورلا شەھىرى | Korla Shehiri | ᠬᠣᠷᠣᠯ ᠬᠣᠲᠠ | 549,324 | 7,219 | 76.09 | |
| Luntai County[10] | 轮台县 | Lúntái Xiàn | بۈگۈر ناھىيىسى | Bügür Nahiyisi | ᠪᠦᠭᠦᠷ ᠰᠢᠶᠠᠨ | 116,166 | 14,185 | 8.18 | |
| Yuli County[10] | 尉犁县 | Yùlí Xiàn | لوپنۇر ناھىيىسى | Lopnur Nahiyisi | ᠯᠣᠪᠨᠠᠭᠤᠷ ᠰᠢᠶᠠᠨ | 96,068 | 59,402 | 1.61 | |
| Ruoqiang County[10] | 若羌县 | Ruòqiāng Xiàn | چاقىلىق ناھىيىسى | Chaqiliq Nahiyisi | ᠴᠠᠺᠢᠯᠢᠺ ᠰᠢᠶᠠ | 35,580 | 199,222 | 0.17 | |
| Qiemo County[10] (Qarqan) | 且末县 | Qiěmò Xiàn | چەرچەن ناھىيىسى | Cherchen Nahiyisi | ᠴᠧᠷᠴᠧᠨ ᠰᠢᠶᠠᠨ | 65,572 | 138,680 | 0.47 | |
| Hejing County[10] | 和静县 | Héjìng Xiàn | خېجىڭ ناھىيىسى | Xéjing Nahiyisi | ᠬᠡᠵᠢᠨ ᠰᠢᠶᠠᠨ | 160,804 | 34,984 | 4.59 | |
| Hoxud County[10] | 和硕县 | Héshuò Xiàn | خوشۇت ناھىيىسى | Xoshut Nahiyisi | ᠬᠣᠱᠤᠳ ᠰᠢᠶᠠᠨ | 72,556 | 12,754 | 5.68 | |
| Bohu County[10] | 博湖县 | Bóhú Xiàn | باغراش ناھىيىسى | Baghrash Nahiyisi | ᠪᠣᠰᠲᠠᠨᠠᠭᠤᠷ ᠰᠢᠶᠠᠨ | 54,788 | 3,597 | 15.23 | |
| Yanqi Hui Autonomous County | 焉耆回族自治县 | Yānqí Huízú Zìzhìxiàn | يەنجى خۇيزۇ ئاپتونوم ناھىيىسى | Yenji Xuyzu Aptonom Nahiyisi | ᠶᠠᠨᠼᠢ ᠬᠣᠲᠣᠩ ᠥᠪᠡᠷᠲᠡᠭᠡᠨ ᠵᠠᠰᠠᠬᠤ ᠰᠢᠶᠠᠨ | 127,628 | 2,429 | 52.54 | |
Notable persons
References
- 巴音郭楞蒙古自治州历史沿革 [Bayingolin Mongol Autonomous Prefecture Historical Development] (in Chinese). XZQH.org. 30 January 2015. Retrieved 7 December 2019.
2003年,巴州总面积472472.1平方千米,{...}2010年第六次人口普查,常住总人口1278486人,
- The official spelling is "Bayingolin" according to 中国地名录. Beijing: SinoMaps Press (中国地图出版社). 1997. p. 300. ISBN 7-5031-1718-4.
- Phillips, Tom (2017-02-21). "China orders hundreds of thousands of private cars to have GPS trackers installed for monitoring". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 2019-12-05. Retrieved 2019-12-05.
- 3-7 各地、州、市、县(市)分民族人口数 (in Chinese). Xinjiang Bureau of Statistics. 15 March 2017. Archived from the original on 11 October 2017. Retrieved 3 September 2017.
- Atwood, Christopher (2004). Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire. Facts on File. p. 39.
- Gardner Bovingdon (2010). "Chapter 2 - Heteronomy and Its Discontents". The Uyghurs - strangers in their own land. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-14758-3.
- Bovingdon, Gardner (2010). "Note 9 (Chapter 2)". The Uyghurs - strangers in their own land. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-14758-3.
- 2000年人口普查中国民族人口资料. Publishing House of Minority Nationalities. September 2003. ISBN 7-105-05425-5.
- Stanley W. Toops (August 2012). Susan M. Walcott; Corey Johnson (eds.). Eurasian Corridors of Interconnection: From the South China to the Caspian Sea. Routledge. pp. 65–66. ISBN 978-1135078751.
- The official spelling according to 中国地名录. Beijing: SinoMaps Press (中国地图出版社). 1997. ISBN 7-5031-1718-4.
External links
- Government website of Bayin'gholin (in Simplified Chinese)
- Government website of Bayin'gholin (in Mongolian)
- Government website of Bayin'gholin (in Uyghur)