Setmelanotide
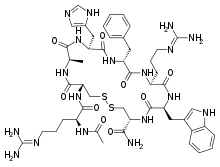
Setmelanotide (INN, USAN; development codes RM-493, BIM-22493, IRC-022493) is a peptide drug and investigational anti-obesity medication which acts as a selective agonist of the MC4 receptor.[1][2] Its peptide sequence is Ac-Arg-Cys(1)-D-Ala-His-D-Phe-Arg-Trp-Cys(1)-NH2. It was first discovered at Ipsen and is being developed by Rhythm Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of obesity and diabetes.[1] In addition, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals is conducting trials of setmelanotide for the treatment of Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS), a genetic disorder which includes MC4 receptor deficiency and associated symptoms such as excessive appetite and obesity.[3] As of December 2014, the drug is in phase II clinical trials for obesity and PWS.[1][4][5] So far, preliminary data has shown no benefit of Setmelanotide in Prader-Willi syndrome.[6]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | RM-493; BIM-22493; IRC-022493; N2-Acetyl-L-arginyl-L-cysteinyl-D-alanyl-L-histidyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-arginyl-L-tryptophyl-L-cysteinamide, cyclic (2-8)-disulfide |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C49H68N18O9S2 |
| Molar mass | 1117.32 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Setmelanotide binds to and activates MC4 receptors in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus and in the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), areas involved in the regulation of appetite, and this action is thought to underlie its appetite suppressant effects.[7] In addition to reducing appetite, setmelanotide increases resting energy expenditure in both obese animals and humans.[8] Importantly, unlike certain other MC4 receptor agonists, such as LY-2112688, setmelanotide has not been found to produce increases in heart rate or blood pressure.[2]
Setmelanotide has been reported to possess the following activity profile (cAMP, EC50): MC4 (0.27 nM) > MC3 (5.3 nM) ≈ MC1 (5.8 nM) > MC5 (1600 nM) ≟ MC2 (>1000 nM).[9] (19.6-fold selectivity for MC4 over MC3, the second target of highest activity.)
References
- Lee EC, Carpino PA (2015). "Melanocortin-4 receptor modulators for the treatment of obesity: a patent analysis (2008-2014)". Pharmaceutical Patent Analyst. 4 (2): 95–107. doi:10.4155/ppa.15.1. PMID 25853469.
- Kievit P, Halem H, Marks DL, Dong JZ, Glavas MM, Sinnayah P, et al. (February 2013). "Chronic treatment with a melanocortin-4 receptor agonist causes weight loss, reduces insulin resistance, and improves cardiovascular function in diet-induced obese rhesus macaques". Diabetes. 62 (2): 490–7. doi:10.2337/db12-0598. PMC 3554387. PMID 23048186.
- "Obesity and Diabetes Caused by Genetic Deficiencies in the MC4 Pathway". Rhythm Pharmaceuticals. Retrieved 2015-05-21.
- Jackson VM, Price DA, Carpino PA (August 2014). "Investigational drugs in Phase II clinical trials for the treatment of obesity: implications for future development of novel therapies". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 23 (8): 1055–66. doi:10.1517/13543784.2014.918952. PMID 25000213. S2CID 23198484.
- "RM-493: A First-in-Class, Phase 2-Ready MC4 Agonist: A New Drug Class for the Treatment of Obesity and Diabetes". Rhythm Pharmaceuticals. Archived from the original on 2015-06-14. Retrieved 2015-05-21.
- Duis J, van Wattum PJ, Scheimann A, Salehi P, Brokamp E, Fairbrother L, et al. (March 2019). "A multidisciplinary approach to the clinical management of Prader-Willi syndrome". Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine. 7 (3): e514. doi:10.1002/mgg3.514. PMC 6418440. PMID 30697974.
- Kim GW, Lin JE, Blomain ES, Waldman SA (January 2014). "Antiobesity pharmacotherapy: new drugs and emerging targets". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 95 (1): 53–66. doi:10.1038/clpt.2013.204. PMC 4054704. PMID 24105257.
- Chen KY, Muniyappa R, Abel BS, Mullins KP, Staker P, Brychta RJ, et al. (April 2015). "RM-493, a melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) agonist, increases resting energy expenditure in obese individuals". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 100 (4): 1639–45. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-4024. PMC 4399297. PMID 25675384.
- Muniyappa R, Chen K, Brychta R, Abel B, Mullins K, Staker P, et al. (June 2014). "A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study to Evaluate the Effect of a Melanocortin Receptor 4 (MC4R) Agonist, RM-493, on Resting Energy Expenditure (REE) in Obese Subjects" (PDF). Endocrine Reviews. Rhythm Pharmaceuticals. Retrieved 2015-05-21.