Alsactide
Alsactide (INN) (brand name Synchrodyn 1-17 or simply Synchrodyn, former development code name Hoechst 433), also known as alisactide, is a synthetic peptide and analogue of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) which is used in Italy as a diagnostic agent in kidney function for adrenal insufficiency.[1][2][3] Like ACTH, alsactide is thought to act as a non-selective agonist of the melanocortin receptors, including the ACTH receptor (MC2R). However, it appears to show a different profile of receptor selectivity relative to ACTH, as it apparently demonstrated no evidence of inhibition of endogenous ACTH in Addison's disease patients.[4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.047.442 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
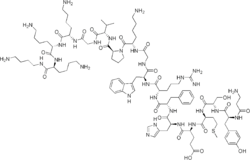
| Formula | C99H155N29O21S |
| Molar mass | 2119.57 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
See also
- Tetracosactide
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 34–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 33–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 12–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- George Kontogeorgos (1 January 2004). Molecular Pathology of the Pituitary. Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. pp. 66–. ISBN 978-3-8055-7740-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.