Lambeosaurinae
Lambeosaurinae is a group of crested hadrosaurid dinosaurs.
| Lambeosaurinae | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Skeleton of Parasaurolophus walkeri, Museum of Evolution Warsaw | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Order: | †Ornithischia |
| Suborder: | †Ornithopoda |
| Family: | †Hadrosauridae |
| Clade: | †Euhadrosauria |
| Subfamily: | †Lambeosaurinae Parks, 1923 |
| Type species | |
| †Lambeosaurus lambei Parks, 1923 | |
| Subgroups | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Classification
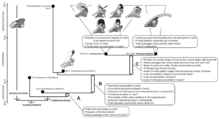
Lambeosaurines have been traditionally split into the tribes or clades Parasaurolophini (Parasaurolophus, Charonosaurus, others (?).) and Lambeosaurini (Corythosaurus, Hypacrosaurus, Lambeosaurus, others.).[2] Corythosaurini (synonym of Lambeosaurini, see below) and Parasaurolophini as terms entered the formal literature in Evans and Reisz's 2007 redescription of Lambeosaurus magnicristatus. Corythosaurini was defined as all taxa more closely related to Corythosaurus casuarius than to Parasaurolophus walkeri, and Parasaurolophini as all those taxa closer to P. walkeri than to C. casuarius. In this study, Charonosaurus and Parasaurolophus are parasaurolophins, and Corythosaurus, Hypacrosaurus, Lambeosaurus, Nipponosaurus, and Olorotitan are corythosaurins.[3] However, later researchers pointed out that due to the rules of priority set forth by the ICZN, Any tribe containing Lambeosaurus is properly named Lambeosaurini, and that therefore the name "Corythosaurini" is a junior synonym, and the definition had Corythosaurus casuarius changed to Lambeosaurus lambei, and the same for Parasaurolophini.[4] In more recent years Tsintaosaurini (Tsintaosaurus + Pararhabdodon) and Aralosaurini (Aralosaurus + Canardia) have also emerged.[5]
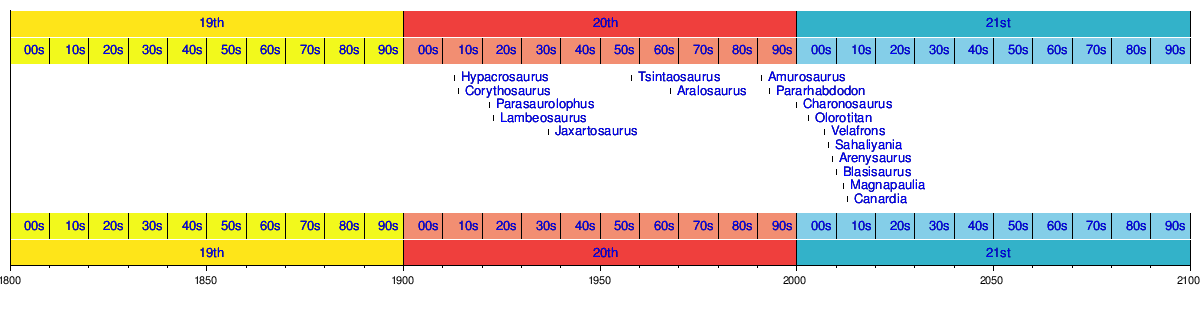
Phylogeny
Hadrosauridae was first defined as a clade, by Forster in a 1997 abstract, as simply "Lambeosaurinae plus Hadrosaurinae and their most recent common ancestor." In 1998, Paul Sereno defined the clade Hadrosauridae as the most inclusive possible group containing Saurolophus (a well-known hadrosaurine) and Parasaurolophus (a well-known lambeosaurine), later emending the definition to include Hadrosaurus, the type genus of the family, which ICZN rules state must be included, despite its status as a nomen dubium. According to Horner et al. (2004), Sereno's definition would place a few other well-known hadrosaurs (such as Telmatosaurus and Bactrosaurus) outside the family, which led them to define the family to include Telmatosaurus by default.[6] The following cladogram was recovered in a 2013 phylogenetic analysis by Albert Prieto-Márquez, and colleagues.[7]
| Lambeosaurinae |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
- Holtz, Thomas R. Jr. (2012) Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages, Winter 2011 Appendix.
- Glut, Donald F. (1997). Dinosaurs: The Encyclopedia. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Co. p. 69. ISBN 0-89950-917-7.
- Evans, David C.; Reisz, Robert R. (2007). "Anatomy and relationships of Lambeosaurus magnicristatus, a crested hadrosaurid dinosaur (Ornithischia) from the Dinosaur Park Formation, Alberta". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 27 (2): 373–393. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2007)27[373:AAROLM]2.0.CO;2.
- Sullivan, R., Jasinsky, S.E., Guenther, M. and Lucas, S.G. (2009). "The first lambeosaurin (Dinosauria, Hadrosauridae, Lambeosaurinae) from the Upper Cretaceous Ojo Alamo Formation (Naashoibito Member), San Juan Basin, New Mexico." New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin, 53: 405-417.
- http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0069835
- Prieto-Márquez, A (2010). "Global phylogeny of Hadrosauridae (Dinosauria: Ornithopoda) using parsimony and Bayesian methods". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 159: 435–502. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2009.00617.x.
- Prieto-Márquez, A.; Dalla Vecchia, F. M.; Gaete, R.; Galobart, À. (2013). Dodson, Peter (ed.). "Diversity, Relationships, and Biogeography of the Lambeosaurine Dinosaurs from the European Archipelago, with Description of the New Aralosaurin Canardia garonnensis". PLoS ONE. 8 (7): e69835. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069835. PMC 3724916. PMID 23922815.



.jpg)