Appalachian League
The Appalachian League of Professional Baseball is a Rookie-class Minor League Baseball league that began play in 1911. It operated as a Class D league (1911–1914), (1921–1925), (1937–1955) and (1957–1962) before becoming a Rookie league in 1963. Teams are located in the Appalachian regions of Virginia, North Carolina, West Virginia and Tennessee. The league's season starts in June, after major league teams have signed players they selected in the annual amateur draft, and ends in September.
| Sport | Baseball |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1911 |
| President | Dan Moushon[1] |
| No. of teams | 10 |
| Country | USA |
| Most recent champion(s) | Johnson City Cardinals (2019) |
| Most titles | Bluefield Blue Jays (14) |
| Classification | Rookie Advanced |
| Official website | www.appyleague.com |
Along with the Pioneer League, it forms the second-lowest rung on the minor league ladder. Although classified as a Rookie league, the level of play is slightly higher than that of the two Rookie leagues based at the parent clubs' spring training complexes, the Gulf Coast League and Arizona League. Unlike these two leagues, Appalachian League games charge admission and sell concessions.
History
The original Appalachian League only existed for four seasons from 1911–1914 and all teams were independent with no MLB affiliation. The original league consisted of the Asheville Moonshiners, the Bristol Boosters, the Cleveland Counts, the Johnson City Soldiers, the Knoxville Appalachians, and the Morristown Jobbers.[2]
The second Appalachian League existed for five seasons from 1921–1925, and, as before, it consisted entirely of independent teams: the Bristol State-Liners, the Cleveland Manufacturers, the Greeneville Burley Cats, the second iteration of the Johnson City Soldiers, the Kingsport Indians, and the Knoxville Pioneers. Two of the 1921 locations have present-day teams in the Appalachian League: Kingsport, Tennessee, with the present-day Kingsport Mets, and Greeneville, Tennessee, with the present-day Greeneville Reds.[2]
The third iteration of the Appalachian league, which started in 1937, was shifted to D-level minor league, the lowest level in the pre-1963 MLB. It consisted of four teams: the Elizabethton Betsy Red Sox, the third iteration of the Johnson City Soldiers, the Newport Canners, and the Pennington Gap Lee Bears.[2]
The start of the 2020 season was postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic before ultimately being cancelled on June 30.[3][4]
Current teams
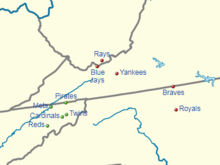
| Division | Team | MLB Affiliation | City | Stadium | Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East | Bluefield Blue Jays | Toronto Blue Jays | Bluefield, West Virginia and Bluefield, Virginia |
Bowen Field at Peters Park | 3,000 |
| Burlington Royals | Kansas City Royals | Burlington, North Carolina | Burlington Athletic Stadium | 3,500 | |
| Danville Braves | Atlanta Braves | Danville, Virginia | American Legion Field | 2,588 | |
| Princeton Rays | Tampa Bay Rays | Princeton, West Virginia | H. P. Hunnicutt Field | 3,000 | |
| Pulaski Yankees | New York Yankees[5] | Pulaski, Virginia | Calfee Park | 2,500 | |
| West | Bristol Pirates | Pittsburgh Pirates | Bristol, Virginia and Bristol, Tennessee | Boyce Cox Field at DeVault Memorial Stadium | 2,000 |
| Elizabethton Twins | Minnesota Twins | Elizabethton, Tennessee | Joe O'Brien Field | 2,000 | |
| Greeneville Reds | Cincinnati Reds | Tusculum, Tennessee | Pioneer Park | 4,000 | |
| Johnson City Cardinals | St. Louis Cardinals | Johnson City, Tennessee | TVA Credit Union Ballpark | 3,800 | |
| Kingsport Mets | New York Mets | Kingsport, Tennessee | Hunter Wright Stadium | 2,000 |
Current team rosters
Complete team list
1911–14
- Harriman Boosters (1911–14, as Bristol Boosters in 1911–13)
- Johnson City Soldiers (1911–13)
- Knoxville Reds (1911–14, as Knoxville Appalachians in 1911)
- Middlesboro Colonels (1911–14, as Asheville Moonshiners in 1911–12)
- Morristown Jobbers (1913–14, as Cleveland Counts in 1911–13; moved to Morristown during 1913 season)
- Rome Romans (1911–13, as Morristown Jobbers in 1911–12)
1921–25
- Bristol State Liners (1921–25)
- Greeneville Burley Cubs (1921–25)
- Johnson City Soldiers (1921–24)
- Kingsport Indians (1921–25)
- Knoxville Pioneers (1921–24)
- Morristown Roosters (1923–25, as Cleveland Manufacturers in 1921–22)
1937–55, 1957–present
|
|
Champions
League champions have been determined by different means since the Appalachian League's formation in 1911. Before 1984, the champions were usually the league pennant winners. With only a few early exceptions, champions since 1984 have been the winner of postseason playoffs.[6]
Hall of Fame
The Appalachian League Hall of Fame was started in 2019.[7]
See also
- Sports league attendances
- Baseball awards § U.S. minor leagues
References
- 2019 Appalachian League Media Guide
- "Minor League Baseball: the Appalachian League (Advanced-Rookie Classification)". Billssportsmaps.com. Archived from the original on 31 July 2014. Retrieved 30 July 2014.
- "A Message From Pat O'Conner". Minor League Baseball. March 13, 2020. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- "2020 Minor League Baseball Season Shelved". Minor League Baseball. June 30, 2020. Retrieved July 1, 2020.
- "Pulaski will be Yanks affiliate for '15 season". MiLB.com. Archived from the original on 2014-09-10.
- "Standings". 2017 Appalachian League Media Guide and Record Book. Minor League Baseball. pp. 39–61. Archived from the original on May 10, 2018. Retrieved August 11, 2017.
- "Hall of Fame". Appalachian League. Minor League Baseball. Retrieved June 20, 2019.