Angkor Borei District
Angkor Borei District (Khmer: ស្រុកអង្គរបូរី) is a district located in Takéo Province, in southern Cambodia. According to the 1998 census of Cambodia, it had a population of 44,980.[1]
Angkor Borei ស្រុកអង្គរបូរី | |
|---|---|
District (srok) | |
 | |
 Angkor Borei Location in Cambodia | |
| Coordinates: 10°59′42″N 104°58′29″E | |
| Country | |
| Province | Takéo |
| Communes | 6 |
| Villages | 34 |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| ISO 3166 code | KH-2101 |
Administration
The district has 6 communes, 34 villages (as of 2019).[2]
| No. | Code | Commune | Khmer | Number of Villages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 210101 | Angkor Borei Commune | ឃុំអង្គរបូរី | 6 |
| 2 | 210102 | Ba Srae Commune | ឃុំបាស្រែ | 8 |
| 3 | 210103 | Kouk Thlok Commune | ឃុំគោកធ្លក | 4 |
| 4 | 210104 | Ponley Commune | ឃុំពន្លៃ | 6 |
| 5 | 210105 | Prek Phtoul Commune (Preaek Phtoul) | ឃុំព្រែកផ្ទោល | 4 |
| 6 | 210106 | Prey Phkoam Commune | ឃុំព្រៃផ្គាំ | 6 |
| Total | 34 | |||
History
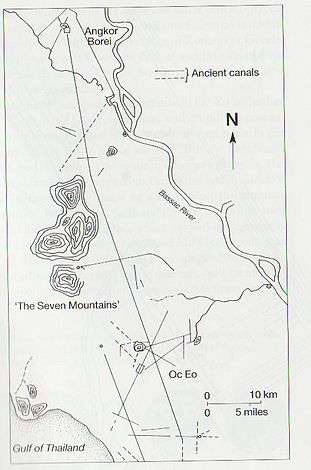
This ancient city was an important settlement of the Kingdom of Funan and may have been its capital. It may have been the Thinae, or Sinae Metropolis located by Claudius Ptolemy as the farthest known city to the east in his Geography.[3] The site was first excavated during the year 1996 and was again excavated in 1999 as part of the Lower Mekong Archaeological Project.[4] During the 1996 excavation the University of Hawaii and Royal University of Fine Arts initiated the excavation and focused on the sociopolitical complexity during 500BC - AD 500. This first excavation, however, was just a preliminary research. The first objectives were as followed:[5]
1) Documentation of the site's layout and the range of its archaeological features
2) Evaluation of the integrity of subsurface materials and description of the site's stratigraphy
3) collection of samples for dating portions of the archaeological site
4) reconstructing the hydrology and natural environment of the early historic period in this region
In this site various archaeological methods were used such as surface survey and mapping, test excavations, auger sampling and coring, and trenching with a backhoe.[6]
Unfortunately, the archeological project was disturbed by looting and illicit trafficking of Khmer antiquities, which continues as a serious problem into the 21st century.[7]
It is the birthplace of Norodom, King of Cambodia from 1860 to 1904.
See also
References
- "General Population Census of Cambodia 1998: Final Census Results" (PDF) (2nd ed.). National Institute of Statistics, Ministry of Planning, Cambodia. August 2002. pp. 260, 267. Retrieved 2010-11-25.
- "Cambodia Gazetteer Database Online". Cambodia NCDD Databases. National Committee for Sub-National Democratic Development (NCDD). 2019. Retrieved 2019-08-24.
- John Caverhill, “Some Attempts to ascertain the utmost Extent of the Knowledge of the Ancients in the East Indies”, Philosophical Transactions, vol.57, 1767, pp. 155-174. Rinith Taing, ‘The mysterious ‘foreigners’ carved into the temples of Sambor Prei Kuk’, Phnom Penh Post, 9 June 2017.
- Miriam T. Stark, et al., “Results of the 1995–1996 Archaeological Field Investigations at Angkor Borei, Cambodia” Archived 2015-09-23 at the Wayback Machinelink= 2015-09-23 at the Wayback Machine , Asian Perspectives, vol.38, no.1, 1999, at University of Hawai’i, pp.7-36.
- Stark, Miriam; Bong Sovath (2001). "Recent Research on emergent complexity in Cambodia's Mekong". Bulletin of the Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association: 85–98. Archived 2012-03-13 at the Wayback Machine
- Stark, Miriam; Bong Sovath (2001). "Recent Research on emergent complexity in Cambodia's Mekong". Bulletin of the Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association: 85–98.
- Miriam T. Stark and P. Brion Griffin, “Archaeological Research and Cultural Heritage Management in Cambodia's Mekong Delta: The Search for the ‘Cradle of Khmer Civilization,’” in Marketing Heritage: Archaeology and the Consumption of the Past, ed. by Yorke Rowan and Uzi Baram, Walnut Creek, California: Altamira Press, 2004, 117–141.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Angkor Borei. |