ABRIXAS
A Broadband Imaging X-ray All-sky Survey, or ABRIXAS was a space-based German X-ray telescope. It was launched on 28 April 1999 in a Kosmos-3M launch vehicle from Kapustin Yar, Russia, into Earth orbit. The orbit had a periapsis of 549.0 kilometres (341.1 mi), an apoapsis of 598.0 kilometres (371.6 mi), an inclination of 48.0° and an eccentricity of 0.00352, giving it a period of 96 minutes.[2][3]
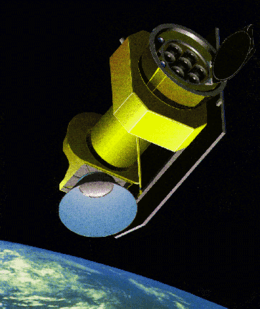 ABRIXAS in orbit. | |
| Mission type | X-ray astronomy |
|---|---|
| Operator | DLR |
| COSPAR ID | 1999-022A |
| SATCAT no. | 25721 |
| Mission duration | 0 years (mission failure) |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Launch mass | 550.0 kilograms (1,212.5 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 28 April 1999, 20:30 UTC |
| Rocket | Kosmos-3M |
| Launch site | Kapustin Yar 107 |
| End of mission | |
| Last contact | 1 May 1999 |
| Decay date | 31 October 2017[1] |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Sun-synchronous |
| Semi-major axis | 6,869.9 kilometers (4,268.8 mi) |
| Eccentricity | 0.00352 |
| Perigee altitude | 549 km (341 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 598 km (372 mi) |
| Inclination | 48.0 degrees |
| Period | 96.00 minutes |
| Epoch | 28 April 1999, 04:30:00 UTC[2] |
The telescope's battery was accidentally overcharged and destroyed three days after the mission started. When attempts to communicate with the satellite when its solar panels were illuminated by sunlight failed, the $20 million project was abandoned.[4] ABRIXAS decayed from orbit on 31 October 2017.
The eROSITA telescope is based on the design of the ABRIXAS observatory.[5] eROSITA was launched on board the Spektr-RG space observatory on 13 July 2019 from Baikonur to be deployed at the second Lagrange point (L2).[6]
References
- https://celestrak.com/
- "NASA – NSSD – Spacecraft – Trajectory Details (ABRIXAS)". NASA. Retrieved 2008-02-27.
- "NASA – NSSDC – Spacecraft – Details (ABRIXAS)". NASA. Retrieved 2008-02-27.
- "ABRIXAS". Astronautix.com. Retrieved 2008-02-28.
- "Spectrum-RG/eRosita/Lobster mission definition document". Russian Space Research Institute. 2005-10-30. Retrieved 2011-02-04.
- Zak, Anatoly (16 April 2016). "Spektr-RG to expand horizons of X-ray astronomy". Russian Space Web. Retrieved 16 September 2016.