2000 South Korean legislative election
Legislative elections were held in South Korea on 13 April 2000.[1]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 273 seats in the National Assembly 137 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 57.2% ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
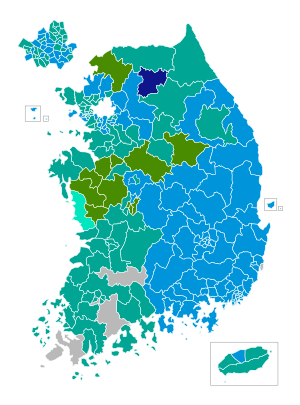 ■ GNP ■ MDP ■ ULD ■ DPP ■ NKPH ■ Others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of the Republic of Korea |
|
|
|
|
Opinion polls suggested that the ruling Democratic Party would win the most seats, but the result was a victory for the conservative Grand National Party (GNP), which won 133 of the 273 seats in the National Assembly. The United Liberal Democrats (ULD) lost two-thirds of their seats due to GNP's victory in Gyeongsangbuk-do, Gangwon-do (South Korea), and also fewer local votes in Chungcheong.
With no party winning a majority, the 16th parliament was the first Hung Parliament in South Korean history.[2]
The Democrats, ULD and Democratic People's Party (DPP) formed a coalition to gain a majority. However, the ULD withdrew support in 2001 and joined the conservative opposition. Seven ULD members subsequently defected from the party and joined the GNP, giving it a majority.
Results
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grand National Party | 7,365,359 | 39.0 | 133 | –21 |
| Millennium Democratic Party | 6,780,625 | 35.9 | 115 | +36 |
| United Liberal Democrats | 1,859,331 | 9.8 | 17 | –33 |
| Democratic People's Party | 695,423 | 3.7 | 2 | New |
| Democratic Labor Party | 223,261 | 1.2 | 0 | New |
| Young Progressive Party | 125,082 | 0.7 | 0 | New |
| New Korean Party of Hope | 77,498 | 0.4 | 1 | New |
| Republican Party | 3,950 | 0.02 | 0 | New |
| Independents | 1,774,211 | 9.4 | 5 | –11 |
| Invalid/blank votes | 252,384 | – | – | – |
| Total | 19,157,124 | 100 | 273 | –26 |
| Registered voters/turnout | 33,482,387 | 57.2 | – | – |
| Source: Nohlen et al. | ||||
References
- Dieter Nohlen, Florian Grotz & Christof Hartmann (2001) Elections in Asia: A data handbook, Volume II, p420 ISBN 0-19-924959-8
- "Korea Elections: A Shocking Eruption of Public Dissatisfaction". The Asia Foundation. 2016-04-27. Retrieved 2016-05-17.
.jpg)
.png)
