1957 Indian general election
The Indian general election of 1957, held from 24 February to 9 June, was the second election to the Lok Sabha, the lower house of the Parliament of India.[1] They were held five years after the first general election, according to the provisions of the Constitution of India. Elections to many state legislatures were held simultaneously.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 494 seats in the Lok Sabha 248 seats were needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
There were 494 seats elected using first past the post voting system. Out of the 403 constituencies, 91 elected two members, while the remaining 312 elected a single member.[2][3] The multi-seat constituencies were abolished before the next election.
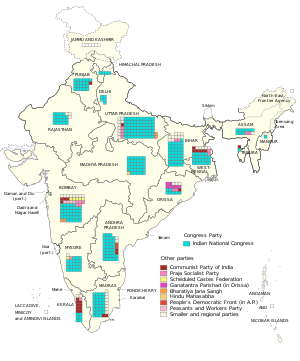
Under the leadership of Jawaharlal Nehru, the Indian National Congress easily won a second term in power, taking 371 of the 494 seats. They gained an extra seven seats (the size of the Lok Sabha had been increased by five) and their vote share increased from 45.0% to 47.8%. The INC won nearly five times more votes than the Communist Party, the second largest party. In addition, 19.3% of the vote and 42 seats went to independent candidates, the highest of any Indian general election.
Results
Results by Party
| Lok Sabha elections 1957 Electoral participation: 55.42% |
% | Won (total 494) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bharatiya Jana Sangh | BJS | 5.97 | 4 |
| Communist Party of India | CPI | 8.92 | 27 |
| Indian National Congress | INC | 47.78 | 371 |
| Praja Socialist Party | PSP | 10.41 | 19 |
| Akhil Bharatiya Hindu Mahasabha | ABHM | 0.86 | 1 |
| Akhil Bharatiya Ram Rajya Parishad | RRP | 0.38 | 0 |
| Chota Nagpur Santhal Parganas Janata Party | CNSPJP | 0.42 | 3 |
| Forward Bloc (Marxist) | AIFB | 0.55 | 2 |
| Ganatantra Parishad | GP | 1.07 | 7 |
| Jharkhand Party | JKP | 0.62 | 6 |
| Peasants and Workers Party of India | PWPI | 0.77 | 4 |
| Indian Union Muslim League | IUML | 0.18 | 1 |
| People's Democratic Front | 0.87 | 2 | |
| Praja Party | PP | 0.12 | 0 |
| Revolutionary Socialist Party | RSP | 0.26 | 0 |
| Scheduled Castes Federation | SCF | 1.69 | 6 |
| Independents | - | 19.14 | 41 |
| Nominated Anglo-Indians | - | - | 2 |
Voting
The first instance of booth capturing in India was recorded in 1957 in the General Elections of that year in Rachiyahi, in Begusarai's Matihani assembly seat.[4][5][6][7]
References
- "ONCE UPON A POLL: Second Lok Sabha elections (1957)". The Indian Express. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
- "Statistical Report on General Election, 1957 : To the Second Lok Sabha Volume-I" (PDF). Election Commission of India. p. 5. Retrieved 11 July 2015.
- "Statistical Report on General Election, 1957 : To the Second Lok Sabha Volume-II" (PDF). Election Commission of India. Retrieved 11 July 2015.
- "Where booth capturing was born".
- "In central Bihar, development runs into caste wall".
- "Empty words in legend's forgotten village".
- "The myth of history's first booth capturing taking place in Begusarai's Rachiyahi".

