175th Tunnelling Company
The 175th Tunnelling Company was one of the tunnelling companies of the Royal Engineers created by the British Army during World War I. The tunnelling units were occupied in offensive and defensive mining involving the placing and maintaining of mines under enemy lines, as well as other underground work such as the construction of deep dugouts for troop accommodation, the digging of subways, saps (a narrow trench dug to approach enemy trenches), cable trenches and underground chambers for signals and medical services.[1]
| 175th Tunnelling Company | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Active | World War I |
| Country | |
| Branch | |
| Type | Royal Engineer tunnelling company |
| Role | military engineering, tunnel warfare |
| Nickname(s) | "The Moles" |
| Engagements | World War I Hooge Hill 60 Battle of Messines |
| Commanders | |
| Notable commanders | S. Hunter Cowan Geoffrey Cassels |
Background
By January 1915 it had become evident to the BEF at the Western Front that the Germans were mining to a planned system. As the British had failed to develop suitable counter-tactics or underground listening devices before the war, field marshals French and Kitchener agreed to investigate the suitability of forming British mining units.[2] Following consultations between the Engineer-in-Chief of the BEF, Brigadier George Fowke, and the mining specialist John Norton-Griffiths, the War Office formally approved the tunnelling company scheme on 19 February 1915.[2]
Norton-Griffiths ensured that tunnelling companies numbers 170 to 177 were ready for deployment in mid-February 1915.[3] In the spring of that year, there was constant underground fighting in the Ypres Salient at Hooge, Hill 60, Railway Wood, Sanctuary Wood, St Eloi and The Bluff which required the deployment of new drafts of tunnellers for several months after the formation of the first eight companies. The lack of suitably experienced men led to some tunnelling companies starting work later than others. The number of units available to the BEF was also restricted by the need to provide effective counter-measures to the German mining activities.[4] To make the tunnels safer and quicker to deploy, the British Army enlisted experienced coal miners, many outside their nominal recruitment policy. The first nine companies, numbers 170 to 178, were each commanded by a regular Royal Engineers officer. These companies each comprised 5 officers and 269 sappers; they were aided by additional infantrymen who were temporarily attached to the tunnellers as required, which almost doubled their numbers.[2] The success of the first tunnelling companies formed under Norton-Griffiths' command led to mining being made a separate branch of the Engineer-in-Chief's office under Major-General S.R. Rice, and the appointment of an 'Inspector of Mines' at the GHQ Saint-Omer office of the Engineer-in-Chief.[2] A second group of tunnelling companies were formed from Welsh miners from the 1st and 3rd Battalions of the Monmouthshire Regiment, who were attached to the 1st Northumberland Field Company of the Royal Engineers, which was a Territorial unit.[5] The formation of twelve new tunnelling companies, between July and October 1915, helped to bring more men into action in other parts of the Western Front.[4]
Most tunnelling companies were formed under Norton-Griffiths' leadership during 1915, and one more was added in 1916.[1] On 10 September 1915, the British government sent an appeal to Canada, South Africa, Australia and New Zealand to raise tunnelling companies in the Dominions of the British Empire. On 17 September, New Zealand became the first Dominion to agree the formation of a tunnelling unit. The New Zealand Tunnelling Company arrived at Plymouth on 3 February 1916 and was deployed to the Western Front in northern France.[6] A Canadian unit was formed from men on the battlefield, plus two other companies trained in Canada and then shipped to France. Three Australian tunnelling companies were formed by March 1916, resulting in 30 tunnelling companies of the Royal Engineers being available by the summer of 1916.[1]
Unit history
Formation
175th Tunnelling Company was formed at Terdeghem in April 1915, and moved soon after into the Railway Wood-Hooge-Armagh Wood area of the Ypres Salient.[1] From its formation until August 1917 the company served under Third Army.[3][7]
Hooge 1915
As part of their continued operations against the Ypres Salient after the Second Battle of Ypres and the Battle of Bellewaarde, the German forces kept seeking to gain the village of Hooge between 24 May and 3 June 1915.[8] In the grounds of the Château de Hooge was a German strongpoint which was proving particularly troublesome to the British forces defending the area. The redoubt had in fact been started by the British but had fallen into German hands.[9]
Major S. H. Cowan, commanding officer of 175th Tunnelling Company, described the situation at Hooge in June 1915: "There is some urgent [mining] work to be done at once in a village [Hooge] on a main road east of Ypres. We hold one half and the job is to get the G[ermans] out of the other, failing that they may get us out and so obtain another hill top from which to overlook the land. It is a significant fact that all their recent attacks round Ypres have been directed on hill tops and have rested content on the same, without trying really hard to advance down the slopes towards us."[10]
In order to break the stalemate, the 175th Tunnelling Company (which was at the time operating with the 3rd Division) dug a tunnel about 66 yards (60 m) long[9] under the German position and placed a mine there. This occurred during a time of relative quiet on the British part of the Western Front, when few major assaults were made. Nonetheless, the average casualty rate for the British and Commonwealth forces was around 300 per day.[11]
The officer in charge of laying the mine at Hooge was Lieutenant Geoffrey Cassels. He wrote: "[Hooge] was a small village in ruins on top of the ridge, Hooge meaning height, astride the Menin Road. On the north side of the road was a chateau with a separate annex standing in its own grounds by a large wood. Behind the chateau was Bellewarde Lake. In front of the chateau and east of the village proper were the racing stables (...). The stables were at the very apex of the salient. They were actually in our front line. The trenches were shallow and primitive, even the front line ones, and to reach the front lines some tunnels had been driven under the road and part of the ruins. No Man's Land between us and the Germans was littered with blackened corpses (...) and the stink was abominable. (...) Our objective was to sink a shaft, then tunnel under the chateau and annex and blow them up."[10]
The work was completed in five and a half weeks. The first attempt at tunnelling for the mine, starting from within a stable, failed because the soil was too sandy. A second shaft was sunk from the ruins of a gardener's cottage nearby. The main tunnel was in the end 190 feet (58 m) long, with a branch off this after about 70 feet (21 m), this second tunnel running a further 100 feet (30 m) on. The intention was to blow two charges under the German concrete fortifications, although the smaller tunnel was found to be off course. The explosive – used for the first time by the British – was ammonal supported by gunpowder and guncotton, making the Hooge mine the largest mine of the war thus far built.[11] The main difficulties for the tunnellers were that the water table is very high, and that the clay expands as soon as it comes into contact with the air.[9]
At 07.00 p.m. on 19 July 1915 the mine was fired. The explosion created a hole some 6.6 yards (6 m) deep and almost 44 yards (40 m) wide.[9] The far side of the crater was then taken and secured by men from the 1st Battalion, Gordon Highlanders and 4th Battalion, Middlesex Regiment. Ten of the latter were killed by debris from the mine as they waited in advanced positions.[11] The mine fired by 175th Tunnelling Company at Hooge on 19 July 1915 was only the second British offensive underground attack in the Ypres Salient. On 17 April 1915, 173rd Tunnelling Company had blown five mines at Hill 60 using gunpowder and guncotton, but none of these mines were even half as powerful as the Hooge charge.[12]
The Germans tried to recover their lost position but were driven back by infantry and a heavy artillery bombardment.[9] By 30 July the German units had managed to take control of the Château de Hooge and the surrounding area.[8] In November 1915, 177th Tunnelling Company arrived at Hooge and continued mining there in the defence of Ypres until August 1917. Fighting in the area continued until 1918, with the Hooge Crater (craters being strategically important in relatively flat countryside) frequently changing sides.[8]
Messines 1916/17
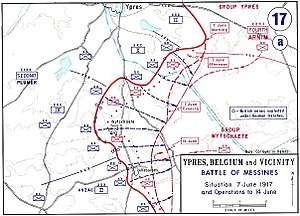

175th Tunnelling Company was extended to the Hill 60 in July 1915,[1] when 172nd Tunnelling Company moved into its place at The Bluff.[1] Deep mining under the German galleries beneath Hill 60 began in late August 1915 with the 175th Tunnelling Company which started a gallery 200 metres (220 yd) behind the British front line and passed 27 metres (90 ft) beneath the German positions. The British underground works consisted of an access gallery (nicknamed Berlin Tunnel) leading to two mine chambers called Hill 60 A (beneath Hill 60) and Hill 60 B (beneath The Caterpillar). The 3rd Canadian Tunnelling Company took over in April 1916 and completed the galleries, the Hill 60 mine being charged with 53,300 pounds (24,200 kg) of explosives in July 1916 and a branch gallery under the Caterpillar filled with a 70,000-pound (32,000 kg) charge in October. The 1st Australian Tunnelling Company took over in November 1916 and maintained the mines at Hill 60 over the winter.[13][14]
Meanwhile, the bulk of 175th Tunnelling Company had moved briefly to Spanbroekmolen in April 1916.[1] Also in April 1916, 175th Tunnelling Company took over work on the deep mines at Kruisstraat from 3rd Canadian Tunnelling Company. 175th Tunnelling Company continued to drive the galleries forward and when the main tunnel reached 320 metres (1,051 ft) it was handed over to 171st Tunnelling Company who were also responsible for Spanbroekmolen.[15]
As part of the prelude to the Battle of Messines, deep mine galleries were dug by the British 171st, 175th and 250th Tunnelling companies and the 1st Canadian, 3rd Canadian and 1st Australian Tunnelling companies, while the British 183rd, 2nd Canadian and 2nd Australian Tunnelling companies built dugouts (underground shelters) in the Second Army area.[16] The mines at Messines were detonated on 7 June 1917, creating 19 large craters.
Vimy Ridge
Having handed over its share of the work at Messines, 175th Tunnelling Company moved to Vimy, an area of busy underground activity for much of the war. British tunnellers took over progressively from the French between February and May 1916.[17] Other units active around Vimy in addition to 175th Tunnelling Company were 172nd, 176th, 182nd, 184th, 185th[18] and 255th Tunnelling Companies.
From spring 1916, the British had deployed five tunnelling companies along the Vimy Ridge, and during the first two months of their tenure in the area, 70 mines were fired, mostly by the Germans.[19] Between October 1915 and April 1917 an estimated 150 French, British and German charges were fired in this 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) sector of the Western Front.[17] In May 1916, a German infantry attack, which forced the British back 640 metres (700 yd), was aimed at neutralising British mining activity by capturing the shaft entrances. From June 1916, however, the Germans withdrew many miners to work on the Hindenburg Line and also for work in coal mines in Germany. In the second half of 1916 the British constructed strong defensive underground positions, and from August 1916, the Royal Engineers developed a mining scheme to support a large-scale infantry attack on the Vimy Ridge proposed for autumn 1916, although this was subsequently postponed.[19] After September 1916, when the Royal Engineers had completed their network of defensive galleries along most of the front line, offensive mining largely ceased[17] although activities continued until 1917. The British gallery network beneath Vimy Ridge eventually grew to a length of 12 kilometres (7.5 mi).[17]
In October 1916, 175th Tunnelling Company moved away again from the Vimy sector[17] and returned to the Ypres Salient.
Lettenberg Bunkers
175th Tunnelling Company then deployed to Loker, about two miles west of Kemmel and near Wijtschate, where it constructed bunkers. Known as the Lettenberg Bunkers, they are located at the edge of a woodland along the road from Kemmel, climbing up a hill towards Loker. These fortifications were constructed in the spring of 1917, although the 175th Tunnelling Company had been digging to create underground headquarters here for some months before that. There are four bunkers, including a first aid post which has a red cross painted on the wall, and a command post located at the far end. There are information boards outside the bunkers.[20]
Hermies 1918
Destroyed the entrance inclines to Hermies catacombs in March 1918, as the enemy advanced from Cambrai.[1]
Somme 1918
Built bridges over the Ancre in the British advanced on the Somme in Autumn 1918.[1]
See also
- Mine warfare
References
An overview of the history of 175th Tunnelling Company is also available in Robert K. Johns, Battle Beneath the Trenches: The Cornish Miners of 251 Tunnelling Company RE, Pen & Sword Military 2015 (ISBN 978-1473827004), p. 217 see online
- The Tunnelling Companies RE Archived May 10, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, access date 25 April 2015
- "Lieutenant Colonel Sir John Norton-Griffiths (1871–1930)". Royal Engineers Museum. Archived from the original on August 10, 2006. Retrieved 2015-12-02.
- Watson & Rinaldi, p. 49.
- Peter Barton/Peter Doyle/Johan Vandewalle, Beneath Flanders Fields - The Tunnellers' War 1914-1918, Staplehurst (Spellmount) (978-1862272378) p. 165.
- "Corps History – Part 14: The Corps and the First World War (1914–18)". Royal Engineers Museum. Archived from the original on June 3, 2010. Retrieved 2015-12-02.
- Anthony Byledbal, "New Zealand Tunnelling Company: Chronology" (online Archived July 6, 2015, at the Wayback Machine), access date 5 July 2015
- Watson & Rinaldi, p. 20.
- Battlefields 14-18, undated, accessed 16 February 2007
- http://www.webmatters.net/belgium/ww1_hooge.htm access date 24 April 2015
- Peter Barton/Peter Doyle/Johan Vandewalle, Beneath Flanders Fields - The Tunnellers' War 1914-1918, Staplehurst (Spellmount) (978-1862272378) pp. 148–154.
- Hooge on ww1battlefields.co.uk, accessed 25 April 2015
- Peter Barton/Peter Doyle/Johan Vandewalle, Beneath Flanders Fields - The Tunnellers' War 1914-1918, Staplehurst (Spellmount) (978-1862272378) p. 148-154, in particular p. 152.
- Edmonds 1948, p. 60.
- Bean 1933, pp. 949–959.
- Holt & Holt 2014, p. 195.
- Edmonds 1948, p. 37–38.
- The Durand Group: Vimy Ridge online, access date 2016-08-03
- "durandvimy"
- Jones 2010, p. 133.
- "World War One Battlefields : Flanders: Kemmel & Bayernwald Trenches". Ww1battlefields.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2015-11-01. Retrieved 2015-10-29.
Bibliography
- Bean, C. E. W. (1941) [1933]. The Australian Imperial Force in France, 1917. Official History of Australia in the War of 1914–1918. IV (11th ed.). Melbourne: Australian War Memorial. ISBN 0-702-21710-7. Retrieved 21 May 2015.
- Edmonds, J. E. (1991) [1948]. Military Operations France and Belgium, 1917: 7 June – 10 November: Messines and Third Ypres (Passchendaele). History of the Great War Based on Official Documents by Direction of the Historical Section of the Committee of Imperial Defence. II (Imperial War Museum and Battery Press ed.). London: HMSO. ISBN 0-89839-166-0.
- Jones, Simon (2010). Underground Warfare 1914–1918. Pen & Sword Military. ISBN 978-1-84415-962-8.
- Holt, Tonie; Holt, Valmai (2014) [1997]. Major & Mrs Holt's Battlefield Guide to the Ypres Salient & Passchendaele. Barnsley: Pen & Sword Books. ISBN 978-0-85052-551-9.
- Graham E. Watson & Richard A. Rinaldi, The Corps of Royal Engineers: Organization and Units 1889–2018, Tiger Lily Books, 2018, ISBN 978-171790180-4.
Further reading
- Alexander Barrie. War Underground – The Tunnellers of the Great War. ISBN 1-871085-00-4.
- The Work of the Royal Engineers in the European War 1914 -1919, – MILITARY MINING.
- Jones, Simon (2010). Underground Warfare 1914-1918. Pen & Sword Military. ISBN 978-1-84415-962-8.
- Arthur Stockwin (ed.), Thirty-odd Feet Below Belgium: An Affair of Letters in the Great War 1915-1916, Parapress (2005), ISBN 978-1-89859-480-2 (online).
External links
- A group photograph of men of 175th Tunnelling Company, taken during the war
- List of tunnelling companies of the Royal Engineers, with short unit histories
- Trench map of Hooge, with location where 175th Tunnelling Company fired the large mine in July 1915
- Battle map of Hooge with mine craters indicated