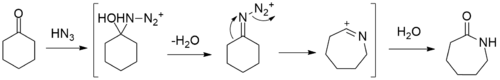Caprolactam
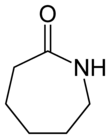
Caprolactam (CPL) is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)5C(O)NH. This colourless solid is a lactam (a cyclic amide) of caproic acid. Global demand for this compound is approximately five million tons per year, and the vast majority is used to make Nylon 6 filament, fiber, and plastics.[2]
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Azepan-2-one (Preferred IUPAC Name)
Hexano-6-lactam (allowed alternative) | |||
| Other names
ε-Caprolactam 1-Aza-2-cycloheptanone 2-Azacycloheptanone Capron PK4 Cyclohexanone iso-oxime Extrom 6N Hexahydro-2-azepinone Hexahydro-2H-azepin-2-one (9CI) Hexanolactam Aminocaproic lactam | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 106934 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.013 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 101802 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H11NO | |||
| Molar mass | 113.160 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Density | 1.01 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 69.2 °C (156.6 °F; 342.3 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 270.8 °C (519.4 °F; 544.0 K) at 1013.25 hPa | ||
| 866.89 g/L (22 °C) | |||
| Vapor pressure | 0.00000008 mmHg (20° C)[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |  | ||
| GHS Signal word | Warning | ||
GHS hazard statements |
H302, H315, H319, H332, H335 | ||
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |||
| Flash point | 125 °C (257 °F; 398 K) | ||
| Explosive limits | 1.4%-8.0%[1] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible) |
none[1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Synthesis and production
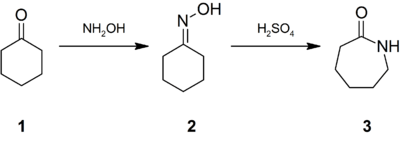
Caprolactam was first described in the late 1800s when it was prepared by the cyclization of ε-aminocaproic acid, the product of the hydrolysis of caprolactam. World demand for caprolactam was estimated to reach five million tons per year for 2015. 90% of caprolactam produced is used to make filament and fiber, 10% for plastics, and a small amount is used as a chemical intermediate.[2] Due to its commercial significance, many methods have been developed for the production of caprolactam. It was estimated that 90% of all caprolactam is synthesised from cyclohexanone (1), which is first converted to its oxime (2). Treatment of this oxime with acid induces the Beckmann rearrangement to give caprolactam (3):[2]
The immediate product of the acid-induced rearrangement is the bisulfate salt of caprolactam. This salt is neutralized with ammonia to release the free lactam and cogenerate ammonium sulfate. In optimizing the industrial practices, much attention is directed toward minimizing the production of ammonium salts.[2]
The other major industrial route involves formation of the oxime from cyclohexane using nitrosyl chloride, and this method accounts for 10% of world production.[2] The advantage of this method is that cyclohexane is less expensive than cyclohexanone.
Other paths to caprolactam include the depolymerization of waste Nylon 6, and the reaction of caprolactone with ammonia.[2] At bench scale, the reaction between cyclohexanone with hydrazoic acid to give caprolactam in the Schmidt reaction has been reported.[3]
Uses
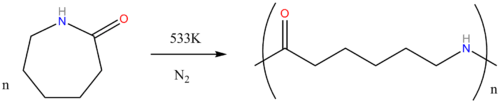
Almost all caprolactam produced goes into the manufacture of Nylon 6. The conversion entails a ring-opening polymerization:
Nylon 6 is widely used in fibers and plastics.
In situ anionic polymerization is employed for cast nylon production where conversion from ε-caprolactam to Nylon 6 takes place inside a mold. In conjunction with endless fiber processing the term thermoplastic resin transfer molding (T-RTM) is often used.
Caprolactam is also used in the synthesis of several pharmaceutical drugs including pentylenetetrazol, meptazinol, and laurocapram.
Safety
Caprolactam is an irritant and is mildly toxic, with an LD50 of 1.1 g/kg (rat, oral). In 1991, it was included on the list of hazardous air pollutants by the U.S. Clean Air Act of 1990. It was subsequently removed from the list in 1996 at the request of the manufacturers.[4] In water, caprolactam hydrolyzes to aminocaproic acid, which is used medicinally.
Currently, there is no official permissible exposure limit set for workers handling caprolactam in the United States. The recommended exposure limit is set at 1 mg/m3 over an eight-hour work shift for caprolactam dusts and vapors. The short-term exposure limit is set at 3 mg/m3 for caprolactam dusts and vapors.[5]
References
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0097". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Josef Ritz; Hugo Fuchs; Heinz Kieczka; William C. Moran. "Caprolactam". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a05_031.pub2.
- Eric J. Kantorowski; Mark J. Kurth (2000). "Expansion to Seven-Membered Rings". Tetrahedron. 56 (26): 4317–4353. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(00)00218-0.
- EPA - Modifications To The 112(b)1 Hazardous Air Pollutants
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards, CDC, retrieved November 8, 2013