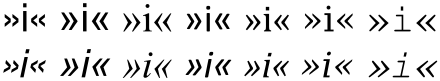Guillemet
Guillemets (/ˈɡɪləmɛt/,[1][2] also UK: /ˈɡiːmeɪ/,[3] US: /ˌɡiː(j)əˈmeɪ, ˌɡɪləˈmɛt/,[4] French: [ɡijmɛ]) are a pair of punctuation marks in the form of sideways double chevrons, « and », used as quotation marks in a number of languages. In some of these languages "single" Guillemets, ‹ and ›, are used for a quotation inside another quotation. Guillemets are not conventionally used in the English language.
| « » | |
|---|---|
Guillemets | |
| In Unicode | U+00AB « LEFT-POINTING DOUBLE ANGLE QUOTATION MARK (HTML « · «) U+00BB » RIGHT-POINTING DOUBLE ANGLE QUOTATION MARK (HTML » · ») |
Terminology
Guillemets may also be called angle, Latin, or French quotes / quotation marks.
Guillemet is a diminutive of the French name Guillaume (equivalent to English William), apparently after the French printer and punchcutter Guillaume Le Bé (1525–1598),[5] though he did not invent the symbols: they first appear in a 1527 book printed by Josse Bade.[6] Some languages derive their word for guillemets analogously: the Irish term is Liamóg, from Liam 'William' and a diminutive suffix.
In Adobe Systems font software, its file format specifications, and in all fonts derived from these that contain the characters, the glyph names are incorrectly spelled guillemotleft and guillemotright (a malapropism: guillemot is actually a species of seabird). Adobe acknowledges the error.[7] Likewise, X11 mistakenly uses XK_guillemotleft and XK_guillemotright to name keys producing the characters.
Shape
Guillemets are smaller than less-than and greater-than signs, which in turn are smaller than angle brackets.
Uses
As quotation marks
Guillemets are used pointing outwards («like this») to indicate speech in these languages and regions:
- Albanian
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani (used alongside "...")
- Belarusian
- Breton
- Bulgarian (rarely used; „...“ is official)
- Catalan
- Chinese (《 and 》 are used to indicate a book or album title)
- Esperanto (usage varies)
- Estonian (marked usage; „...“ prevails)
- Franco-Provençal
- French (spaced out by non-breaking spaces « like this », except in Switzerland)
- Galician
- Greek
- Italian
- Japanese (《 and 》 are used to indicate a book or album title)
- Northern Korean (in Southern Korean " is used)
- Kurdish
- Norwegian
- Persian
- Polish (acceptable and defined to indicate a quote inside a quote by some language standards, but less common. See also: Polish orthography)
- Portuguese (used mostly in European Portuguese, due to its presence in typical computer keyboards; considered obsolete in Brazilian Portuguese)
- Romanian; only to indicate a quotation within a quotation
- Russian, and some languages of the former Soviet Union using Cyrillic script („...“ is also used for nested quotes and in hand-written text.)
- Spanish (uncommon in daily usage, but commonly used in publishing)
- Swiss languages
- Turkish
- Ukrainian
- Vietnamese (previously, used in South Vietnam, now "..." is official)
Guillemets are used pointing inwards (»like this«) to indicate speech in these languages:
- Croatian (marked usage; „...” prevails)
- Czech (marked usage; „...“ prevails)
- Danish ("..." is also used)
- Esperanto (very uncommon)
- German (except in Switzerland; preferred for printed matters; „...“ is preferred in handwriting)
- Hungarian (only used „inside a section »as a secondary quote« marked by the usual quotes“ like this)
- Polish (used to indicate a quote inside a quote as defined by dictionaries; more common usage in practice. See also: Polish orthography)
- Serbian (marked usage; „...“ prevails)
- Slovak (marked usage; „...“ prevails)
- Slovene („...“ and "..." also used)
- Swedish (this style, and »...» are rarely used; ”...” is the common and correct form)
Guillemets are used pointing right (»like this») to indicate speech in these languages:
Ditto mark
In Quebec, the right-hand guillemet, », called a guillemet itératif, is used as a ditto mark.[8]
UML
Guillemets are used in Unified Modeling Language to indicate a stereotype of a standard element.
Mail merge
Microsoft Word uses guillemets when creating mail merges. Microsoft use these punctuation marks to denote a mail merge "field", such as «Title», «AddressBlock» or «GreetingLine». Then on the final printout, the guillemet-marked tags are replaced by each instance of the corresponding data item intended for that field by the user.
Encoding
Double guillemets are present in many 8-bit extended ASCII character sets. They were at 0xAE and 0xAF (174 and 175) in CP437 on the IBM PC, and 0xC7 and 0xC8 in Mac OS Roman, and placed in several of ISO 8859 code pages (namely: -1, -7, -8, -9, -13, -15, -16) at 0xAB and 0xBB (171 and 187).
Microsoft added the single guillemets to CP1252 and similar sets used in Windows at 0x8B and 0x9B (139 and 155) (where the ISO standard placed C1 control codes).
The ISO 8859 locations were inherited by Unicode, which added the single guillemets at new locations:
- U+00AB « LEFT-POINTING DOUBLE ANGLE QUOTATION MARK
- U+00BB » RIGHT-POINTING DOUBLE ANGLE QUOTATION MARK
- U+2039 ‹ SINGLE LEFT-POINTING ANGLE QUOTATION MARK
- U+203A › SINGLE RIGHT-POINTING ANGLE QUOTATION MARK
Despite their names, the characters are mirrored when used in right-to-left contexts.
Keyboard entry
The double guillemets are standard keys on AZERTY and French Canadian QWERTY keyboards and some others.
| « | » | ‹ | › | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOS+Windows[lower-alpha 1] | Alt+174 | Alt+175 | ||
| Windows[lower-alpha 2] | Alt+0171 | Alt+0187 | Alt+0139 | Alt+0155 |
| Windows US-International keyboard | Alt Gr+[ | Alt Gr+] | ||
| Macintosh[lower-alpha 3] | ⌥ Opt+\ | ⌥ Opt+⇧ Shift+\ | ⌥ Opt+⇧ Shift+3 | ⌥ Opt+⇧ Shift+4 |
| Macintosh French keyboard | ⌥ Opt+7 | ⌥ Opt+⇧ Shift+7 | ||
| Macintosh Norwegian keyboard | ⌥ Opt+⇧ Shift+V | ⌥ Opt+⇧ Shift+B | ||
| Compose key (Unix/Linux/etc) | Compose<< | Compose>> | Compose.< | Compose.> |
| ChromeOS, Linux (US international & UK extended keyboards) |
Alt Gr+Z | Alt Gr+X | Alt Gr+⇧ Shift+Z | Alt Gr+⇧ Shift+X |
| HTML | « | » | ‹ | › |
- OEM code page set to CP437 or CP850
- ANSI code page set to CP1252
- This applies to all English-language keyboard layouts supplied with the Apple operating system, e.g. "Australian", "British", "Canadian", "Irish", "Irish Extended", "U.S." and "U.S. Extended". Other language layouts may differ.
See also
- A related pair of symbols, 'angle brackets' (a single chevron),
⟨and⟩, is used for another purpose, in mathematics and computing. - Chevron
- Keyboard (computing)
- Quotation mark
References
- "guillemet". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- "Guillemet". Collins English Dictionary. HarperCollins. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- "guillemet". Oxford Dictionaries UK Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- "guillemet". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- "Character design standards, Latin 1: Punctuation Design Standards. § Pointing quotation marks – Guillemets". Microsoft Typography. Archived from the original on 2012-11-03. Retrieved 2020-06-12.
- Trésor de la langue française informatisé – guillemet
- Adobe Systems Inc. (1999). PostScript Language Reference: The Red Book (3rd ed.). Addison Wesley. Character set endnote 3, page 783. ISBN 978-0-201-37922-8. OCLC 40927139.
- "Banque de dépannage linguistique: Guillemets itératifs" [Linguistic help desk: Iterative quotes] (in French). Office québécois de la langue française. Retrieved 30 December 2019.
External links
| Look up guillemet in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Guillemets. |