Geography of Martinique
Martinique is an island in the Caribbean Sea, southeast of Cuba and north of Trinidad and Tobago. It is part of the French West Indies.
| Nickname: Island of Flowers | |
|---|---|
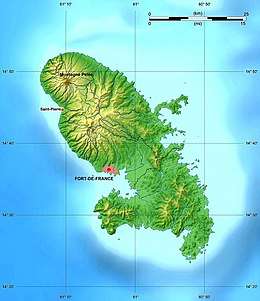 Map of Martinique | |
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Caribbean Sea |
| Coordinates | 14°40′N 61°00′W |
| Archipelago | Windward Islands |
| Area | 1,060 km2 (410 sq mi) |
| Coastline | 350 km (217 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,397 m (4,583 ft) |
| Highest point | Montagne Pelee |
| Administration | |
France | |
| Overseas department | Martinique |
| Largest settlement | Fort-de-France (pop. 134,727) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 429,510 (2008) |
| Pop. density | 405.2/km2 (1,049.5/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | African and African-white-Indian mixture 90%, white 5%, Indian Tamil or East Indian, Chinese less than 5% |
Statistics
Area:
total:
1,100 km²
land:
1,060 km²
water:
40 km²
Area - comparative: slightly more than six times the size of the City of Washington, D.C.
Land boundaries: 0 km
Maritime claims:
exclusive economic zone:
200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
territorial sea:
12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
Climate: tropical; moderated by trade winds; rainy season (June to October); vulnerable to devastating hurricanes every eight years on average; average temperature 17.3 degrees Celsius; humid
Natural resources: coastal scenery and beaches, cultivable land
Land use:
arable land:
8%
permanent crops:
8%
permanent pastures:
17%
forests and woodland:
44%
other:
23% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 40 km² (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: hurricanes, flooding, and volcanic activity (an average of one major natural disaster every five years)
Extreme points
- Northernmost point - Pointe de Macouba
- Easternmost point - Cap Ferré
- Southernmost point - headland between Pointe des Salines and Pointe d'Enfer
- Westernmost point - unnamed headland near Anse Belleville
- Highest point - Mont Pelee 1,397 m
- Lowest point - Caribbean Sea 0 m
Terrain
Martinique can be separated by the north, central, and southern portions of the island. The north contains mountainous terrain and a volcano, Mt. Pelee. Black sand beaches exist in this region due to volcanism. The central zone is covered by the Pitons du Carbet- a mountain chain that reaches 1,207 meters (3,960 ft). Fields and pastures occupy the south along with numerous beaches. [1]
See also
References
![]()
- "Geography of Martinique, Caribbean island - MartinicaOnline". martinicaonline.com. Retrieved 2019-05-20.