Celts
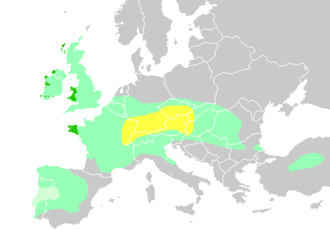
The Celts are a category of European peoples with a common ethnic, cultural and linguistic heritage. They used to be an adversary of the Roman Empire. Today, the peoples of Brittany, Cornwall, Ireland, the Isle of Man, Scotland and Wales make up the six Celtic nations with surviving Celtic languages. Additionally, the people of Galicia in Spain claim Celtic heritage, although no Celtic language survives in the region.
Understand
The concept of a Celtic culture is tenuous, and has only been used in modern times. The Celtic languages are a branch of the Indo-European languages with some traits in common, and a recorded history back to the 6th century BC.
Roman Empire

Most written sources about the Celts in ancient times are from the Roman Empire. The Celts were the dominant ethnic group in Gaul (which made up France and neighbouring countries) and Britannia.
In the fourth century BCE a Celtic chieftain known to history under the name "Brennus" led an army that managed to defeat and sack Rome, only withdrawing after the Romans paid a considerable ransom in gold.
The Roman Army conquered Gaul in the Gallic Wars. The Gallic peoples were Romanized, making Latin language and Roman religion dominant.
Talk
The Celtic languages alive today are Welsh, Irish, Scottic Gaelic, Manx, Cornish and Breton. Still, virtually everyone in Britain and Ireland is fluent in English, and Breton speakers in Brittany are also fluent in French. The modern Galician language is not Celtic, rather it is a Romance language closely related to Portuguese.