Assam
Assam (Assamese: অসম) is a land of blue hills, green valleys and a red river — the majestic and sacred Brahmaputra. It is known for its famous tea, its silk and its biodiversity, and is also rich in archeological heritage. Situated in the north eastern region of India, just below the eastern Himalayan foothills, it is surrounded by the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura and Meghalaya, which together with Assam are known collectively as the seven sisters, and by the nations of Bhutan and Bangladesh. The borders of China and Myanmar are within the range of 80 to 100 km.
.svg.png)
In spite of its merits as a place to visit, Assam is decidedly off the beaten track for tourists.
Regions
Assam can be divided into four distinct regions. The regions and the specific tourist interests in these are:
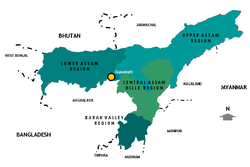
- The Upper Assam (Ujoni Oxom) Region - Kaziranga National Park, historical old capital city of Rongpur (Xiwoxagor/Sibsagar - Gaurixagor/Gaurisagar), ancient capital city and royal burial mounds at Charaideo the first capital of the Ahom rulers, Majuli - claimed to be the largest river island in the world, centre of Vaishnav monasteries and typical villages and cultural life of the Mishing ethno-cultural group, several other wildlife sanctuaries and habitats including the Joydihing rainforest and DibruSaikhowa with its population of feral horses (Brahmaputra's) close to Dibrugarh, cultural life of ethno-cultural groups such as Taiphakes, Taikhamtis, Singphos, Morans and of general Assamese population, Digboi - first Asian petroleum refinary with oil museum and the heritage wells, the WW-II famous Stillwell Road and the natural and cultural environment along it, archaeological site of Deopahar near Numaligarh refinery.
- The Central Assam Hills Region (Karbi Anglong and North Cachar) - the historic Maibong, scenic Haflong, fabled Jatinga (known for the bird suicide myth), hotwater spring at Umrangshu, cultural life at the villages of Karbi, Dimasa and Tiwa ethno-cultural groups, etc.
- The Southern Assam or Barak Valley Region -
- The Lower Assam (Namoni Oxom) Region - the historic and the largest city Guwahati, wildlife habitats such as Manas National Park, Pobitora, and Chakrasila; traditional silk industry at Soalkuchi (Xuwalkuchi), bronze and bell metal industry at Sarthebari (Xorthebary), archaeological sites such as Ambari (Guwahati), Madan Kamdev, Suryapahar, and Hajo; cultural life at the villages of general Assamese and of Bodo, Rabha, Hajong, and Garo ethno-cultural groups, rafting at several rivers, the religious places such as Hajo.
Cities
History of urban development goes back to almost two thousand years in the region. Existence of ancient urban areas such as Pragjyotishapura (Guwahati), Hatapesvara (Tezpur), and Durjaya, and medieval towns such as Charaideu, Garhgaon, Rongpur, Jorhat, Khaspur, and Guwahati, are well recorded.
Guwahati with its more than two thousand years of history is the largest urban centre and a million plus city in Assam. The city has experienced multifold growth during past three decades to grow as the primate city in the region; the city's population was approximately 0.9 million (considering Guwahati Metropolitan Development Authority (GMDA) area) during the census of 2001.

Major urban areas are:
- 🌍 Bongaigaon — commercial and industrial hub, home to many monuments of Assamese culture
- 🌍 Borgang — experience the rich folklore and culture of rural Assam in a picturesque landscape
- 🌍 Dibrugarh — home to several parks, gardens and temples
- 🌍 Dispur — capital of Assam.
- 🌍 Golaghat — an old urban centre for Assam, but nevertheless home to wildlife sanctuaries and a UNESCO-listed national park, beautiful views amid ancient ruins, and sacred Hindu and Christian sites from the 17th and 19th centuries
- 🌍 Guwahati — largest city in Assam.
- 🌍 Jorhat — considered by some to be the cultural center of Assam home to the historical city of Sivasagar
- 🌍 Nagaon — Kaziranga National Park is nearby
- 🌍 Rangia —
- 🌍 Silchar — Bhuban Hills, tea gardens and the former capital of the Old Cachari Kingdom (Khaspur).
- 🌍 Tezpur — also said to be the cultural capital of Assam, with many historical ruins with the Himalayans as a backdrop
- 🌍 Tinsukia — famous for its endless stretches of tea gardens
Other destinations
Assam has several attractive destinations; majority of these are national parks, wildlife and bird sanctuaries, areas with archaeological interests and areas with unique cultural heritage. Moreover, as a whole, the region is covered by beautiful natural landscapes.
National parks and wildlife sanctuaries:
- 🌍 Dibru-Saikhowa National Park — is a wonderful habitat of numerous birds; there are feral horses on the islands of the Brahmaputra close to the park.
- 🌍 Kaziranga National Park — a World Heritage Site of UNESCO is roughly a 400-km² wild life park is the largest habitat for one horned rhinoceros and several other unique flora and fauna. Kaziranga is a grassland situated in the central Assam region on the bank of the Brahmaputra; roughly 200 km. east of Guwahati.
- 🌍 Manas National Park — the wildlife park is in the foothills of Eastern Himalayas, where the river Manah flows with picturesque turns and clean water and sandy beaches. Although Manas is primarily a tiger reserve, it possesses numerous other valuable flora and fauna; the park is situated roughly 150 km west of Guwahati.
- 🌍 Nameri National Park — One of the most scenic national park of Assam, Nameri comes as a delight for the nature loving and bird watching traveler. The bird-life is particularly superb. Also, chances of spotting a Tiger is very high.
- 🌍 Orang National Park (known as mini Kaziranga National Park ), Assam — marshes, streams and grasslands provide a habitat for the Indian rhinoceros, Asian elephant, wild buffalo and tiger. It provides a home for many migratory species of birds and reptiles
- There are several other wildlife sanctuaries across the length and breadth of Assam.
Archaeological:
- Charaideo - the ancient capital of the Kingdom of Assam with hundreds of burial mounds called Moidams for kings and nobles.
- Dhansiri/Dhonxiri Valley archaeological region
- Guwahati archaeological region - Guwahati is an ancient city; there are several archaeological sites with temples, tanks, ramparts, etc. The Assam State Museum located close to historic Dighali Pukhuri (a large tank) is worth visiting.
- Hajo archaeological region - the ancient city of Apunarbhaba; there are remains of several ancient temples and other structures.
- Kapili Valley archaeological region
- Madan Kamdev - a 10th-century ancient city close to Guwahati; A large site of architectural, sculptural remains with numerous objects. Excavations are still going on.
- Maibong
- Sibsagar archaeological region - the nerve centre and the capital of the Kingdom of Assam under the Ahom Dynasty - earlier known as the city of Rongpur; the region has several palaces, temples, large tanks, ramparts, etc.
- Surya Pahar Goalpara archaeological region
- Tezpur archaeological region include Da Parbatia ruins and the Bamuni hills
Heritage, cultural and others:
Understand


History
The state of Assam is in a transitional region between South Asia and South-East Asia. Prior to Indian independence in 1947, Assam had been a part of British India since the British annexed the Kingdom of Assam and its tributary states in 1826 following the Treaty of Yandaboo. Assam used to be a larger state. Sylhet Division, formerly part of Assam, was allotted to Pakistan in the 1947 United Nations India Partition and subsequently became part of Bangladesh after the Bangladesh Liberation War in 1971, while Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Mizoram and Meghalaya were carved out of Assam during the 1960s and 70s. With an area of 78,438 km2, Assam in its current configuration is almost equivalent to the size of Ireland or Austria.
Assam was known as the Kingdom of Pragjyotisha-Kamarupa during the first millennium AD and was broken into smaller states during the beginning of the second millennium; however, later, for almost 600 years starting in the 13th century, the region was again transformed into a united sovereign country as the Kingdom of Assam under the later dynasties such as the Ahoms and Koches.
Assam has been a world leader in production of tea for more than past one hundred years and produces around 25 percent of the world's tea. Traditionally it is also a producer of high-quality silk, locally called paat bred on mulberry leaves, and the only place in the world where all four major silk types are cultivated, the others being the golden silk Muga unique to Assam, the Ahimsa silk Eri bred on castor leaves, and tassar.
A paradise for nature lovers
Assam and surrounding regions have to be a paradise for the nature lovers and researchers. The region's unique natural settings, hydro-geomorphic environment and biodiversity have no parallel in Asia. Within an eighty to hundred kilometres of journey by land, one can travel from a flat flood plain with tropical rainforests and wet paddy fields to mountainous regions of Alpine-Himalayan climatic conditions at very high altitude. Geomorphic studies conclude that the Brahmaputra, the life-line of Assam is a paleo-river; older than the Himalayas. The river with steep gorges and rapids in Arunachal Pradesh entering Assam, becomes a braided river (at times 16 km wide) and with tributaries, creates a flood plain (Brahmaputra Valley: 80–100 km wide, 1000 km long). The hills of Karbi Anglong, North Cachar and those in and close to Guwahati (also Khasi-Garo Hills) now eroded and dissected are originally parts of the South Indian Plateau system. In the south, the Barak originating in the Barail Range (Assam-Nagaland border), flows through the Cachar district with a 40–50 km wide valley and confluences with the Brahmaputra in Bangladesh.
Assam is one of the richest biodiversity zones in the world and consists of tropical rainforests, deciduous forests, riverine grasslands, bamboo orchards and numerous wetland ecosystems; Many are now protected as national parks and reserved forests. The Kaziranga, home of the rare Rhinoceros, and Manas are two UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Assam. Pabitora has the highest density of rhinos. The reserve forests of Joypur, Upper Dihing and Dirak are a stretch of pristine rainforests. The region is the last refuge for numerous other endangered species such as Golden Langur or Honali Bandor (Trachypithecus geei), White-winged Wood Duck or Deohanh (Cairina scutulata), Bengal Florican or Ulumora, Black-breasted Parrotbill, Pygmy Hog or Nolgahori, Greater Adjutant or Hargila, Hispid Hare or Khagorikota, Slow Loris or Lajuki Bandor, Swamp Francolin or Koira and so on. Some other endangered species with significant population in Assam are Tiger, Elephant, Hoolock Gibbon, Jerdon's Babbler and so on. Assam is also known for orchids the more well known being the foxtail or kopou and blue vanda or bhatou.
Climate and disasters
With the "Tropical Monsoon Rainforest Climate", Assam is temperate (Summer max. at 35-38 and winter min. at 6-8 degrees Celsius) and experiences heavy rainfall and high humidity. However, temperature is much lesser in the hilly areas in the Central Assam. The climate is characterised by heavy monsoon downpours reducing summer temperature and foggy nights and mornings in winter . Thunderstorms known as Bordoicila are frequent during the afternoons. Spring (March–April) and Autumn (September–October) are usually pleasant with moderate rainfall and temperature.
The region is prone to natural disasters with annual floods (in specific areas) and frequent mild earthquakes. Floods usually occur during monsoon (mid June till late August) and many a times can create trouble by destroying roads and railway linkages at places. Strong earthquakes are rare; three of these were recorded in 1869, 1897 (8.1 on the Richter scale); and in 1950 (8.6).
Cultural heritage
Assam is also a region, which can be termed as a crucible of cultures. It is a true meeting place of South Asian and South East Asian cultures, where the principal language Assamese (Oxomeeya) exhibits hybridity between Indo-Iranian, Tibeto-Burman and Tai-Kadai group of languages. Apart from the hybrid Assamese population, there are several distinct ethno-cultural groups such as Bodo, Karbi, Mishing, Dimasa, Tiwa, Rabha, Hasong, Taiphake, Taikhamti, Taiaiton, Singphow, Bru, Garo, etc. with distinct languages, dialects, food habits, architecture and settlement pattern, textile design, dance, music, musical instruments, beilef, etc.
State of tourism
It is important to understand that in the past 60 years, the Government of India's restrictions on the foreigners in the region such as the Restricted Area Permit System (RAP - finally abolished in Assam and neighbouring Meghalaya in the 1990s), acted as major hindrances for the foreign tourists and foreign interest groups to legally enter in to Assam and gradually pushed Assam in to isolation from the world. Assam today is a terra incognita to the new generations in the developed world; while the old generation British, other Europeans, Americans and Japanese still remember 'Assam' whatever may be the cause varying from colonial administration, to tea and oil industry or to WWII. For past 60 years, tourism promotion and development was a neglected subject. At the same time during the same time period, negligible numbers of Assamese have come out from Assam to other places; Assamese have been happy inside Assam, inside their native places and inside their houses, which recently has seen a sea-change with thousands of students and skilled labourers coming out to different cities in India. Therefore, as a not well-known place, Assam has long way to go to establish herself as a foremost tourist destination. However, Assam possesses everything that is required for developing herself as a leader of travel and tourism in the world and most importantly Assamese are one of the most hospitable people.
Talk
Assamese is the principal language and the lingua franca in the region. Assamese and Bodo are the local official languages in Assam while Bengali is used as the same in Barak Valley. There are several other local languages such as Mishing, Karbi, Dimasa, Garo, Hmar, Bru, Taiphake, Taikhamti, etc. used by the specific ethno-cultural groups in different pockets. However, most educated people speak English and Hindi with local accents. Bengali is also spoken in many parts of Assam, especially Guwahati and Silchar, where there are large Bengali communities. Moreover, there are large numbers of other Indian language and dialect speakers such as Punjabi, Marwari, Bhojpuri, Gujarati, etc., particularly in the urban centres.
Usually, all official signs and documents are written in both Assamese and English, using British spelling. The Government of India establishments Indian Railways, ONGC, et al. have sign boards in three languages - Assamese, English and Hindi. Commercial and street signs are usually written in Assamese and English and in Bengali in the Barak Valley. As English has a wider base, foreigners need not to worry about not becoming fluent Assamese or any other local language, although it is an additional advantage for a tourist to a know few sentences of a local language.
Get in
By plane
There is good air-connectivity to Assam from elsewhere in India. Guwahati's Lokapriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport (GAU IATA) is the busiest in Assam and other major airports are in Dibrugarh (DIB IATA), and Silchar (IXS IATA). Air India along with several other private airlines operates daily services from all the major cities such as Delhi, Kolkata, Mumbai, Bangalore, etc. Moreover, there are other airports in Tezpur, Jorhat, etc. with less frequent flights connecting cities such as Kolkata and other cities of North East Region. Arriving by plane, however, gives a wonderful welcome aerial view of the green valley surrounded by blue hills in Assam. The major airlines operating in the region are:
- Air India
- Spicejet
- https://www.goindigo.in/ Indigo Airlines]
- Go Airlines
- Air Asia
For the international travellers from East Asia or South East Asia, the most easiest route to travel to Assam is via Kolkata. There are several direct flights from Kolkata to Guwahati, Dibrugarh, Silchar and Jorhat. Journey time in a direct flight from Kolkata to Guwahati is of less than 45 minutes, while to Dibrugarh (the eastern most civil airport in Assam) is of around 90 minutes. Similarly for travellers from Europe, Middle East, Central Asia and African countries either via Delhi and Mumbai or even Kolkata route is preferable. However, Delhi and Kolkata have higher frequency of flights to Guwahati. A Delhi-Guwahati direct flight takes 2hr 30min of journey time. There is no longer an international flight here.
By rail
Three major routes of North East Frontier Railways (NF Railways) cover Assam and provide linkage to elsewhere in India. Guwahati railway station is the largest in Assam and is served by direct trains from most of the major cities in India. The Rajdhani Express (fully air-conditioned) from New Delhi (takes 27 hours) and Saraighat Express from Howrah in Kolkata (takes 17 hours) are the fastest ones. There are many direct trains from Delhi (including the Rajdhani Express) and Kolkata for Dibrugarh in Upper Assam. Usually, Dibrugarh is an additional night's journey (12 hr) from Guwahati.
By car
There are highways from Indian states in the west and buses run between Siliguri (to Siliguri buses are available from Kolkata, Darjeeling and Gangtok) and Guwahati; However, travelling by bus may not be comfortable in this patch and travel time is usually longer than that of trains. Road connectivity to surrounding Seven Sister States is good, however may take different durations depending on the location of the state.
Tamu in western Myanmar is connected to a reasonably good highway to Assam via Manipur; Tamu in Myanmar border is closer to Mandalay. The historic Stilwell Road between Assam-Myanmar-China from Ledo in Upper Assam to Myitkina in Myanmar and further to Kunming in China is right now not fully operationalised.
There are also roads connecting Bhutan.
Get around
By bus and car
Buses are the most common medium of travel in Assam. Buses in Assam are generally well maintained and comfortable. There are regular bus services connecting important places within Assam and to neighbouring states. Long distance buses generally are called Night Super Bus (because they usually travel only at after sunset) are more comfortable with reclining seats. Assam State Transport Corporation (ASTC) is state run bus company with a very exhaustive network. Some private players have large networks as well.
Taxi cabs can be a good option for travelling inside Assam and to the surrounding region. In majority cities and even small towns private taxi-cabs are available for rent for local travel as well for inter-city travel. The taxi-cabs can be also rented on daily basis. For a traveller, it is easier to hire a taxi from the hotel he or she is staying; usually the hotels can arrange or provide with information on the local car rental agencies. Self driving may not be advisable for many reasons - dangerous traffic, frequent agitations and 'bandh's and insurgency in certain areas to name some.
By train
Although having a fairly extensive railway network, trains are less convenient than buses or taxis for travelling short distances within Assam - inter-city or inter-regional trains are not very frequent within Assam. Moreover, the Assam's rail network is fragmented due to different gauge size. The services on narrow gauge and meter gauge lines are irregular and uncomfortable. Broad gauge service links Guwahati with major cities in upper Assam (Dibrugarh, Jorhat and Tinsukia), which is comfortable but little more time consuming than the buses; However, from Guwahati, one may try using the Rajdhani Express (fully Airconditioned) for an over-night journey to reach Dibrugarh or Tinsukia. The railway tickets are bookable online or available at the electronic ticketing counters in the stations. It is important to have a reservation for an overnight train journey, to obtain a berth in a comfortable A/C or non A/C sleeper coach. For reservation, booking should be made 2 months before the journey; however, in majority trains 'Tatkal' service is available.
By plane
Air travel from Guwahati to Upper Assam or Southern Assam districts can be quicker and easier. Guwahati is linked with Dibrugarh, Jorhat, Tezpur and Silchar with several flights. However, it is important to book a ticket early. A flight between Guwahati and Dibrugarh takes roughly 45 minutes.
See

- Kaziranga National Park is on the south bank of the Brahmaputra river. It is home and one of the last refuges to rhinoceros of Assam and covers an area of 430 km².
- Manas National Park
Do
- Brahmaputra Cruise - A private firm, Assam-Bengal Navigation offers river cruise on Brahmaputra. This tour covers almost whole of the stretch of river lying in Assam.
- Jadav Payeng InitiativeThis village is famous for the man made forest & mishing tribe. They assist in Assam's eco-cultural tours & travel.
- Greener Pastures- An eco-tourism organization which provides responsible tours to offbeat and exotic destinations of Northeast India. Activities include trekking, tribal tours, wildlife journeys, river cruises, tea tours and adventure sports such as caving and rafting.
- Pedalroads Adventures - An adventure tour company based in Guwahati offering cycling and trekking tours across the northeastern states.
Eat
It is worthwhile to taste ethnic Assamese cuisine which comprises rice with regional curries, including choices of fish, lamb, chicken and duck. Assamese meals are usually accompanied by various side dishes like mash potatoes (Alu Pitika) or pickles of small fried fishes.
Rice
Rice is the most important ingredient in the state's cuisine. The large varieties of rice found in the region has led to speculation that the grain was first domesticated in the Assam-Yunnan region. Both the indica as well as the japonica varieties are grown in Assam. The most popular class of rice is the joha or scented rice. As a staple diet rice is eaten either steam boiled (ukhua) or sundried (aaroi). Some very fine varieties of rice namely, Karaballam or kauribadam etc. are available in Assam only. Rice is eaten as a snack in many different forms: roasted and ground (xandoh), boiled in its husk and flattened (chira), puffed (akhoi). There is also a variety of rice grown that can be just soaked and eaten (kumol saul).
Fish
The next most important ingredient is fish, harvested from the many rivers, ponds and lakes in the region. There is no traditional ethnic community in Assam that does not eat fish. Some of the most popular big fishes are the Rohu, the Hilsa and the chital (big), khoria (medium) (Chitala chitala), Maagur, Xingi, Borali, Bhokua, Xaal, Xol, etc. The small varieties of fish available and eaten in Assam include Puthi, Borolia, Mua, cheniputhi, tengera, lachin, bhagun and pabho.
- The most popular dish from Assam, the tenga (fish sour), is an indispensable part of a proper meal in Assam. The most popular tenga is made with tomatoes, though the ones made with kajinemu (thick skinned elongated lemon) and thekera (dried Mangosteen,) are also popular
- Another favourite is small fish roasted in banana leaves (paatotdia).
- Hukuti is a special fish dish prepared from dried small fish (puthi maas) pounded with an arum stem and dried and stored in bamboo tubes. Variations of this exist among the ethnic communities of Northeast India in general and Assam in particular, are dried and fermented small fish puthy mas (Ticto barb), three to four in numbers are roasted along with lavish amounts of green chillies, tomatoes, ginger and garlic (all roasted). The ingredients are then pounded in a mortar to make a coarse paste and served with rice.
The Assamese meat and fish dish is characterized by low amount of spices and oil, higher quantity of ginger, norosingho paat (curry leaves) and lemon juice. This is quite different from Bengali dishes in taste. Pork and to some extent, beef dishes are particularly favorites in the tribal areas in Assam. Beef is not taken by the majority of Assamese as they practice Hinduism; however, beef is popular among Assamese Muslims, although general people also have pork, but that is not taken by the Assamese Muslims. The basic cooking method is boiling. Onla, of the Bodos, is made with ground rice and special herbs, and constitutes a complete meal in itself. Other meats include squab, duck, chicken, mutton, venison, and turtle although venison and turtle meat are legally prohibited. The combination of duck – white gourd and squab – papaya or banana flower is very popular. Meat is curried in spicy gravy.
Typical Assamese dishes
- Chutney is made of coriander, spinach, tomato, heartleaf, curry leaf, chilli, lentil, chickpea etc. Xukan masor chutney (chutney made of dried fish) is popular among the tribal communities. Salad is made of carrot, radish, tomato, cucumber, beetroot, etc.
- The khar is a signature class of preparations made with a key ingredient, also called khar. The traditional ingredient is made by filtering water through the ashes of a banana tree, which is then called kola khar . A traditional meal invariably begins with a khar dish, made of raw papaya, pulses or any other main ingredient. Xôkôta: It is a severely bitter type of preparation. It is prepared with dry jute leaf, urad bean and khar.
- Kharoli is fermented mashed mustard (Brassica campestris var. toria) seed to which a khar has been added, and kahudi to which an acidic agent (lemon juice, dried mangosteen) has been added. Pitikas are also made from roasted or steamed vegetables (tomatoes and eggplants being very popular). Small fishes, Asiatic pennywort, matikaduri, tengamora leaves, heartleaf, dôrôn (Leucus longifolia), etc. roasted separately wrapped in banana leaves and mashed into pitika along with mustard oil, salt, chilli etc. are called patotdia (literally, 'in a leaf').
- Pickles are there made of mango, Indian gooseberry, hog plum, olive, Tamarind, star fruit, mangosteen, radish, carrot, elephant apple, Indian jujube, chilli, lime, garlic, etc.
- Poitabhat is a favourite dish in Assam during the summer season. Cooked rice is soaked overnight in order to prepare poitabhat and served the next day garnished with mustard oil, onion, chilli, pickles, pitika (smashes), etc.
- Pokori is a fritter is made of flower and tender leaves of pumpkin, tender leaves of bottle gourd, eggplant, tender leaves of Night-flowering Jasmine, etc.
- Side dishes called pitika - is a signature characteristic of this cuisine. The most popular is aloo pitika - mashed potatoes) garnished with raw onions, mustard oil, green chillies and sometimes boiled eggs. khorisa tenga is mashed fermented bamboo shoot, sometimes pickled in mustard oil and spices.
- The tenga is a light and sour fish dish, another signature class of preparations. The souring ingredient could be mangosteen, lemon, etc., but the most popular is that made with tomatoes. Fish dishes made with fermented bamboo shoot are generally sour, but they are not called tengas. Fish is fried in mustard oil or curried with bottle gourd or spinach. Another tenga dish is prepared with matimah (urad bean) and outenga (elephant apple). Bottle gourd also can be added to it. Tengamora or noltenga and lentil is also a distinct tenga curry.
Assamese Snacks
- Bora saul is a variety of glutinous rice found in Assam. It has an important role in Assamese traditional occasions like Bihu. It is used in Jolpan (snacks) and Pitha (ricecake or pancake). Soaked and ground bora saul is used in preparing Pitha. Boiled bora saul is served as Jolpan with curd or milk, jaggery or sugar.
- Chira (Flattened rice, also called beaten rice) is a dehusked rice which is flattened into flat light dry flakes. These flakes of rice swell when added to liquid, whether hot or cold, as they absorb water, milk or any other liquids. It can be eaten raw by immersing it in plain water or milk or curd, with salt or sugar or jaggery to taste, or lightly fried in oil.
- Ghila pitha is a type of pancake so called because of its knee cap sized shape. Knee cap is called Ghila in Assamese. Rice flour of Bora saul, one kind of glutinous rice or any common rice is used in it. A paste made of rice flour and jaggery is prepared first and then fried in cooking oil at a certain quantity. Salt is also used instead of jaggery to make salty Ghila pitha. It is generally prepared and served in Bihu in Assam.
- Kumol saul is a unique type of rice from Assam that can be eaten without cooking. It is rendered fluffy and edible by being soaked in water for a short time. The rice may be eaten with milk or curd, jaggery, yogurt after being immersed in warm water for just fifteen minutes or so.
- Muri (puffed rice) is made by heating sand in a pot, and then throwing in grains of rice. The rice may be washed in brine to provide seasoning. The rice puffs up and is separated from the sand by a strainer. It is served with hot milk or curd and jaggery or sugar.
- Pitha is a ricecake or pancake, a thin flat cake prepared from a batter and cooked on a hot griddle or frying pan. It is an inseparable part of Jolpan in Assam. It is a special class of rice preparation generally made only on special occasions like Bihu in Assam. Made usually with soaked and ground rice, they could be fried in oil, roasted over a slow fire or baked and rolled over a hot plate.
- Suji (Semolina) is also one type of common jolpan, a type of dessert. Like pithaguri it is heated on a frying pan and water is added to make it a paste and then served with hot milk.
- Til Pitha is a type of pancake. It is a special class of rice preparation and generally made only on special occasions like Bihu in Assam. Bora saul, a glutinous type of rice is soaked and ground. Then a certain quantity of this rice flour is baked, filled up with sesame seeds, ground coconut and dried rind of orange, jaggery, etc. and pressed and rolled with many folders. This rice cake is also called Hesa pitha since it is pressed after rolling it as folder by folder.
Major cities like Guwahati, Tezpur, Jorhat and Dibrugarh offer a wide variety of restaurants and eat outs. Restaurants are normally very cheap and a good meal will cost about $0.50 to $1 per person. There are also ambient restaurants which serve all kinds of Indian and Assamese dishes for about less than $5 – $8 per person.
Drink

Alcohol: Rohi
Tea: Assam is famous for tea internationally. It has a large tea growing industry. Most plantations are located in the upper Assam. 70% tea is exported outside India. People drink tea with/without milk and also sometimes containing ginger and spices such as cardamom.
Water: Problematic due to lack of sanitary facilities and sewage treatment. It is safest to assume water is unsafe for drinking without being chemically treated or boiled, which is one reason to stick to tea or bottled water.
Cope
Radio Stations
- AIR Guwahati / Akashvani Guwahati) - 729 kHz, 1035 kHz, 4940 kHz, 7280 kHz, 100.8 MHz
- Gupshup FM - 94.3
- Radio Oolala (Positive Radio Pvt. Ltd.) - 91.9 MHz
- Big 92.7 FM, Guwahati (Adlabs Films Ltd.) - 92.7 MHz
- Gyan Vani, Guwahati - 107.8 MHz
- AIR Dibrugarh / Akashvani Dibrugarh - 567 kHz
- AIR Jorhat / Akashvani Jorhat - 103.4 MHz
- AIR Tezpur / Akashvani Tezpur - 1125 kHz
- AIR Diphu / Akashvani Diphu) - 1485 kHz
- AIR Haflong / Akashvani Haflong - 100.2 MHz
- AIR Nagaon / Akashvani Nagaon - 102.7 MHz
- AIR Kokrajhar / Akashvani Kokrajhar - 1512 kHz
- AIR Dhubri / Akashvani Dhubri - 103.3 MHz
- AIR Silchar / Akashvani Silchar - 828 kHz
Newspapers
- The Assam Tribune
- The Sentinel
- The Asomiya Pratidin
- Janasadharan
Go next
- Aizawl and other parts of Mizoram
- Darjeeling and Kalimpong
- Gangtok and other parts of Sikkim
- Imphal, Logtak Lake and other parts of Manipur
- Kohima, Zhukou Valley and other parts of Nagaland
- Kolkata, Delhi, Mumbai and other parts of India
- Mandalay in Myanmar via Moreh (Manipur) and Tamu (Myanmar)
- Namdapha National Park in Arunachal
- Samdrup Jongkhar - Bhutanese town on the border with Assam
- Shillong and Cherrapunji in Meghalaya
- Tawang - A Himalayan picturesque place with winter snow and a large Buddhist Monastery approximately 100 km north of the town of Tezpur.
- Thimphu, Paro and other parts of Bhutan