Zhari Namco
Zhari Namco or Zhari Nanmu or Lake Trari Nam (Tibetan: བཀྲ་རི་གནམ་མཚོ, Wylie: bkra ri gnam mtsho , Chinese: 扎日南木错) is a salt lake in Tibet, China. It is bounded on the west by the Ngari Prefecture of Coqên County, and on the east by the Ngamring County of Shigatse Prefecture. Zhari Namco is 996.9 square kilometres (384.9 sq mi), with a drainage area of 15,433.2 square kilometres (5,958.8 sq mi), an elevation of 4,613 metres (15,135 ft), length 54.3 kilometres (33.7 mi) and mean width 18.36 kilometres (11.41 mi) (maximum width 26.2 kilometres [16.3 mi]).[1] It is located east of Coqên Town in southern Tibet.[2]

Map including Zhari Namco
| Zhari Namco | |
|---|---|
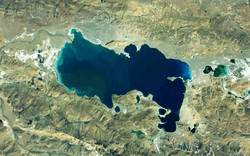 Satellite Image of Zhari Namco | |
| Coordinates | 30°55′N 85°38′E |
| Type | Endorheic, Saline, Permanent, Natural |
| Primary inflows | Cuoqin Zangbu, Dalong Zangbu |
| Catchment area | 15,433.2 km2 (5,958.8 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | China |
| Max. length | 54.3 km (34 mi) |
| Max. width | 26.2 km (16 mi) |
| Surface area | 996.9 km2 (400 sq mi) |
| Shore length1 | 183 km (100 mi) |
| Surface elevation | 4,613 m (15,135 ft) |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
Climate
| Climate data for Zhari Namco | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | −2.7 (27.1) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
2.2 (36.0) |
7.1 (44.8) |
10.9 (51.6) |
14.9 (58.8) |
14.7 (58.5) |
13.9 (57.0) |
12.0 (53.6) |
7.3 (45.1) |
1.2 (34.2) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
6.6 (43.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −9.7 (14.5) |
−8.1 (17.4) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
3.1 (37.6) |
7.6 (45.7) |
8.8 (47.8) |
8.3 (46.9) |
5.7 (42.3) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
−5.8 (21.6) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −16.7 (1.9) |
−15.2 (4.6) |
−10.9 (12.4) |
−8.1 (17.4) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
0.4 (32.7) |
2.9 (37.2) |
2.7 (36.9) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
−7.4 (18.7) |
−12.7 (9.1) |
−15.5 (4.1) |
−7.1 (19.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 13 (0.5) |
8 (0.3) |
15 (0.6) |
11 (0.4) |
8 (0.3) |
15 (0.6) |
53 (2.1) |
59 (2.3) |
24 (0.9) |
10 (0.4) |
1 (0.0) |
5 (0.2) |
222 (8.6) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org | |||||||||||||
Notes
- Sumin, Wang; Hongshen, Dou (1998). Lakes in China. Beijing: Science Press. p. 399. ISBN 7-03-006706-1.
- Maps (Map). Google Maps.
gollark: I mean, four is three more than one.
gollark: But nobody likes writing FOUR words.
gollark: It means "if and only if".
gollark: (iff is not a typo, before anyone does things)
gollark: Well, I would say that someone is a shallow person iff they do/say shallow things.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
