Yavapai–Apache Nation
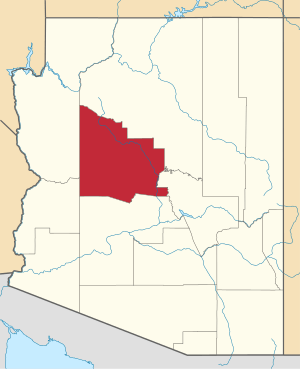
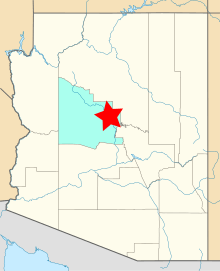
The Yavapai–Apache Nation is a federally recognized Native American tribe in Verde Valley, Arizona. Tribal members share two culturally distinct backgrounds and speak two indigenous languages, the Yavapai language and the Western Apache language. The Yavapai–Apache Nation Indian Reservation, at 34°37′10″N 111°53′46″W, consists of five non-contiguous parcels of land located in three separate communities in eastern Yavapai County. The two largest sections, 576 acres (233 ha) together – almost 90 percent of the reservation's territory, are in the town of Camp Verde. Smaller sections are located in the town of Clarkdale 60.17 acres (24.35 ha), and the unincorporated community of Lake Montezuma (5.8 acres (2.3 ha)). The reservation's total land area is 642 acres (260 ha). The total resident population of the reservation was 743 persons as of the 2000 census. The 2010 Census reported 1,615 people on the reservation. Of these, 512 lived in Camp Verde, 218 in Clarkdale, and only 13 in Lake Montezuma.


History
The Yavapai–Apache have lived in the southwest since 1100 C.E. Their use of the land helped them to survive as hunters and gatherers. Chief YumaFrank, Chief Viola Jimulla, and Carlos Montezuma were some of the first leaders of this nation. Beginning in 1865 the Yavapai were moved to several reservations such as: Colorado River Reservation, Fort McDowell, RioVerde, San Carlos, Camp Verde, Middle Verde, Clarkdale, and Prescott.[1]
Attractions
The Yavapai–Apache Nation operates the Cliff Castle Casino, a popular gaming, recreation, dining and lodging attraction in the Verde Valley.
See also
- Yavapai people
- Apache people
- Dilzhe'e Apache
References
- Rasmussen, R.E.H American Indian Tribes. Salem Press, 2000. 978-0-89356-063-8.
- Yavapai–Apache Nation Reservation, Arizona United States Census Bureau
- Rasmussen, R.E.H American Indian Tribes. Salem Press, 2000.
External links
- Yavapai–Apache Nation, official website
- Yavapai–Apache Nation, Arizona Intertribal Council
- Cliff Castle casino and hotel