Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome
Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch (WR) syndrome ([ˈviːdəman ˈʁa͜ʊtən.ʃtʁa͜ʊx]), also known as neonatal progeroid syndrome,[1] is a rare autosomal recessive progeroid syndrome. There have been over 30 cases of WR.[2] WR is associated with abnormalities in bone maturation, and lipids and hormone metabolism.[3]
| Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Neonatal progeroid syndrome |
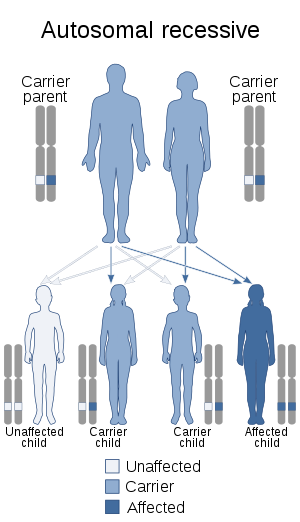 | |
| This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
Presentation
Affected individuals exhibit intrauterine and postnatal growth retardation, leading to short stature and an aged appearance from birth. They have physical abnormalities including a large head (macrocephaly), sparse hair, prominent scalp veins, inward-folded eyelid (entropion), widened anterior fontanelles, hollow cheeks (malar hypoplasia), general loss of fat tissues under the skin (lipoatrophy), delayed tooth eruption, abnormal hair pattern (hypotrichosis), beaked nose, mild to severe mental retardation and dysmorphism.[4]
Genetics
This condition has been associated with mutations in the POLR3A gene.[5] This gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 10 (10q22.3).
This gene encodes the largest subunit (A) of the DNA directed RNA polymerase III. This subunit includes the catalytic site of RNA polymerase 111.
Mutations in this gene have been associated with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and hypomyelinating leukodystrophy with or without oligodontia.
Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
Marfan lipodystrophy syndrome (MFLS) has sometimes been confused with Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome, since the Marfanoid features are progressive and sometimes incomplete.[6]
MFLS is caused by mutations near the 3'-terminus of FBN1 that cause a deficiency of the protein hormone asprosin and progeroid-like symptoms with reduced subcutaneous white adipose tissue.[7]
History
WR was first reported by Rautenstrauch and Snigula in 1977,[8] and the earliest reports made subsequently have been by Hans-Rudolf Wiedemann in 1979,[9] Devos in 1981[10] and Rudin in 1988.[11]
References
- "WIEDEMANN RAUTENSTRAUCH SYNDROME". NORD Rare Disease Report Abstract. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- "Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome". Orphanet. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- Arboleda, H; Quintero, L; Yunis, E (1997). "Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch neonatal progeroid syndrome: Report of three new patients". Journal of Medical Genetics. 34 (5): 433–7. doi:10.1136/jmg.34.5.433. PMC 1050956. PMID 9152846.
- Toriello, HV (1990). "Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome". Journal of Medical Genetics. 27 (4): 256–7. doi:10.1136/jmg.27.4.256. PMC 1017029. PMID 2325106.
- Wambach JA, Wegner DJ, Patni N, Kircher M, Willing MC, Baldridge D, Xing C, Agarwal AK, Vergano SAS, Patel C, Grange DK, Kenney A, Najaf T, Nickerson DA, Bamshad MJ, Cole FS, Garg A (2018) Bi-allelic POLR3A Loss-of-Function variants cause autosomal-recessive Wiedemann-Rautenstrauch syndrome. Am J Hum Genet
- Jacquinet A, Verloes A, Callewaert B, Coremans C, Coucke P, De Paepe A, Kornak U, Lebrun F, Lombret J, Pierard GE, Robinson PN, Symoens S, Van Maldergem L, Debray FG (2014). "Neonatal progeroid variant of Marfan syndrome with congenital lipodystrophy results from mutations at the 3' end of FBN1 gene". Eur. J. Med. Genet. 57 (5): 230–234. doi:10.1016/j.ejmg.2014.02.012. PMID 24613577.
- "OMIM Entry - #616914 - MARFAN LIPODYSTROPHY SYNDROME; MFLS". omim.org. Retrieved 2016-12-06.
- Rautenstrauch, T; Snigula, F; Krieg, Thomas; Gay, Steffen; Müller, P. K. (1977). "Progeria: A cell culture study and clinical report of familial incidence". European Journal of Pediatrics. 124 (2): 101–11. doi:10.1007/BF00477545. PMID 319005.
- Wiedemann, HR (1979). "An unidentified neonatal progeroid syndrome: Follow-up report". European Journal of Pediatrics. 130 (1): 65–70. doi:10.1007/BF00441901. PMID 569581.
- Devos, EA; Leroy, JG; Frijns, JP; Van Den Berghe, H (1981). "The Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch or neonatal progeroid syndrome. Report of a patient with consanguineous parents". European Journal of Pediatrics. 136 (3): 245–8. doi:10.1007/BF00442991. PMID 7262096.
- Rudin, C.; Thommen, L.; Fliegel, C.; Steinmann, B.; Bühler, U. (1988). "The neonatal pseudo-hydrocephalic progeroid syndrome (Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch)". European Journal of Pediatrics. 147 (4): 433–8. doi:10.1007/BF00496430. PMID 3294017.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |