Wibault 220
The Wibault 220 or Wibault R.N.3 220 was a twin-engined French night reconnaissance aircraft. Two were built in 1930 to a government contract.
| Wibault 220 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Night reconnaissance aircraft |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Société des Avions Michel Wibault |
| Designer | Michel Wibault |
| First flight | May 1930 |
| Number built | 2 |
Design
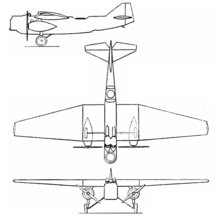
Michel Wibault was one of the pioneers of all-metal aircraft, along with Hugo Junkers and Claudius Dornier.[1] The Wibault 220, designed for the night reconnaissance role and with a crew of three (hence the R.N.3 designation), had both metal structure and covering, the latter longitudinally corrugated for stiffness where required. Its high, cantilever wing had a rectangular plan centre-section and trapezoidal outer panels. The latter also tapered in section, mostly on the underside, providing a little dihedral.[2] High aspect ratio, unbalanced ailerons filled the outer panels' trailing edges. The wing was built around two І-section spars.[3] Like other Wibault aircraft built before the Wibault 280, the ribs projected through the wing surface, which was constructed from metal strips with turned up edges.[3][4]
The Wibault 220 was powered by two 450 hp (340 kW) Gnome-Rhône 9Ac Jupiter nine-cylinder radial engines, each wing-mounted under the outer centre-section. They were attached at three points on the front and rear spars by a system of duralumin plates and steel tubes and were enclosed in teardrop cowlings with their cylinder heads exposed for cooling.[2]
Its flat-sided fuselage was dural framed, with all sides covered in corrugated dural sheet. The upper- and undersides had rounded deckings. The nose was semi-cylindrical in plan and contained an open cockpit for the navigator, who was provided with a flexibly mounted pair of machine guns. The pilot was also in an open cockpit, which was built into the wing leading edge; the rear gunner/observer's position was a little behind the trailing edge, equipped with another pair of flexibly mounted guns. Its floor had an opening into which a reconnaissance camera could be fitted. The gunner also had access to a ventral gun position. Behind him the fuselage tapered slightly to a conventional, cantilever tail with its triangular tailplane mounted on top and carrying narrow chord elevators. The fin was also triangular, with a tall, trapezoidal rudder which extended to the keel.[3]
The Wibault 220 had fixed, conventional landing gear with its mainwheels on V-struts hinged to the lower fuselage frames. The wheels were positioned below the engines, to which they were connected by vertical Messier oleo legs so that the track was a generous 4.80 m (15 ft 9 in). The tailskid also had a Messier shock absorber and was steerable.[3]
Development
The French Senate approved the order for two examples of the Wibault 220 in March 1930[5] and both were reported as under construction in April.[6] By late May 1930 one was being tested at Villacoublay[7] and by early June Raoul Ribière had made several flights.[8] After that, nothing more about the 220 appears in the French aviation journals.
Specifications
Data from L'Année aéronautique 1930-31[9] except where noted
General characteristics
- Crew: Three: pilot, navigator, gunner
- Length: 12 m (39 ft 4 in)
- Wingspan: 18.22 m (59 ft 9 in)
- Height: 4 m (13 ft 1 in)
- Wing area: 52.80 m2 (568.3 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 2,481 kg (5,470 lb)
- Gross weight: 3,616 kg (7,972 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 735 l (162 imp gal; 194 US gal)[3]
- Powerplant: 2 × Gnome-Rhône 9Ac Jupiter [10] 9-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engines, 340 kW (450 hp) each
- Propellers: 2-bladed
Performance
- Maximum speed: 197 km/h (122 mph, 106 kn) at 3,000 m (9,800 ft) (all performance figures with full load)
- Range: 1,200 km (750 mi, 650 nmi) [10]
- Service ceiling: 5,850 m (19,190 ft) reached in 43 min
- Time to altitude: 10 min 34 sec to 3,000 m (9,800 ft)
Armament
- Guns: 5 × 7.7 mm (0.303 in) Lewis guns; 2 in nose, paired on flexible mount, 2 in dorsal cockpit, paired on flexible mount, 1 in a ventral mount. Some sources report a single Lewis gun in nose.[10]
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Wibault 220. |
- Andrews, CF; Morgan, E.B. (1988). Vickers Aircraft since 1908 (2nd ed.). London: Putnam. p. 208. ISBN 0 85177 815 1.
- Aircraft circulars Of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics no.124 (PDF). Washington: NACA. 1930.
- Frachet, André (31 July 1939). "L'avion Michel Wibault, type 220". Les Ailes (476): 3.
- "Wibault". Flight. XXII (90): 1435. 12 December 1930.
- Hirschauer (1930). Sénat no.124, Rapport Ministère de l'Air.
- "Visite aux usines Wibault". Les Ailes (459): 4. 3 April 1930.
- "D'aérodrome en aérodrome - A Villacoublay". Les Ailes (467): 12. 29 May 1930.
- "D'aérodrome en aérodrome - A Villacoublay". Les Ailes (467): 13. 5 June 1930.
- Hirschauer, L.; Dollfus, Ch. (1930–1931). L'Année aéronautique. Paris: Dunod. p. 51.
- Bruno Parmentier (28 November 2001). "Wibault 220". Retrieved 3 September 2016.