Vela 3A
Vela 3A (also known Vela 5, Vela Hotel 5 and OPS 6577[2]) was a U.S. reconnaissance satellite to detect explosions and nuclear tests on land and in space; the first of the third pair of Vela series satellites; taken together with Vela 3B and ERS 17 satellites.
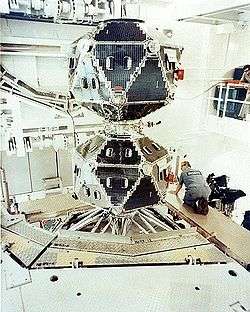 Vela satellite. | |
| Operator | USAF |
|---|---|
| COSPAR ID | 1965-058A[1] |
| SATCAT no. | 1458 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | TRW |
| Launch mass | 150 kilograms (330 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | July 20, 1965, 08:27 UTC |
| Rocket | Atlas Agena D 2A |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral LC-13 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Highly Elliptical |
| Perigee altitude | 84,534 kilometres (52,527 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 96,238 kilometres (59,800 mi) |
| Inclination | 35.2° |
| Period | 5,148.16 minutes |
| Epoch | July 20, 1965 |
%2C_Vela_3B_(Vela_6)_and_ERS-17_satellites%2C_July_20_1965.jpg)
The secondary task of the ship was space research (X-rays, gamma rays, neutrons, magnetic field and charged particles). Sister Vela 3B was in a similar orbit, but 180 degrees from it, i.e. on the opposite side of the globe.
The satellite was rotationally stabilized (2 rps). The ship could work in real time mode (one data frame per second) or in data recording mode (one frame every 256 seconds). The first mode was used for the first 40% of the mission's duration. About 1 transmission was received every 4 hours. The second mode was used until the next pair of Vela satellites were launched.
The ship remains in orbit around Earth.
Instruments
- X-ray and charged particle detector
- Gamma ray and charged particle detector
- Neutron detector
- X-ray scintillation counter
- Solid state detector
- Geiger-Muller counters
- Magnetometer
- Extreme Ultraviolet detector
See also
References
- NASA GSFC. "Vela 3A". Retrieved July 28, 2019.

- Antonín Vítek. "1965-058A – Vela 3". Space 40. Retrieved July 28, 2019.