Ulm–Sigmaringen railway
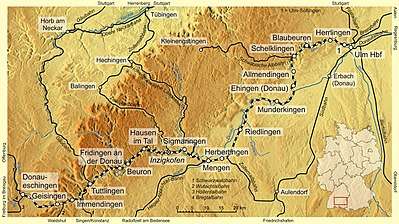
The Ulm–Sigmaringen railway is a 92.670-kilometre-long railway in Baden-Württemberg in south-western Germany, which is largely single-tracked and for the most part not electrified. It runs from Ulm via Blaubeuren and Riedlingen to Sigmaringen mostly in the valley of the Danube. The line is part of the once important long-distance connection from Munich to Freiburg im Breisgau.
| Ulm–Sigmaringen railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Baden-Württemberg, Germany | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Termini | Ulm Sigmaringen | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line number | 4540 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line length | 92.670 km (57.582 mi) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum radius | 224 m (735 ft) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating speed | 160 km/h (99 mph) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
It forms part of the Danube Valley Railway of Baden-Württemberg. The line is famous especially for its charming course through the Upper Danube Nature Park (Naturpark Obere Donau), and is particularly attractive to bicycle tourists. The Royal Württemberg State Railways built the line as part of the railway projects undertaken between 1865 and 1873. Since 1901, the Danube Valley Railway, together with the Höllentalbahn, form part of the pan-regional railway link from Ulm to Freiburg im Breisgau.
Danube Valley Railway (Baden-Württemberg)
The line forms part of the Danube Valley Railway (German: Donautalbahn or Donaubahn) of Baden-Württemberg, along with the Inzigkofen–Sigmaringen section of the Tübingen–Sigmaringen railway, the Tuttlingen–Inzigkofen railway, the Immendingen–Tuttlingen section, which is sometimes considered to form part of the Stuttgart–Hattingen railway, and the Donaueschingen–Immendingen section of the Black Forest Railway (Baden).
Route details
The Ulm–Sigmaringen railway runs alongside the Danube river and crosses it several times. At Ehingen (Donau), the line leaves what is known as the Danube valley today, and follows the valley formed by the Danube in times past, along the rivers Schmiech, Ach, and Blau. The railway touches the border of the Swabian Jura (Schwäbische Alb) between Allmendingen and Blaustein, and meets its eponymous river again at the line's terminus in Ulm.
The Donauradweg (Danube Bicycle Trail), which also goes from Donaueschingen to Ulm, and continues on to Vienna, runs parallel to the line for much of the way. The Danube Valley Railway has a reputation as one of the most beautiful railways in Germany, and its charming course through the Upper Danube Nature Park (Naturpark Obere Donau), and the boom in bicycle tourism on the Donauradweg, have made the line especially popular with bicyclists and hikers. The railway traverses three districts of the state of Baden-Württemberg, as well as Ulm, which is not a constituent of a district, and is managed by three public transport associations (Verkehrsbund). In Ulm, as well as in the districts of Alb-Donau and Biberach, namely between the stations Ulm Hauptbahnhof and Riedlingen, the Danube Valley Railway is part of the Donau-Iller-Nahverkehrsverbund (DING) transport association. In the district of Sigmaringen, between Herbertingen and Sigmaringen , the railway is part of the Verkehrsverbund Neckar-Alb-Donau transport association (naldo).
The route is largely unelectrified and, with the exception of the Ulm Hbf–Herrlingen section, is single-track. It is fully equipped for tilting technology.
Pan-regional significance
Together with the Höllentalbahn, which runs between Freiburg im Breisgau and Donaueschingen, the Black Forest Railway (Baden) between Donaueschingen, Immendingen and the Tuttlingen–Inzigkofen railway and a short section of the Tübingen–Sigmaringen railway, the Ulm–Sigmaringen railway forms what is easily the shortest railway connection between the major cities of Ulm and Freiburg, both located in Baden-Württemberg. The line was therefore significant outside of the immediate region, especially in terms on connections between Augsburg and Munich to Freiburg, and from Ulm via Tuttlingen into Switzerland. However, the importance of this pan-regional East-West connection has been markedly reduced in recent times, primarily due to the relatively low average speed on the line. This low speed is caused by the limitations imposed by the single track, which means often lengthy halts at node stations, and required stops at crossing points. In addition, the route along the Schmiech and Blau rivers also adds to the length of the trip. Today, connections via Stuttgart and Karlsruhe are significantly quicker for the trip from Munich or Ulm to Freiburg. In addition, in 2003 the Deutsche Bahn discontinued the Kleber-Express, which had used large portions of the Danube Valley Railway since 1954 to make a daily direct trip between Munich and Freiburg. This meant the end of the use of the line in providing direct connections between major cities in the area.
History
Border politics and first railway construction initiatives
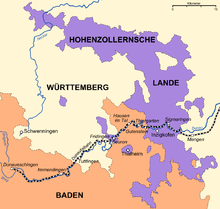
The Danube Valley Railway was never conceived as one comprehensive railway from Ulm to Donaueschingen, and certainly not all the way to Freiburg im Breisgau, but came together as individual pieces of several railway projects, which were constructed over the course of about 25 years. Especially the borders between the states of Baden, Württemberg, and the Province of Hohenzollern, which became part of Prussia in 1850, made such comprehensive railway planning difficult. In just the section between Mengen in Württemberg and Immendingen in Baden, the Danube Valley Railway crosses state borders a total of ten times. The section between Ulm and Immendingen was built by the Royal Württemberg State Railways (Königlich Württembergischen Staats-Eisenbahnen or K.W.St.E.), while the section between Immendingen and Donaueschingen was constructed by the Baden State Railways (Badische Staatseisenbahnen). Prussia did not take part in the construction of the line, even though parts of it do run across the areas belonging to the Province of Hohenzollern.
Initial considerations of a rail line from Ulm along the Danube can be dated back to the 1850s. As was the case in other areas, cities and towns along the Danube started railway committees, which worked on finding support for the construction of a railway. In 1861, 17 of these committees published a memorandum, which argued for the construction of a line from Ulm via Ehingen, Mengen, Messkirch, and Singen to Schaffhausen in Switzerland, with a connection to Tuttlingen as well as to the Black Forest Railway (Baden), which was still in its planning phase at the time. In addition, the construction of a railway along the Danube as part of a trans-European line between Vienna and Paris was under discussion. A connection between Ulm and Vienna already existed in the 1860s, and since Paris was already connected to Chaumont, Haute-Marne, closing the gap via construction of a railway from Ulm along the Danube to Donaueschingen, then further through the Schwarzwald to Freiburg, and across the Rhine river and the Vosges mountain range to Chaumont, found proponents amongst the committees along the Danube, and other parties, as the shortest route between Paris and Vienna. However, not only were there major topographical issues, which were difficult to solve given the knowledge of the day, but the many border crossings necessary to build this railway also added to the list of problems with the concept.
1865–1873: Construction of the Ulm–Sigmaringen and Tuttlingen–Donaueschingen sections
Württemberg started with plans on a smaller scale, and, after negotiations with Baden and Prussia, received the right to build a railway to Sigmaringen in Hohenzollern, as well as to connect to the rail network of the state of Baden via the Hegau-Ablach Valley Railway in Mengen, which meant a connection to the western edge of the Bodensee. On 28 April 1865, the legislative body (Landtag) of the state of Württemberg passed into law a bill to construct a railway from Ulm along the rivers Blau, Ach, and Schmiech to Ehingen, and further along the Danube to Sigmaringen. An alternative route, which would have been much shorter and less expensive, and which would have branched off the already extant Südbahn at Erbach and followed the course of the Danube, was dropped in favour of a railway that would connect the towns of Blaubeuren und Schelklingen to the rail network. Crucial to this decision was the influence wielded by the member of the legislature from Blaubeuren, Ferdinand von Steinbeis, who was given an honorary citizenship of the town of Blaubeuren for his support.[2] Construction started in 1865, and on 13 June 1868, the section between Ulm and Blaubeuren was opened for service.

In 1869 Ehingen was connected to the line, and the railway reached the town of Scheer on the border between Württemberg and Hohenzollern in 1870, with Charles I of Württemberg using the occasion to travel the line on a special train to Mengen. For the construction of the numerous tunnels and bridges across the Danube, the Royal Württemberg State Railways in particular hired workers from Italy. The advent of the Franco-Prussian War in 1870/71, as well as issues with the construction of some of the bridges, delayed the completion of the section from Scheer to Sigmaringen until 1873.
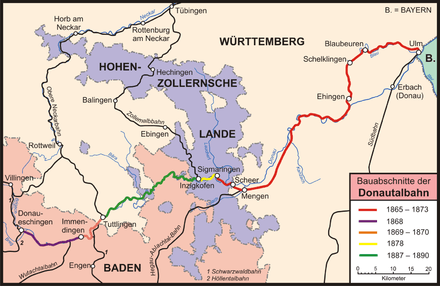
When the Royal Württemberg State Railways put into service the first section of the Danube Valley Railway between Ulm and Blaubeuren in 1868, construction by the Baden State Railways on the Schwarzwaldbahn in Baden from Singen to Offenburg had reached an advanced stage. On 15 June 1868, two days after the opening of the Danube Valley Railway section, the Black Forest Railway section between Engen and Donaueschingen was also opened for service, which, between Immendingen and Donaueschingen, follows the course of the Danube. Württemberg, which was following the progress of the Black Forest Railway construction with great interest, now formulated the goal to connect their rail network to the new line in Baden. However, building an extension to the Danube Valley Railway from Sigmaringen to the connection point in Immendingen in Baden, which would have meant the early completion of the line, was not in the plans. Instead, Württemberg wanted to extend the Upper Neckar Railway, which parted ways from the Fils Valley Railway near Plochingen, and then reached Reutlingen, Tübingen, and, in 1867, Rottenburg am Neckar, with the extension going through Horb and Rottweil, and further through the Neckar valley in a south-westerly direction to the border between the two states, to establish a connection to the Black Forest Railway there. In addition to a route between Rottweil and Villingen, another railway was built from Rottweil to Tuttlingen, which was completed on 15 July 1869. Württemberg then further constructed the connecting line from Tuttlingen to Immendingen through the Danube valley, which was completed on 26 July 1870. This meant that the section between Tuttlingen and Immendingen was completed as a connecting line to the Black Forest Railway, and the section between Immendingen and Donaueschingen was completed as part of the Black Forest Railway.
In 1873, railway lines now ran between Ulm and Sigmaringen, as well as between Tuttlingen and Donaueschingen. The connecting section between Tuttlingen and Sigmaringen was still outstanding. This gap was filled with the construction of the Tuttlingen–Inzigkofen railway, built between 1887 and 1890.
1890–1950: Expansion and destruction

The high expectations, which the military had placed in the Danube Valley Railway in connection with the other railways in the southwest of Germany, were not met in either World War I or World War II. Up until World War I, there were just a few efforts at expanding the Danube Valley Railway from the single-track formation it had featured since 1890. In 1912, the connection to the new shunting yard for the city of Ulm, which was located in Söflingen, was expanded by the Royal Württemberg State Railways to twin tracks on the 3-kilometre-long section between Söflingen and Ulm Hauptbahnhof. By 1913, twin tracks had been laid to Herrlingen. Also prior to World War I, the state of Württemberg had planned to expand the section between Tuttlingen and Immendingen, which was also used by long-distance trains on the Stuttgart–Hattingen railway, to feature twin tracks. The advent of World War I put a stop to these plans, and the plans were then cancelled in favour of the construction of a new railway between Tuttlingen and Hattingen in Baden, which had trains from the Gäubahn running on it, starting in 1934. The section of the Danube Valley Railway between Tuttlingen and Immendingen therefore saw much less traffic, and has been kept as a single-track rail line to today. The expansion of the Schwarzwaldbahn (Baden) to feature twin tracks, which was completed in 1921, had the side effect of expanding the westerly section of the Danube Valley Railway, between Immendingen and Donaueschingen, to feature twin tracks soon after the end of World War I.

Plans formulated by the Deutsche Reichsbahn for military reasons in 1937 to expand to twin tracks the section between Herrlingen and Immendingen, which had been entirely single-tracked, had strong proponents during the course of World War II, but were not further pursued after the end of the war. After the completion of the Danube Valley Railway, the railway property around the railway node Ulm were expanded several times, namely between 1899 and 1911 by the Royal Württemberg State Railways, and between 1924 and 1928 by the Deutsche Reichsbahn. In Tuttlingen, which became a railway node with the completion of the section from Inzigkofen, the railway division Stuttgart (Reichsbahndirektion Stuttgart) replaced the entire station and property between 1928 and 1933 with new construction.

The completion of the Höllentalbahn from Donaueschingen to Freiburg in 1901 made possible for the first time a direct connection between Ulm and Freiburg, something that had been under discussion since the 1850s. Starting in 1909, express trains were used to make this trip, which, starting in 1912, sometimes continued on to Colmar in the Alsace region. From 1913, express service was also provided from Munich via the Donautalbahn to Freiburg, which sometimes featured trains with a dining car. The average speed on the line, notwithstanding the use in long-distance connections, remained rather low, at under 50 km/h. With the exception of a few service issues during the two wars, service provided by express trains and local service trains, which stopped at every station and halt on the line, remained stable until 1945. This service was initially largely provided by the steam locomotives of the Württemberg C class,[note 1] which were heavily used to the mid-1920s, but were then replaced by the Bavarian class P 3/5 H locomotives. After 1929, until the end of World War II, the modern engines of the class DRG Class 24 saw service. Freight service was of little significance on the Danube Valley Railway due to the lack of industrialization along the route.
Towards the end of World War II, Allied air strikes reached the cities and towns along the railway. In December 1944, Allied bomber squadrons completely destroyed Ulm Hauptbahnhof, as well as the nearby shunting yard at Söflingen. Heavy damage was also caused during the course of 1944 at the stations in Mengen and Tuttlingen. The railway itself escaped most harm, and was serviceable, with some limitations, throughout the war. Heavy damage to the line was then caused by the retreating Wehrmacht, which blew up several railway bridges, disabling through traffic on the Danube Valley Railway until 1950. Sections of the line were back in service as soon as 1946.
Since 1950: Rebuilding and service improvements

Major improvements in the railway infrastructure on the Donautalbahn were not undertaken, with the exception of the reconstruction of the destroyed railway property at Ulm Hauptbahnhof by 1962, and the electrification of the short section between Immendingen and Donaueschingen, completed in 1977. The Deutsche Bundesbahn did modernize some of the signaling equipment, but also removed many of the passing tracks, and closed the shunting yard at Söflingen as well as several stations experiencing reduced passenger numbers. In the early 1990s, the Bundesbahn sold several railway properties along the line to private companies; for example, large parts of the railway property at the station in Tuttlingen are in private hands, and the entire station hall in Scheer has been privatized. However, closure of sections of the Donautalbahn never did become reality. In the 1950s and 1960s, a collection of older, and an ever-changing variety of steam locomotives saw express train service on the line. Until about 1955 engines of the class Württemberg C dominated the picture, but starting in 1953, the Bavarian class S 3/6 started to replace the Württemberg C, until 1961. Then it was the turn of the class DRG Class 03 until 1971, which started to be replaced from 1966 by the diesel locomotives of the DB Class V 200.

In terms of local service, until 1963 it was initially the Württemberg T 5 leading the trains, which started to be replaced from 1961 by the DRG Class 64. As was the case before the war, freight service was of little significance, and the freight that was carried on the line was handled by the DRB Class 50 steam locomotives until 1976, which started to be replaced, from 1969, by the diesel-powered DB Class V 90. As early as the 1950s, passenger service would sometimes see the use of diesel rail cars. The first diesel-powered vehicle on the Donautalbahn was the VT 60. Starting in 1961, units of the Uerdingen railbus, which dominated traffic in the 1970s, were added into service, and these units were seen up to 1995, but were replaced from 1988 with the diesel units of the DB Class 628, which provided most local passenger service until the turn of the century, and can still be seen now and then on the Donautalbahn today. The diesel engines of the DB Class V 160 led the longer-distance trains starting in 1966, and the DB Class 218 locomotives were added to this service in 1975. The service schedule in the 1950s was similar to the pre-1945 schedule, with the exception that through-traffic from Ulm to France was eliminated, as well as, starting in 1953, the elimination of direct service between Munich and Freiburg, which was replaced in 1954 by the Kleber-Express, using the route Memmingen–Aulendorf–Herbertingen instead of running via Ulm.
The express service offering remained stable until about the 1980s, and the average speed on the line by that time had been increased to 70 km/h. However, the local service schedule was reduced by the Deutsche Bundesbahn by the beginning of the 1990s. In 1988, the Bundesbahn introduced synchronized schedules on the Donautalbahn, which was boosted by a few trains operating outside of the repetitive schedule. Every two hours, services operated as regional express trains from Ulm to Donaueschingen, and on via the Höllentalbahn to Titisee-Neustadt, where a train change to the electrically-operated trains to Freiburg was necessary. In 1996, the DB boosted service by adding other trains, running every two hours between Sigmaringen and Ulm, which then meant trains once an hour on the section between Sigmaringen and Ulm. In 2003, the section between Immendingen and Fridingen was integrated into the Ringzug network, which meant an improvement in service for the western part of the Donautalbahn. By 2004, the Deutsche Bahn AG had expanded the section between Sigmaringen and Ulm to be certified for the use of tilting technology trains.
Operations
Passenger service
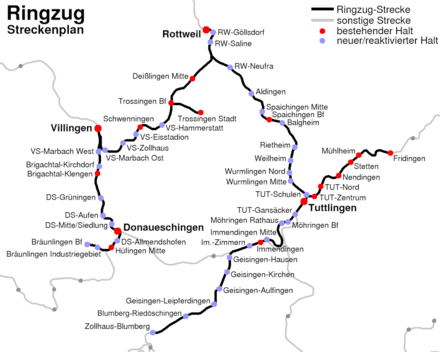
Today, service runs every two hours in the form of RegionalExpress (RE) trains between Donaueschingen and Ulm, and this service further takes the Höllentalbahn to Neustadt in the Black Forest. Another set of trains, running every two hours on a schedule in between the first service, travel between Sigmaringen and Ulm, which means trains once an hour on the section between Sigmaringen and Ulm. In the section between Ehingen and Ulm, additional RegionalBahn trains run every hour, boosting service on this section yet further to two trains per hour. These RB trains travel on from Ulm via the Illertalbahn to Memmingen. Similar service is provided between Herbertingen and Sigmaringen, where, in addition to the hourly trains Neustadt-Ulm and Sigmaringen-Ulm, on the section between Sigmaringen and Aulendorf, hourly trains on the Zollernalbbahn further boost service.


On the section between Immendingen and Fridingen, the Donautalbahn was integrated into the Ringzug network. Trains of the Hohenzollerische Landesbahn travel between Rottweil and Tuttlingen on the Gäubahn (Stuttgart–Singen), then on the Donautalbahn to Immendingen, and further on the Wutach Valley Railway to Zollhaus-Blumberg. Under the week, this service is provided hourly, and every two hours on weekends. Between Fridingen and Tuttlingen, train schedules are not synchronized, and individually scheduled trains operate, with no service on weekends on that section. Between May and October, this section is used on the weekend by the Naturpark-Express, which travels between Sigmaringen, Tuttlingen, and Blumberg, and has additional capacity to carry bicycles.
Between Immendingen and Donaueschingen, the service provided every two hours by the RE trains between Neustadt and Ulm is boosted by service provided every two hours by trains on the Schwarzwaldbahn (Baden) between Konstanz and Offenburg, which results in hourly service on that section. Except for the Ringzug trains and the Naturpark-Express, which are operated by the Hohenzollerische Landesbahn, all other service is provided by subsidiaries of the Deutsche Bahn AG. The top speed for long-distance trains from Neustadt to Ulm is still under 70 km/h, and has not improved in recent times.
Freight service
The Hohenzollerische Landesbahn (HzL) uses the Donautalbahn for limited freight service. Between Sigmaringendorf und Ulm the HzL operates freight trains primarily to transport salt.[3] HzL also operates trains to transport freight cars to the tank farm of the energy company Tyczka Totalgaz in Sigmaringen, to a forge in Fridingen, and to a shredding company on Herbertingen. Agricultural equipment manufactured at the factory of the company CLAAS in Bad Saulgau make their way via Mengen across the Donautalbahn. In the district of Alb-Donau, the railway is used by the cement manufacturers Schwenk in Allmendingen and HeidelbergCement in Schelklingen for their transport needs, and the same is true for the paper-and-pulp company Sappi in Ehingen and the company Bohnacker in Rottenacker.[4]
Equipment
The RegionalExpress trains between Neustadt and Ulm and between Ulm and Sigmaringen are largely operated by units of the DBAG Class 611. The Ringzug trains, the RegionalBahn service between Tübingen and Aulendorf, and parts of the RB service between Ehingen and Memmingen, are operated by units of the Stadler Regio-Shuttle RS1. Between Ehingen and Memmingen, units of the DB Class 628 also see service. The Interregio-Express trains of the Zollernalbbahn from Stuttgart via Sigmaringen to Aulendorf, which travel on the Donautalbahn in the section between Sigmaringen and Herbertingen, also use the Class 611 units. The Naturpark-Express is serviced by NE 81 diesel units. For the RegionalExpress trains running between Konstanz and Offenburg, which travel on the Donautalbahn between Donaueschingen and Immendingen, the DB AG uses electric locomotives of the class 146, and double-decker cars. Freight service is primarily handled by DB Class V 90.
Plans

In 2006, after the shortfall of funds allocated to regionalize local rail service, the section of the Donautalbahn between Inzigkogen and Tuttlingen had been practically put out of service. Today, however, the continued existence of the line is assured,[5] and there are even plans to expand sections of the railway. The westerly section of the Donautalbahn, between Donaueschingen and Immendingen, has been discussed in terms of being added to the Ringzug network. Between Sigmaringen and Ulm, the hope is that with the use of tilting technology trains, top speeds of 160 km/h may be reached, which would connect the two points with a trip time of under one hour. Certifying the section between Sigmaringen and Tuttlingen for tilting technology is also being discussed, which would significantly drop the trip time there as well. A study by the name Bodan Rail 2020, which looked into the potential provided by rail service in the greater Bodensee area, namely between southern Germany, the Vorarlberg region in Austria, the north of Switzerland, and Liechtenstein, predicted the tripling or even quadrupling of passenger counts on the Donautalbahn section between Tuttlingen and Ulm, if trip times were reduced by the use of tilting technology.[6]

Shorter trip times, as well as the move of the single-track train crossing points between Tuttlingen and Sigmaringen, would also be the pre-requisites for the development of a Stadtbahn Tuttlingen, which has been under discussion since 2006. This model would use the Donautalbahn, which runs through the city center, as well as residential and industrial areas in the Tuttlingen area, as a city rail line (Stadtbahn), and would connect the communities east of Tuttlingen, which are poorly served by the Ringzug, to this network.[7] Probably the most ambitious plans are the ones for a S-Bahn network Ulm/Neu-Ulm. These plans, extant since the 1990s, envision the construction of a new rail line, which would branch off the existing Donautalbahn in Ehingen (Donau) and go to Erbach (Donau) on the Südbahn. This new railway would see only the RegionalExpress trains going from Ulm via Sigmaringen to Neustadt (Schwarzwald), which would significantly cut the trip times. The old section between Ehingen via Blaubeuren, which is densely populated, would be served by a new S-Bahn in the Ulm area. The new section has been tagged with a cost of 75 million Euros. The regional association Donau-Iller supports these plans, which are opposed by the state government of the state of Baden-Württemberg.[8][9]
Listing in the Kursbuch
The Donautalbahn cannot be found under a single listing in the Kursbuchstrecke (KBS) listing of the Deutsche Bahn.
- KBS 755 includes the entire Donautalbahn route, but also includes large portions of the Höllentalbahn. In addition, listings under KBS 755 do not list many of the services provided on the Donautalbahn, such as the service Ehingen (Donau)–Ulm–Memmingen, or the Ringzug services, which are found in other KBS listings.
- KBS 756 includes all services on the section Ehingen–Ulm. In addition, all of the services provided on the Illertalbahn on the section Ulm–Memmingen are also included, plus the services on the Schwäbische Albbahn on the section Münsingen–Schelklingen.
- KBS 759.2, which is the primary KBS for the Schwäbische Albbahn, also includes the services on the Donautalbahn in the section Schelklingen–Ulm.
- KBS 766, which is the primary KBS for the Zollernalbbahn, covers all service offerings of both the Zollernalbbahn and the Donautalbahn in the section Herbertingen–Sigmaringen.
- KBS 743, which covers parts of the Gäubahn, the Donautalbahn, as well as all of the services on the Wutach Valley Railway, covers the Donautalbahn section from Fridingen to Immendingen, and also covers the Ringzug services.
- KBS 740, which is the primary KBS of the Gäubahn (Stuttgart–Singen), covers the section Immendingen–Tuttlingen of the Donautalbahn.
References
Notes
- The types of engines used on the Danube Valley Railway in its early days are very difficult to ascertain. Especially before 1894, the available literature does not specify the locomotives used. After this time, Hans-Wolfgang Scharf (see Sources) attempts to determine the engines in use by looking at the classes of locomotives being kept in train depots on and near the Danube Valley Railway.
Footnotes
- Railway Atlas 2017, pp. 104–05, 163.
- Gmeiner, Siegfried. "Wer war Ferdinand von Steinbeis?". Archived from the original on 2011-07-19. Retrieved 2009-04-16.
- Bahn-Report: 79. May 2007. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "Ehinger Tagblatt, Nachrichten und Anzeigen für die Region Ulm, Bodensee, Alb-Donau, Göppingen, Geislingen, Ehingen, Tübingen, Reutlingen, Crailsheim, Alb-Donau-Kreis, Hohenlohe-Franken, Neckar-Alb, Neckar-Fils". SÜDWEST PRESSE. 9 November 2007. Archived from the original on 20 February 2012.
- Stuttgarter Zeitung, 27 September 2006
- "Bodan Rail 2020-Studie". Plan 6.7 and Plan 9.14. Archived from the original on 2017-09-22. Retrieved 2019-07-16. The study compares passenger counts of 1997 with predicted numbers of 2020. The study was concluded in 2001.
- Local version of the Schwäbischen Zeitung Tuttlingen (Gränzbote), 21 August 2006
- "Landtag von Baden-Württemberg" (PDF). 7 March 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 September 2007.
- "Landtag von Baden-Württemberg" (PDF). 20 October 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 October 2007.
Sources
- Hermann, Willi; et al. (2004). Die Donautalbahn. Gesammelte Aufsätze zur Fridinger Geschichte (in German). Vol. 16. Tuttlingen: the Heimatkreis Fridingen.
- Leute, Richard (1988). "100 Jahre Donautalbahn". Tuttlinger Heimatblätter (in German). pp. 8–26. (Other issues of the Tuttlinger Heimatblätter also discuss the Danube Valley Railway in the past decades.)
- Scharf, Hans-Wolfgang (1997). Die Eisenbahn im Donautal und im nördlichen Oberschwaben. Freiburg [Breisgau]: EK-Verlag. ISBN 3-88255-765-6. (out-of-print; this is the main source, upon which the article is largely based)
- Der 3er Ringzug: Eine Investition für die Zukunft der Region Schwarzwald-Baar-Heuberg. Villingen-Schwenningen: Zweckverband Ringzug Schwarzwald-Baar-Heuberg. 2006. (includes descriptions of all of the Donautalbahn properties between Immendingen-Zimmern and Fridingen)
- Eisenbahnatlas Deutschland [German railway atlas]. Schweers + Wall. 2017. ISBN 978-3-89494-146-8.