Trichocephalida
The Trichocephalida (Trichinellida or Trichurida in other classifications) is an order of parasitic nematodes.
| Trichocephalida | |
|---|---|
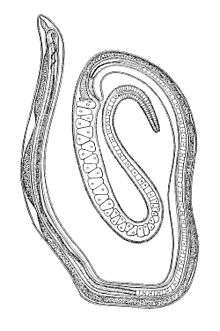 | |
| Trichosomoides crassicauda, young female with male in vagina, drawing in Hall, 1916 [1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Nematoda |
| Class: | Enoplea |
| Subclass: | Dorylaimia |
| Order: | Trichocephalida |
| Families | |
|
Anatrichosomatidae Yamaguti, 1961 | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Trichinellida | |
Taxonomy
The order Trichocephalida includes, according to modern classifications,[2] the single suborder Trichinellina Hodda, 2007, which itself includes the single superfamily Trichinelloidea Ward, 1907, which itself includes 6 families:
- Family Anatrichosomatidae Yamaguti, 1961 (1 genus, 5 species) including the single genus Anatrichosoma
- Family Capillariidae Railliet, 1915[3] (1 subfamily, 18-22 genera according to classifications,[4] 390 species) including Capillaria
- Family Cystoopsidae Skrjabin, 1923 (2 subfamilies, 2 genera, 7 species)
- Family Trichinellidae Ward, 1907 (4 genera, 16 species) including Trichina
- Family Trichosomoididae Hall, 1916[1] (2 subfamilies, 5 genera, 25 species) including Huffmanela
- Family Trichuridae Ransom, 1911 (1 subfamily, 6 genera, 107 species) including Trichuris
Note that another slightly different arrangement of families exists,[4] with the Family Trichosomoididae including Anatrichosoma in a subfamily Anatrichosomatinae.
Biology

All members of this order are histiotrophic, meaning that in at least one stage of their life cycle, they develop in cells or tissues. They are all parasites in vertebrates in their adult stage. The anterior end is narrower than the posterior end in most of these worms, and the esophagus is slender and embedded in cells called stichocytes which form a stichosome. Eggs of members of this order have bipolar or biopercular plugs (except in a few species).
References
| Wikispecies has information related to Trichocephalida |
- Hall, M.C. 1916: Nematode parasites of mammals of the orders Rodentia, Lagomorpha and Hyracoidea. Proceedings of the U.S. National Museum, 50, 1–247 Free PDF.
- Hodda, M. 2011: Phylum Nematoda Cobb 1932. In: Zhang, Z.-Q. (ed.) 2011: Animal biodiversity: an outline of higher-level classification and survey of taxonomic richness. Zootaxa, 3148: 63–95. ISBN 978-1-86977-849-1 (paperback) ISBN 978-1-86977-850-7 (online edition) Free PDF
- Railliet, A. 1915: L'emploi des médicaments dans le traitement des maladies causées par des Nématodes. Recueil de Médecine Vétérinaire, Paris, 91, 490–513. [not seen]
- Moravec, F. 2001: Trichinelloid Nematodes parasitic in cold-blooded vertebrates. Academia, Praha, 432 pp. (list of genera of Capillariidae in pages 30-32) (ISBN 8020008055)