Timeline of the 2018 Pacific hurricane season
The 2018 Pacific hurricane season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific—east of 140°W—and began on June 1 in the central Pacific—between the International Date Line and 140°W, and ended on November 30. These dates typically cover the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific basin.[1]
| Timeline of the 2018 Pacific hurricane season | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
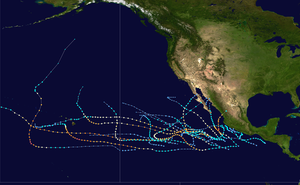 Season summary map | |||||
| Season boundaries | |||||
| First system formed | May 10, 2018 | ||||
| Last system dissipated | November 5, 2018 | ||||
| Strongest system | |||||
| Name | Walaka | ||||
| Maximum winds | 160 mph (260 km/h) (1-minute sustained) | ||||
| Lowest pressure | 920 mbar (hPa; 27.17 inHg) | ||||
| Longest lasting system | |||||
| Name | Sergio | ||||
| Duration | 13.50 days | ||||
| |||||
Four time zones are utilized in the basin: Central for storms east of 106°W, Mountain between 114.9°W and 106°W, Pacific between 140°W and 115°W,[2] and Hawaii–Aleutian for storms between the International Date Line and 140°W. However, for convenience, all information is listed by Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) first with the respective local time included in parentheses. This timeline includes information that was not operationally released, meaning that data from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center is included. This timeline documents tropical cyclone formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, and dissipations during the season.
Timeline of events
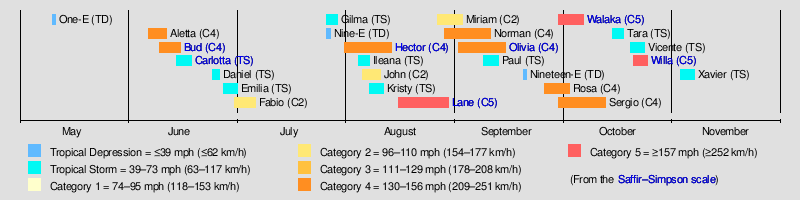
May
May 10
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) 12.1°N 125.4°W – Tropical Depression One-E forms from an area of low pressure roughly 1,225 mi (1,970 km) southwest of Cabo San Lázaro, Baja California Sur.[3]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) 12.3°N 126.2°W – Tropical Depression One-E reaches peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 35 mph (55 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 1,007 mbar (29.7 inHg), approximately 1,250 mi (2,010 km) southwest of Cabo San Lázaro, Baja California Sur.[3]
May 11
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) 12.7°N 129.3°W – Tropical Depression One-E degenerates into a remnant low roughly 1,390 mi (2,235 km) west-southwest of Cabo San Lázaro, Baja California Sur.[3]
May 13
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) 13.4°N 130.1°W – One-E's remnants dissipate roughly 1,390 mi (2,235 km) southwest of Punta Eugenia, Baja California Sur.[3]
May 15
- The 2018 Eastern Pacific hurricane season officially begins.[1]
June
June 1
- The 2018 Central Pacific hurricane season officially begins.[1]

June 6
- 00:00 UTC (7:00 p.m. CDT June 5) at 14.0°N 105.4°W – Tropical Depression Two-E develops from an area of low pressure roughly 325 mi (525 km) south-southwest of Punta San Telmo, Michoacán.[4]
- 06:00 UTC (12:00 a.m. MDT) at 14.2°N 106.1°W – Tropical Depression Two-E intensifies into Tropical Storm Aletta roughly 335 mi (540 km) south-southwest of Punta San Telmo, Michoacán.[4]
June 7
- 18:00 UTC (12:00 p.m. MDT) at 15.1°N 109.6°W – Tropical Storm Aletta intensifies into a Category 1 hurricane roughly 425 mi (685 km) southwest of Punta Pérula, Jalisco.[4]
June 8
- 00:00 UTC (6:00 p.m. MDT June 7) at 15.4°N 110.1°W – Hurricane Aletta intensifies into a Category 2 hurricane roughly 435 mi (700 km) southwest of Punta Pérula, Jalisco.[4]
- 06:00 UTC (12:00 a.m. MDT) at 15.6°N 110.6°W – Hurricane Aletta intensifies into a Category 3 hurricane about roughly 450 mi (725 km) southwest of Punta Pérula, Jalisco.[4]
- 12:00 UTC (6:00 a.m. MDT) at 15.7°N 111.0°W – Hurricane Aletta intensifies into a Category 4 hurricane roughly 470 mi (755 km) southwest of Punta Pérula, Jalisco. Simultaneously, the storm reaches peak intensity with winds of 140 mph (220 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 943 mbar (27.8 inHg).[4]
June 9
- 00:00 UTC (6:00 p.m. MDT June 8) at 16.0°N 112.0°W – Hurricane Aletta weakens into a Category 3 hurricane roughly 490 mi (790 km) south-southwest of Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur.[4]
- 12:00 UTC (6:00 a.m. MDT) at 16.2°N 113.0°W – Hurricane Aletta weakens into a Category 2 hurricane roughly 500 mi (805 km) south-southwest of Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur.[4]
- 18:00 UTC (12:00 p.m. MDT) at 16.1°N 113.5°W – Hurricane Aletta weakens into a Category 1 hurricane roughly 520 mi (835 km) south-southwest of Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur.[4]
- 18:00 UTC (1:00 p.m. CDT) at 12.1°N 100.5°W – Tropical Depression Three-E forms about 330 mi (530 km) south of Acapulco.[5]
June 10
- 00:00 UTC (6:00 p.m. MDT June 9) at 15.9°N 114.0°W – Hurricane Aletta weakens into a tropical storm roughly 545 mi (875 km) south-southwest of Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur.[4]
- 00:00 UTC (7:00 p.m. CDT June 9) at 12.7°N 101.3°W – Tropical Depression Three-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Bud about 305 mi (490 km) south of Acapulco.[5]
- 18:00 UTC (1:00 p.m. CDT) at 15.1°N 103.8°W – Tropical Storm Bud intensifies into a Category 1 hurricane about 280 mi (450 km) south of Manzanillo, Colima.[5]

June 11
- 06:00 UTC (12:00 a.m. MDT) at 16.1°N 105.6°W – Hurricane Bud intensifies into a Category 2 hurricane about 225 miles (360 km) south-southwest of Manzanillo, Colima.[5]
- 12:00 UTC (8:00 a.m. PDT) at 15.9°N 114.0°W – Tropical Storm Aletta degenerates into a remnant low roughly 640 mi (1,030 km) south-southwest of Cabo San Lázaro, Baja California Sur.[4]
- 12:00 UTC (6:00 a.m. MDT) at 16.4°N 106.4°W – Hurricane Bud intensifies into a Category 3 hurricane about 280 miles (450 km) south-southwest of Cabo Corrientes, Mexico.[5]
June 12
- 00:00 UTC (6:00 p.m. MDT June 11) at 17.3°N 107.4°W – Hurricane Bud reaches peak intensity with winds of 140 mph (220 km/h) and a pressure of 943 mbar (hPa; 27.85 inHg), while located about 240 miles (390 km) south-southwest of Cabo Corrientes, Mexico.[5]
- 12:00 UTC (6:00 a.m. MDT) at 18.0°N 108.1°W – Hurricane Bud weakens into a Category 3 hurricane about 230 miles (365 km) southwest of Cabo Corrientes, Mexico.[5]
June 13
- 00:00 UTC (6:00 p.m. MDT June 12) at 18.5°N 108.5°W – Hurricane Bud weakens into a Category 1 hurricane about 310 miles (500 km) south-southeast of Cabo San Lucas, Mexico.[5]
- 12:00 UTC (6:00 a.m. MDT) at 19.2°N 108.7°W – Hurricane Bud weakens into a tropical storm about 265 miles (430 km) south-southeast of Cabo San Lucas, Mexico.[5]

June 14
- 18:00 UTC (1:00 p.m. CDT) at 14.9°N 100.0°W – Tropical Depression Four-E develops from an area of low pressure about 140 miles (220 km) south of Acapulco, Mexico.[6]
June 15
- 02:00 UTC (8:00 p.m. MDT June 14) at 23.0°N 109.7°W – Tropical Storm Bud makes landfall near San José del Cabo, about 15 miles (25 km) east-northeast of Cabo San Lucas, Mexico.[5]
- 12:00 UTC (6:00 a.m. MDT) at 25.3°N 110.0°W – Tropical Storm Bud weakens into a post-tropical cyclone about 140 miles (220 km) south-southwest of Huatabampito, Mexico.[5]
- 18:00 UTC (1:00 p.m. CDT) at 15.8°N 99.6°W – Tropical Depression Four-E intensifies into Tropical Storm Carlotta about 80 miles (125 km) south of Acapulco, Mexico.[6]
June 16
- 06:00 UTC (12:00 a.m. MDT) – Aletta's remnants dissipate roughly 640 mi (1,030 km) southwest of Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur. [4]
- 06:00 UTC (12:00 a.m. MDT) – Bud's remnants dissipate, while located more than 35 miles (55 km) southwest of Huatabampito, Mexico.[5]
June 17
- 00:00 UTC (7:00 p.m. CDT June 16) at 16.4°N 99.5°W – Tropical Storm Carlotta reaches peak intensity with winds of 65 mph (100 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 997 mbar (hPa; 29.44 inHg), located around 45 miles (70 km) southeast of Acapulco, Mexico.[6]
- 18:00 UTC (1:00 p.m. CDT) at 17.0°N 101.7°W – Tropical Storm Carlotta weakens into a tropical depression about 45 miles (70 km) south of Zihuatanejo, Mexico.[6]
June 19
- 00:00 UTC (7:00 p.m. CDT June 18) at 18.1°N 103.5°W – Tropical Depression Carlotta degenerates into a remnant low roughly 85 miles (135 km) west of Lázaro Cárdenas, Mexico.[6]
- 06:00 UTC (1:00 a.m. CDT) – Carlotta's remnants dissipate approximately 85 miles (135 km) west of Lázaro Cárdenas, Mexico.[6]

June 24
- 00:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. CDT June 22) at 13.7°N 115.5°W – Tropical Depression Five-E develops from an area of low pressure about 730 miles (1,175 km) southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[7]
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) at 15.5°N 115.8°W – Tropical Depression Five-E intensifies into Tropical Storm Daniel approximately 635 miles (1,020 km) southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[7]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) at 16.6°N 116.0°W – Tropical Storm Daniel reaches peak intensity with winds of 45 mph (75 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 1004 mbar (hPa; 29.65 inHg), approximately 585 miles (940 km) southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[7]
June 25
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) at 19.2°N 117.8°W – Tropical Storm Daniel weakens to a tropical depression roughly 565 miles (905 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[7]
June 26
- 06:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. PDT June 25) at 19.8°N 119.0°W – Tropical Depression Daniel degenerates to a remnant low roughly 615 miles (990 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[7]
June 27
- 18:00 UTC (12:00 p.m. MDT) at 12.8°N 108.1°W – Tropical Depression Six-E forms approximately 505 miles (810 km) southwest of Manzanillo, Colima.[8]
June 28
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) – Daniel's remnants dissipate more than 1,015 miles (1,635 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[7]
- 12:00 UTC (6:00 a.m. MDT) at 14.2°N 111.8°W – Tropical Depression Six-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Emilia approximately 610 miles (985 km) south of the southern tip of Baja California.[8]
June 29
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) at 16.0°N 115.8°W – Tropical Storm Emilia attains peak intensity with winds of 60 mph (95 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 997 mbar (hPa; 29.44 inHg), roughly 610 miles (980 km) from the southern tip of Baja California.[8]
June 30
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) at 17.4°N 118.8°W – Tropical Storm Emilia weakens into a tropical depression roughly 685 miles (1,100 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[8]
- 18:00 UTC (1:00 p.m. CDT) at 11.0°N 103.8°W – Tropical Depression Seven develops from an area of low pressure approximately 560 miles (900 km) south-southwest of Manzanillo, Colima.[9]
July
July 1
- 06:00 UTC (12:00 a.m. MDT) at 11.6°N 105.8°W – Tropical Depression Seven intensifies into Tropical Storm Fabio about 525 miles (850 km) south-southwest of Manzanillo, Mexico.[9]

July 2
- 00:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. PDT July 1) at 20.0°N 124.7°W – Tropical Depression Emilia weakens into a remnant low roughly 965 miles (1,555 km) west of the southern tip of Baja California.[8]
- 12:00 UTC (6:00 a.m. MDT) at 12.9°N 110.4°W – Tropical Storm Fabio intensifies into a Category 1 hurricane roughly 690 miles (1110 km) south of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula.[9]
July 3
- 06:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. PDT July 2) at 14.7°N 113.6°W – Hurricane Fabio intensifies into a Category 2 hurricane approximately 610 miles (985 km) southwest of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula.[9]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) at 15.5°N 116.0°W – Hurricane Fabio attains its peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 110 mph (175 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 964 mbar (hPa; 28.47 inHg) about 640 miles (1,035 km) southwest of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula.[9]
July 4
- 06:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. PDT July 3) – Emilia's remnants dissipate more than 1,495 miles (2,410 km) west of the southern tip of Baja California.[8]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) at 17.4°N 121.0°W – Hurricane Fabio weakens to a Category 1 hurricane roughly 810 miles (1,300 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula.[9]
July 5
- 06:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. PDT July 4) at 19.0°N 123.4°W – Hurricane Fabio weakens to a tropical storm approximately 905 miles (1,455 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula.[9]
July 6
- 06:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. PDT July 5) at 21.3°N 128.5°W – Tropical Storm Fabio degenerates to a post-tropical cyclone about 1,190 miles (1,910 km) west of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula.[9]
July 9
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) – Fabio's remnants dissipate more than 1,840 miles (2,960 km) west of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula.[9]
July 26
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) at 13.0°N 121.6°W – Tropical Depression Eight-E forms roughly 1,035 miles (1,665 km) southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[10]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) at 13.4°N 123.2°W – Tropical Depression Eight-E intensifies into Tropical Storm Gilma approximately 1,085 miles (1,745 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[10]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) at 10.9°N 135.0°W – Tropical Depression Nine-E forms roughly 1,435 miles (2,315 km) east-southeast of Hilo, Hawaii.[11]
July 27
- 06:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. PDT July 26) at 14.2°N 126.3°W – Tropical Storm Gilma reaches peak intensity with winds of 45 mph (75 km/h) and a pressure of 1005 mbar (hPa; 29.68 inHg), while located approximately 1,210 miles (1,945 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[10]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) at 14.7°N 129.2°W – Tropical Storm Gilma weakens into a tropical depression approximately 1,375 miles (2,215 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[10]
July 28
- 00:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. PDT July 27) – Tropical Depression Nine-E dissipates roughly 1,210 miles (1,945 km) southeast of Hilo, Hawaii.[11]
July 29
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) at 16.1°N 137.9°W – Tropical Depression Gilma degenerates to a remnant low roughly 1,150 miles (1,850 km) east of Hilo, Hawaii.[10]
July 31
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) at 12.3°N 115.1°W – Tropical Depression Ten-E develops from an area of low pressure about 805 miles (1,295 km) southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[12]
August
August 1
- 00:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. PDT July 31) – Gilma's remnants dissipate while located roughly 405 miles (650 km) southeast of Hilo, Hawaii.[10]
- 00:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. PDT July 31) at 13.0°N 117.6°W – Tropical Depression Ten-E intensifies into Tropical Storm Hector approximately 845 miles (1,360 km) southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[12]
August 2
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) at 14.2°N 123.9°W – Tropical Storm Hector intensifies into a Category 1 hurricane approximately 1,090 miles (1,750 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[12]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) at 14.1°N 125.8°W – Hurricane Hector intensifies into a Category 2 hurricane while located roughly 1,155 miles (1,860 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[12]
August 3
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) at 14.1°N 128.3°W – Hurricane Hector weakens to a Category 1 hurricane while located roughly 1,340 miles (2,160 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[12]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) at 14.1°N 129.3°W – Hurricane Hector re-intensifies into a Category 2 hurricane while located roughly 1,400 miles (2,255 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[12]
August 4
- 00:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. PDT August 3) at 14.2°N 130.3°W – Hurricane Hector intensifies into a Category 3 hurricane approximately 1,455 miles (2,345 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[12]
- 18:00 UTC (1:00 p.m. CDT) at 12.3°N 94.5°W – Tropical Depression Eleven-E forms from an area of low pressure approximately 270 miles (435 km) south-southeast of Puerto Angel, Oaxaca.[13]

August 5
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. CDT) at 13.3°N 97.1°W – Tropical Depression Eleven-E intensifies into Tropical Storm Ileana approximately 170 miles (275 km) south-southeast of Puerto Angel, Oaxaca.[13]
- 12:00 UTC (7:00 a.m. CDT) at 13.7°N 105.0°W – Tropical Depression Twelve-E forms while located roughly 335 mi (540 km) south-southwest of Punta San Telmo, Michoacán.[14]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) at 14.4°N 138.0°W – Hurricane Hector intensifies into a Category 4 hurricane approximately 1,250 miles (2,015 km) east-southeast of South Point, Hawaii.[12]
August 6
- 00:00 UTC (6:00 p.m. MDT August 5) at 14.5°N 106.3°W – Tropical Depression Twelve-E intensifies into Tropical Storm John while located roughly 325 mi (525 km) southwest of Punta San Telmo, Michoacán.[14]
- 06:00 UTC (08:00 p.m. HST August 5) at 14.7°N 139.9°W – Hurricane Hector enters the Central Pacific Hurricane Center's (CPHC) area of responsibility.[12]
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. CDT) at 15.8°N 101.2°W – Tropical Storm Ileana peaks with winds of 65 mph (100 km/h) and a pressure of 998 mbar (29.47 inHg) approximately 170 miles (490 km) southeast of Manzanillo, Mexico.[13]
- 18:00 UTC (08:00 a.m. PDT) at 15.1°N 142.5°W – Hurricane Hector reaches peak intensity with winds of 155 mph (250 km/h) and a pressure of 936 mbar (27.64 inHg) approximately 890 miles (1,430 km) east-southeast of Hilo, Hawaii.[12]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. PDT) at 15.9°N 107.9°W – Tropical Storm John intensifies into a Category 1 hurricane while located roughly 310 mi (500 km) southwest of Punta Pérula, Jalisco.[14]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. PDT) at 14.8°N 122.6°W – Tropical Depression Thirteen-E forms while located roughly 960 mi (1,545 km) southwest of Cabo San Lázaro, Baja California Sur.[15]
August 7
- 00:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. PDT August 6) at 14.6°N 123.6°W – Tropical Depression Thirteen-E intensifies into Tropical Storm Kristy while located roughly 1,015 mi (1,635 km) southwest of Cabo San Lázaro, Baja California Sur.[15]
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. CDT) – Tropical Storm Ileana is absorbed by Hurricane John.[13]
- 12:00 UTC (6:00 a.m. MDT) at 17.7°N 109.5°W – Hurricane John intensifies into a Category 2 hurricane while located roughly 310 mi (500 km) southwest of Cabo Corrientes, Jalisco.[14]
- 18:00 UTC (12:00 p.m. MDT) at 18.3°N 110.1°W – Hurricane John reaches peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 110 mph (175 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 964 mbar (28.5 inHg) while located roughly 315 mi (505 km) south of Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur.[14]
August 8
- 06:00 UTC (12:00 a.m. MDT) at 19.6°N 111.5°W – Hurricane John weakens into a Category 1 hurricane while located roughly 245 mi (395 km) south-southwest of Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur.[14]
- 12:00 UTC (02:00 a.m. HST) at 16.4°N 153.2°W – Hurricane Hector weakens into a Category 3 hurricane approximately 260 miles (420 km) south-southeast of Hilo, Hawaii.[12]
August 9
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) at 23.9°N 116.7°W – Hurricane John weakens into a tropical storm while located roughly 275 mi (445 km) southwest of Punta Abreojos, Baja California Sur.[14]
August 10
- 06:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. PDT August 9) at 17.8°N 129.9°W – Tropical Storm Kristy reaches peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 70 mph (110 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 991 mbar (29.3 inHg) while located roughly 1,170 mi (1,885 km) west-southwest of Punta Eugenia, Baja California Sur.[15]
- 06:00 UTC (08:00 p.m. HST August 9) at 17.2°N 163.7°W – Hurricane Hector re-strengthens into a Category 4 hurricane approximately 385 miles (620 km) east of Johnston Island.[12]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. PDT) at 26.3°N 120.3°W – Tropical Storm John degenerates into a remnant low while located roughly 340 mi (545 km) west-southwest of Punta Eugenia, Baja California Sur.[14]
.jpg)
August 11
- 06:00 UTC (08:00 p.m. HST August 10) at 17.2°N 163.7°W – Hurricane Hector weakens into a Category 3 hurricane approximately 130 miles (215 km) north-northeast of Johnston Island.[12]
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) at 21.7°N 131.2°W – Tropical Storm Kristy weakens into a tropical depression while located roughly 1,095 mi (1,760 km) southwest of Point Conception, California.[15]
- 18:00 UTC (08:00 a.m. HST) at 19.6°N 170.4°W – Hurricane Hector weakens into a Category 2 hurricane approximately 210 miles (335 km) north-northwest of Johnston Island.[12]
August 12
- 12:00 UTC (02:00 a.m. HST) at 22.4°N 173.6°W – Hurricane Hector weakens into a Category 1 hurricane approximately 320 miles (520 km) southeast of Midway Island.[12]
- 12:00 UTC (5:00 a.m. PDT) at 22.4°N 132.4°W – Tropical Depression Kristy degenerates into a remnant low while located roughly 1,100 mi (1,770 km) southwest of Point Conception, California.[15]
August 13
- 00:00 UTC (02:00 p.m. HST August 12) at 24.2°N 176.4°W – Hurricane Hector weakens into a tropical storm approximately 285 miles (455 km) south-southeast of Midway Island.[12]
- 00:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. PDT August 6) at 22.4°N 133.4°W – Kristy's remnants dissipate roughly 1,140 mi (1,835 km) southwest of Point Conception, California.[15]
- 18:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. PDT) at 26.3°N 120.3°W – John's remnants dissipate roughly 365 mi (585 km) west-southwest of San Quintín, Baja California.[14]
- 18:00 UTC (08:00 a.m. HST) at 25.1°N 179.5°W – Hurricane Hector crosses the International Dateline and enters the Japan Meteorological Agency's area of responsibility.[12]
August 14
- 00:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. PDT) at 11.0°N 120.6°W – Tropical Depression Fourteen-E forms 1,075 mi (1,730 km) southwest of the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula.[16]
August 15
- 15:00 UTC (8:00 a.m. PDT) at 10.7°N 123.6°W – Tropical Depression Fourteen-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Lane about 1,235 mi (1,990 km) southwest of the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula.[16]
October 15
- 06:00 UTC (1:00 a.m. CDT) at 17.6°N 104.1°W – Tropical Depression Twenty-Two-E intensifies into Tropical Storm Tara while located roughly 65 mi (105 km) southwest of Punta San Telmo, Michoacán.[17]
October 16
- 00:00 UTC (7:00 p.m. CDT October 15) at 18.4°N 104.3°W – Tropical Storm Tara reaches peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 65 mph (100 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 995 mbar (29.4 inHg) while located roughly 45 mi (70 km) south of Manzanillo, Colima.[17]
- 18:00 UTC (1:00 p.m. CDT) at 18.9°N 104.9°W – Tropical Storm Tara dissipates roughly 40 mi (65 km) west-southwest of Manzanillo, Colima.[17]
November
November 2
- 12:00 UTC (6:00 a.m. MDT) at 14.2°N 109.9°W – Tropical Depression Twenty-Five-E forms from an area of low pressure about 520 mi (835 km) southwest of Manzanillo, Colima.[18]
November 3
- 00:00 UTC (6:00 p.m. MDT November 2) at 14.4°N 108.5°W – Tropical Depression Twenty-Five-E strengthens into Tropical Storm Xavier about 425 mi (685 km) southwest of Manzanillo, Colima.[18]
November 4
- 12:00 UTC (6:00 a.m. CST) at 17.4°N 105.3°W – Tropical Storm Xavier reaches peak intensity with winds of 65 mph (105 km/h) and a pressure of 996 mbar (hPa; 29.41 inHg), about 130 mi (215 km) southwest of Manzanillo, Colima.[18]
November 6
- 00:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. MST November 5) at 18.9°N 107.2°W – Tropical Storm Xavier degenerated into a low about 250 mi (400 km) east of Socorro Island.[18]
November 9
- 06:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. MST November 8) – Xavier's remnants dissipate while located more than 345 mi (555 km/h) west-southwest of Socorro Island.[18]
November 30
- The 2018 Pacific hurricane season officially ended.[1]
Notes
α This value is an operational intensity for a storm within the National Hurricane Center's area of responsibility and is subject to change in the post storm analysis.
β This value is an operational intensity for a storm within the Central Pacific Hurricane Center's area of responsibility and is subject to change in the post storm analysis.
See also
- List of Pacific hurricanes
- Pacific hurricane season
- Timeline of the 2018 Atlantic hurricane season
References
- Christopher W. Landsea; Neal Dorst; Erica Rule (June 2, 2011). "G: Tropical Cyclone Climatology". Hurricane Research Division: Frequently Asked Questions. Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. G1) When is hurricane season ?. Retrieved May 28, 2018.
- Robbie J. Berg (May 28, 2015). Tropical Depression One-E Discussion Number 1 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 28, 2018.
- Berg, Robbie (12 July 2018). Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Depression One-E (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 26 March 2019.
- Avila, Lixion A. (31 July 2018). Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Aletta (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 26 March 2019.
- Blake, Eric S. (24 October 2018). Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Bud (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 27 March 2019.
- Pasch, Richard J. (19 December 2018). Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Carlotta (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 28 March 2019.
- Beven II, John L. (11 February 2019). Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Daniel (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 28 March 2019.
- Stewart, Stacy R. (21 August 2018). Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Emilia (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 28 March 2019.
- Brown, Daniel P. (14 November 2018). Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Fabio (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 28 March 2019.
- Cangialosi, John P. (6 November 2018). Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Gilma (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 28 March 2019.
- Zelinsky, David A. (24 August 2018). Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Depression Nine-E (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 28 March 2019.
- Berg, Robbie (26 October 2018). Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Hector (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 28 March 2019.
- Avila, Lixion A. (9 November 2018). Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Ileana (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 28 March 2019.
- Blake, Eric S. (20 November 2018). Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane John (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- Latto, Andrew S.; Pasch, Richard J. (6 March 2019). Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Kristy (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- Beven II, John L.; Wroe, Derek (16 December 2019). Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Lane (PDF) (Report). National Hurricane Center and Central Pacific Hurricane Center. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- Brown, Daniel P. (8 February 2019). Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Xavier (PDF). National Hurricane Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 27 March 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 2018 Pacific hurricane season. |
- The National Hurricane Center's advisory archive for 2018
| Preceded by 2017 |
Pacific hurricane season timelines 2018 |
Succeeded by 2019 |