The Climate Registry
The Climate Registry (TCR) is a non-profit organization governed by U.S. states and Canadian provinces and territories. TCR designs and operates voluntary and compliance greenhouse gas (GHG) reporting programs globally, and assists organizations in measuring, reporting and verifying the carbon in their operations in order to manage and reduce it. TCR also consults with governments nationally and internationally on all aspects of GHG measurement, reporting, and verification.[1]
History
Established in 2007, The Climate Registry was formed to continue the work of the California Climate Action Registry (CCAR). Created by the State of California in 2001, CCAR promoted and protected businesses’ early actions to manage and reduce their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Through the state mandate, CCAR established protocols to guide emissions inventories and manage an online reporting tool, the Climate Action Registry Reporting Tool (CARROT), to serve as a central database for emissions reports. Members of CCAR served as true leaders in environmental responsibility and were among the first in the world to measure their emissions according to comprehensive and rigorous standards and make their emissions publicly accessible online. Together, CCAR and its members influenced California climate change policy, including Assembly Bill 32 (AB 32), and worked to ensure proper recognition from the state for early actions to reduce emissions. Recognizing climate change is a global issue and that success in emissions reporting must be based on consistent data in an integrated system that stretched beyond California’s borders, CCAR was instrumental in establishing TCR with the mission of expanding CCAR’s emissions reporting work to include all of North America. CCAR accepted its last emissions inventory reports for 2009 in December 2010 and officially transitioned its members to The Climate Registry. CCAR is now a program of The Climate Registry’s sister organization, the Climate Action Reserve.[1]
Participants
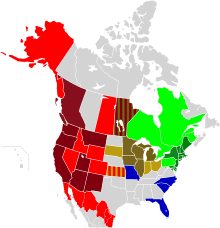
At the launch of The Climate Registry, the following were the participants:[2] [3]
Canadian provinces:[4]
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
As of September 24, 2009 all Canadian Provinces and Territories are participating in the greenhouse gas registry. [5]
|
|
|
See also
- Emissions & Generation Resource Integrated Database
- Emissions trading
- Energy policy of the United States
- Energy use in the United States
- Global warming
- Greenhouse gas emissions in the USA
- Greenhouse gas inventory
- Kyoto Protocol
- Midwestern Greenhouse Gas Reduction Accord
- Project Vulcan
- Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative
- Western Regional Climate Action Initiative
References
- "About Us | The Climate Registry". www.theclimateregistry.org. Retrieved January 26, 2017.
- Press Release, The Climate Registry, published 2007-05-08, accessed 2007-05-16
- Press Release, Government of Ontario, published 2008-01-16, accessed 2008-03-19
- Source: "Provinces Joins North American Climate Registry (June 3rd 2008:VOCM)
- , The Climate Registry, published 2009-09-24