Sog County
Sog County (Tibetan: སོག་རྫོང་།, Wylie: sog rdzong, ZYPY: Sog Zong ), Sogxian, or Suoxian (simplified Chinese: 索县; traditional Chinese: 索縣; pinyin: Suǒ Xiàn) is a county under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Nagqu of the Tibet Autonomous Region.
Sog County 索县 • སོག་རྫོང་། | |
|---|---|
County | |
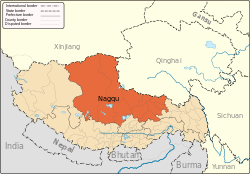
.png) Location of Sog County (red) within Nagqu City (yellow) and the Tibet Autonomous Region | |
 Sog County Location of the seat in the Tibet AR | |
| Coordinates: 31°53′17″N 93°47′06″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Autonomous region | Tibet |
| Prefecture-level city | Nagqu |
| Seat | Sog |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
Geography
Sog Dzong lies in the extreme western part of the former province of Kham. To its west is Chamdo and to its right Nagchu. Sogdzong is located between the Drachen and Driru, on the Sogchu River. It is the source of Gyalmo Ngulchu.
Climate
| Climate data for Sog County, 4024 m asl (1981–2010 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.4 (57.9) |
13.4 (56.1) |
22.0 (71.6) |
22.4 (72.3) |
25.4 (77.7) |
29.0 (84.2) |
31.0 (87.8) |
29.5 (85.1) |
28.0 (82.4) |
22.1 (71.8) |
15.0 (59.0) |
14.6 (58.3) |
31.0 (87.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −0.8 (30.6) |
1.5 (34.7) |
5.7 (42.3) |
9.6 (49.3) |
13.3 (55.9) |
16.4 (61.5) |
18.5 (65.3) |
18.3 (64.9) |
15.5 (59.9) |
10.3 (50.5) |
4.6 (40.3) |
0.7 (33.3) |
9.5 (49.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −8.9 (16.0) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
2.7 (36.9) |
6.7 (44.1) |
10.4 (50.7) |
12.4 (54.3) |
11.9 (53.4) |
9.3 (48.7) |
3.7 (38.7) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
2.5 (36.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −17.0 (1.4) |
−13.5 (7.7) |
−8.3 (17.1) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
0.2 (32.4) |
4.3 (39.7) |
6.2 (43.2) |
5.5 (41.9) |
2.9 (37.2) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
−10.6 (12.9) |
−15.9 (3.4) |
−4.4 (24.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −31 (−24) |
−28.5 (−19.3) |
−22.7 (−8.9) |
−15 (5) |
−8.7 (16.3) |
−3.6 (25.5) |
−4 (25) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
−7 (19) |
−18 (0) |
−23.2 (−9.8) |
−30.4 (−22.7) |
−31 (−24) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 10.6 (0.42) |
7.9 (0.31) |
9.5 (0.37) |
20.4 (0.80) |
64.1 (2.52) |
124.8 (4.91) |
126.3 (4.97) |
110.3 (4.34) |
97.1 (3.82) |
39.6 (1.56) |
5.6 (0.22) |
7.7 (0.30) |
623.9 (24.54) |
| Average precipitation days | 2.7 | 3.0 | 3.1 | 5.3 | 12.8 | 18.2 | 17.2 | 16.2 | 15.9 | 8.1 | 1.9 | 1.7 | 106.1 |
| Source: Météo Climat[1][2] | |||||||||||||
Economy
Crops include barley, wheat, radish, potatoes, etc. and yaks, sheep, goat, cows, and horses are reared. Nomads move four times annually according to seasons. The county contains Tsangdain Monastery, built in 1667, resembling the Potala Palace.[3]
gollark: --magic py 5
gollark: --magic py 5
gollark: \<:p_mosfet:798503052012552202>
gollark: <:p_mosfet:798503052012552202>
gollark: ++magic py await ctx.send("Bee")
References
- "Chine climate normals 1981-2010" (in French). Retrieved 11 November 2019.
- "Weather extremes for Sog Xian". Météo Climat. Retrieved 11 November 2019.
- "Tibet's three "Potala Palaces"". China-Tibet Online. Retrieved 9 April 2012.
Transport
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.