Slickenside
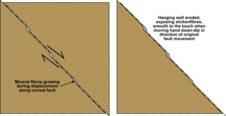
In geology, a slickenside is a smoothly polished surface caused by frictional movement between rocks along the two sides of a fault. This surface is normally striated in the direction of movement. The plane may be coated by mineral fibres that grew during the fault movement, known as slickenfibres, which also show the direction of displacement. Due to irregularities in the fault plane exposed slickenfibres typically have a stepped appearance that can be used to determine the sense of movement across the fault. The surface feels smoother when the hand is moved in the same direction that the eroded side of the fault moved (see diagram for explanation), as the surface steps down in that direction, like the scales on a fish when stroked from the head.

In pedology, the study of soils in their natural environments, a slickenside is a surface of the cracks produced in soils containing a high proportion of swelling clays. Slickensides are a type of cutan. In the Australian Soil Classification, slickensides, along with lenticular structural aggregates, are an indicator of a vertosol.[1]
Gallery
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Slickensides. |
 Slickensides on a fault plane, south wall of Bear Valley Strip Mine. Lens cap 5.8cm wide.
Slickensides on a fault plane, south wall of Bear Valley Strip Mine. Lens cap 5.8cm wide. Slickensides on a fault plane in Corona Heights Park, San Francisco
Slickensides on a fault plane in Corona Heights Park, San Francisco
Slickensides on the Moon
On the Moon, a boulder with slickensides, discovered in a debris-strewn small crater at Station 9 near Rima Hadley, was photographed during a moonwalk by the crew of Apollo 15.[2][3][4]
Notes
- Isbell, Raymond F. (1996). The Australian Soil Classification (1st ed.). Collingwood, Victoria: CSIRO Publishing. ISBN 0-643-05813-3.
- https://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/apollo/catalog/70mm/magazine/?82 Apollo Image Atlas (Lunar and Planetary Institute), 70 mm Hasselblad Image Catalog, Apollo 15 photographs AS15-82-11101, AS15-82-11102, AS15-82-11103 and AS15-82-11104
- https://www.hq.nasa.gov/alsj/a15/a15.sta9.html Apollo 15 Lunar Surface Journal – Instant Rock at Station 9
- https://history.nasa.gov/alsj/a15/A15SampleCat_1.pdf Catalog of Apollo 15 Rocks – Part 1. 15015-15299
References
- Allaby, A. and Allaby, M. (Eds). 1990. The Concise Oxford Dictionary of Earth Sciences. New York, USA: Oxford University Press.
- McDonald, R. C. et al. 1990. The Australian Soil and Land Survey Field Handbook, 2nd Ed. Melbourne, Australia: Inkata Press.
- Microtectonics, by C.W.Passchier and R.A.J.Trouw, 2nd rev. and enlarged ed., 2005, XVI, 366 p., 322 illus., with CD
External links
- . Encyclopedia Americana. 1920.