Selennyakh Range
The Selennyakh Range (Russian: Селенняхский хребет, Selennyakhsky Khrebet; Yakut: Силээннээх) is a range of mountains in far North-eastern Russia. Administratively the range is part of the Sakha Republic of the Russian Federation.[2] The town of Deputatsky, capital of the Ust-Yansky District, is located in the area of the range.
| Selennyakh Range | |
|---|---|
| Селенняхский хребет / Силээннээх | |
 Selennyakh Range Location in the Sakha Republic, Russia | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Saltag-Tas |
| Elevation | 2,021 m (6,631 ft) |
| Coordinates | 68°30′N 140°30′E [1] |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 250 km (160 mi) NNW / SSE |
| Geography | |
| Location | Sakha Republic, Far Eastern Federal District |
| Parent range | Momsko-Chersk Region, East Siberian System |
| Geology | |
| Type of rock | Gneiss, shale, crystalline limestone, sandstone and siltstone with granite intrusions |
| Climbing | |
| Easiest route | From Deputatsky |
Geography
The Selennyakh Range extends from NNW to SSE for almost 250 kilometres (160 mi) north of the northern end of the Moma Range and east of the Khadaranya Range. It is parallel to the latter and separated from it by the Moma-Selennyakh Depression, a wide intermontane basin, where the river Selennyakh flows and that continues southeastwards along the western side of the Moma Range. The Aby Lowland lies to the east and to the north the Yana-Indigirka Lowland. To the northeast it connects with the Kyun-Tas, at the western end of the Polousny Range, and to the northwest with the far north of the Chersky mountain system.[1] In some works the Selennyakh Range is included as a part of the Chersky Range mountain system.[3]
The highest point of the Selennyakh Range is the Saltag-Tas (Салтага-Тас), a 2,021 metres (6,631 ft) high ultra-prominent ridge located in the southern part, nearly 90 kilometres (56 mi) to the south of Deputatsky.[4] Other subranges of the wider Selennyakh are the Nemkuchan Range in the northeast —a small ridge along the river of the same name facing the Kyun-Tas, the Esteriktyakh-Tas in the east, and the Tommot Massif and Andrey-Tas at the southern end.[5]
The main rivers of the range are the Uyandina and Selennyakh rivers, both left tributaries of the Indigirka, as well as the Chondon, which flows northwards into the Laptev Sea.[2]
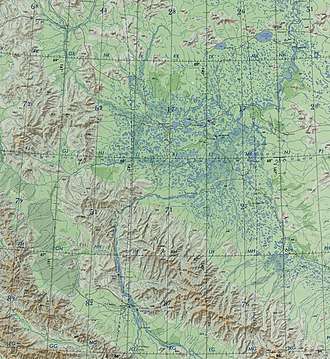 The Selennyakh Range at the top left corner and the Aby Lowland on the upper right half of the picture. |
Flora
Permafrost prevails in the area of the range. The river valleys of the range have sparse larch forests, and above 600 metres (2,000 ft) there is a narrow pre-tundra belt in which alder and dwarf cedar predominate. In the higher altitudes there is mountain tundra.[2]
See also
References
- Google Earth
- Selennyakhsky Khrebet / Great Soviet Encyclopedia; in 35 vols. / Ch. ed. Yu. S. Osipov. 2004–2017.
- Chersky Range // Great Russian Encyclopedia in 35 vols. / Ch. ed. Yu.S. Osipov . - M , 2004–2017.
- "Инженерно-геологические аспекты освоения месторождений олова Яно-Индигирской провинции (С-В Якутия)" [Engineering and geological aspects of the development of tin deposits in the Yano-Indigir province (St. Yakutia)]. geoinfo.ru. Retrieved 2019-11-27.
- Аркадий Андреев, Горы Якутии (Mountains of Yakutia), p. 26