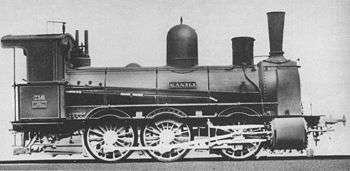
Saxon V V
The Saxon Class V was a triple-coupled, goods train, tender locomotive operated by the Royal Saxon State Railways. In 1925, the Deutsche Reichsbahn regrouped the locomotives 25 into their DRG Class 53.6–7.
| Saxon Class V V DRG Class 53.6–7 PKP Class Th101 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
| Manufacturer: | Sächsische Maschinenfabrik, Chemnitz Sigl, Vienna | |||
| Years of manufacture: | 1885–1890 | 1890–1896 | 1898–1901 | 1920 |
| Quantity: | 18 | 85 | 61 | 1 |
| Numbers: | 1012–1029 53 601–615 | 1001–1103 53 616–679 | 1104–1164 53.680–729 | 1000 53 751 |
| Retired: | by 1930 | |||
| Axle arrangement: | C n2v | |||
| Gauge: | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) | |||
| Length over buffers: | 14,718 mm | |||
| Empty weight: | 37.0 t | 37.5 t | 39.0 t | 41.5 t |
| Service weight: | 41.6 t | 42.0 t | 43.7 t | 46.2 t |
| Adhesive weight: | 41.6 t | 42.0 t | 43.7 t | 46.2 t |
| Axle load: | 13.9 t | 14.0 t | 14.1 t | 15.4 t |
| Top speed: | 45 km/h | |||
| Indicated power: | N/K | |||
| Driving wheel diameter: | 1,390 mm | 1,390 mm | 1,400 mm | 1,420 mm |
| Valve gear: | Allan valve gear, inside gear | |||
| No. of cylinders: | 2 | |||
| HP cylinder diameter: | 460 mm | 480 mm | 500 mm | 500 mm |
| LP cylinder diameter: | 650 mm | 700 mm | 700 mm | 700 mm |
| Piston stroke: | 610 mm | |||
| Boiler overpressure: | 12 bar | |||
| No. of heating pipes: | 173 | 173 | 167 | 204 |
| Heating pipe length: | 4,369 mm | 4,369 mm | 4,369 mm | 4,000 mm |
| Grate area: | 1.41 m2 | 1.41 m2 | 1.41 m2 | 1.8 m2 |
| Radiative heating area: | 8.2 m2 | 8.2 m2 | 8.2 m2 | 7.7 m2 |
| Tube heating area: | 106.9 m2 | 106.9 m2 | 103.2 m2 | 115.4 m2 |
| Evaporative heating area: | 115.1 m2 | 115.1 m2 | 111.37 m2 | 123.1 m2 |
| Tender: | sä 3 T 5,65 / sä 3 T 7,5 | sä 3 T 9 | ||
History
The Class V V locomotives were a development of a predecessor design, the Class V. A new feature was the compound engine, which had already proved itself on the Prussian G 42.
In 1885 the locomotive "KÄNZLI" became the first unit to be delivered by the Sächsische Maschinenfabrik in Chemnitz to the Royal Saxon State Railways. Because the locomotives performed well, from 1887 to 1901 a total of 164 examples were built in three construction batches that only differed marginally from one another. Eleven locomotives of the second batch, with railway numbers 858 – 868 (new: 1001–1011) were built by Sigl in Vienna.
Another example was produced based on a boiler made for the Turkish State Railways, TCDD, which was unable to be delivered due to the First World War. So the boiler was used to make another of these locomotives for the Saxon state railways which, in 1920, was given the running number 1000.
Several locomotives were lost during the First World War so, in 1920, the Deutsche Reichsbahn only took over 130 engines of Saxon Class V V. In 1925 they were given the new running numbers, 53 601 – 53 751. They were all retired and scrapped by 1930. Not a single example has survived.
The 14 locomotives that remained in Poland after 1918, were later taken over by the Polish state railway, PKP, and were given numbers Th101-1 – Th101-14. Several examples were also left behind in Belgium and were grouped by the state railway, SNCB, under the numbers 7726, 7733, 7736, 7737, 7735, 7738, 7781 and 7783.
Technical features
The locomotives had a boiler made of three shells with a semicircular cover, which was in the area of the firebox between the frame plates. A notable feature was the large, rounded steam dome in the middle of the boiler. Compared with the Class V the boiler pressure was raised by about 1/3 to 12 bar. The Ramsbottom safety valve sat immediately in front of the front wall of the driver's cab, the sandbox was placed immediately behind the chimney. Like most Saxon locomotives the V V usually had a Krempen chimney, but several were also fitted with Kobel chimneys in order to be able to fire Bohemian brown coal.
The steam engine was designed as a two-cylinder compound engine with inside Allan valve gear. As a starting system the "KÄNZLI" had one manufactured by von Borries. The series locomotives built from 1887 were given Lindner starting systems. The larger low-pressure cylinders were arranged on the left. To guarantee the necessary profile freedom, both cylinders were installed at a slight angle.
The driving and coupled wheels were fixed to the frame. Whether the middle axle had a reduced wheel flange is not known. The drive went to the second axle.
To begin with most of the locomotives had a steam brake that operated on the second and third coupled axles. The prototype locomotive, No. 736 "KÄNZLI", was initially fitted with a Heberlein brake(!). Several locomotives were later converted to Westinghouse compressed air brakes, the one delivered in 1920, No. 1000, had this on delivery.
Several locomotives that were used on Sekundärbahn duties, were also equipped with steam-operated bells.
The engines were given tenders of Saxon Class sä 3 T 5,65 or sä 3 T 7,5. The one delivered in 1920, No. 1000, had a Class sä 3 T 9 tender.
References
- Näbrich, Fritz; Meyer, Günter; Preuß, Reiner (1983). Lokomotivarchiv Sachsen 2 (in German). Berlin: transpress VEB Verlag für Verkehrswesen.
- Preuß, Erich; Preuß, Reiner (1991). Sächsische Staatseisenbahnen (in German). Berlin: transpress Verlagsgesellschaft. ISBN 3-344-70700-0.