Savings account
A savings account is a bank account at a retail bank whose features include the requirements that only a limited number of withdrawals can take place, it does not have cheque facilities and usually do not have a linked debit card facility, it has limited transfer facilities and cannot be overdrawn. Traditionally, transactions on savings accounts were widely recorded in a passbook, and were sometimes called passbook savings accounts, and bank statements were not provided; however, currently such transactions are commonly recorded electronically and accessible online.
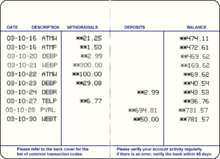 The passbook was the traditional record of savings account transactions before the use of the internet. |
| Part of a series on financial services |
| Banking |
|---|
|
Types of banks
|
|
Funds transfer |
|
People deposit funds in savings accounts for a variety of reasons, including as a safe place where to hold their cash. Savings accounts normally pay interest. A number of countries require savings accounts to be protected by deposit insurance and some countries provide a government guarantee for at least a portion of the savings account balance.
There are a number of types of savings accounts for particular purposes, such as for young savers, for retirees, Christmas club accounts, investment accounts, money market accounts, besides other. Some accounts require a minimum deposit, a deposit on a regular basis, notice of withdrawal, and other special conditions.
Almost all savings accounts accrue compound interest over time.
Regulations
United States
In the United States, Sec. 204.2(d)(1) of Regulation D (FRB) limits withdrawals from savings accounts to 6 pre-authorized transfers or withdrawals (excluding withdrawals via an automated teller machine) per month or a statement cycle of at least four weeks. There is no limit to the number of deposits into the account. Violations of the regulation may result in a service charge, or may result in the account being changed to a checking account.
Regulation D sets smaller reserve requirements for savings account balances. In addition, customer’s can plan withdrawals to avoid fees and earn interest, which contributes to more stable savings account balances on which banks can lend. A savings account linked to a checking account at the same financial institution can help avoid fees due to overdrafts and reduce banking costs.[1]
References
- Amy Fontinelle. "Banking: Savings Accounts 101".
External links
- Savings Account Definition | Investopedia
- Savings Accounts Regulation D | MoneyRates.com
- What is a Savings Account - NerdWallet