Salesian Sisters of Don Bosco
The Salesian Sisters of Don Bosco, formally known as the Daughters of Mary Help of Christians (Latin: Figlie di Maria Ausiliatrice; abbreviated FMA) are a female religious institute formed by Saint Maria Mazzarello in 1872. They were founded to work alongside Saint John Bosco and his Salesians of Don Bosco in his teaching projects in Turin. They continue to be a teaching order worldwide.
 Maria Mazzarello, the founder | |
| Abbreviation | FMA |
|---|---|
| Founder | Maria Domenica Mazzarello |
| Type | Centralized Religious Institute of Consecrated Life of Pontifical Right (for Women) |
| Headquarters | Via dell'Ateneo Salesiano, 81, 00139 Roma, Italy |
| Location | |
Membership | 14000 members (2017) |
Superior general | Sr. Yvonne Reungoat, F.M.A. |
Key people | Maria Mazzarello |
Main organ | Salesian of Don Bosco |
| Website | cgfmanet.org |
History
On August 5, 1872 in Mornese, Alessandria, Italy, the first Daughters of Mary Help of Christians gathered with Don Bosco and Msgr. Joseph Sciandra, the Bishop of Acqui, to celebrate their admission to the novitiate and their first professions. On that day St. Mary Domenica Mazzarello was also elected the first superior.[1]
A year later their first boarding school and primary school was recognized by the educational authorities of Castelletto d’Orba. On October 8, 1874, the Salesian Sisters were able to open their first house in Borgo San Martino. They carried on the tradition of the Salesian Oratory (a place where young people could gather to enjoy themselves, learn, and grow in their faith, safe from harm), ran workshops to educated young women to help them to be self-sufficient, and taught. The work of the Salesians Sisters was not limited to a schoolroom as they participated in social justice works and teaching trades to young women and girls.[2]
Sr. Mary Mazzarello and her first companions were able to profess their perpetual vows, after studying with the Sisters of St. Anne for their religious formation, on August 28, 1875 in the presence of Don Bosco.[2]
Their first house outside of Italy was opened in 1877 in Nice, France. November 9 of the same year Mother Mazzarello and the first missionaries were received in an audience by Pope Pius IX, a great friend and supporter of Don Bosco. Five days later the first missionary sisters departed for Uruguay.[2]

After many years of revision, discussion and consultation, Don Bosco was able to give to the Daughters of Mary Help of Christians the first printed version of their Constitutions on the feast of the Immaculate Conception, December 8, 1878. In February 1879 the motherhouse of the congregation moved from Mornese to Nizza Monferrato.[3]
The year 1880 saw the second missionary expedition of the Salesian Sisters to Patagonia (Argentina), as they followed their Salesian brothers who had prepared the way for their arrival. In 1881, Mother Mazzarello took ill and died at Nizza Monferrato on May 14, at age 44.[3] At the time of her death there were 26 houses and 166 Sisters.
In 1888, the FMA established their first house in Chile.[3]
When the Sisters arrived in Battersea, London in 1902 only one of the first group of could speak English. They set to in their role supporting the educational work of the Salesians, supervising the domestic arrangements for the community and the pupils. They also found time to undertake some informal education by running an out-of-school club for the disadvantaged children of the area. This was the first of many such clubs that continue to be run by the Sisters up and down the country. World War II brought to an end the work in Dovercourt and Soho where both houses were so badly damaged as to render them uninhabitable.[4]
In 1908, the first Salesian Sisters arrived in the U.S. and settled in New Jersey. From there, Salesian youth and outreach programs spread to Canada and throughout New England, as well as other parts of the country, including Florida, Louisiana, Texas, and California.[1]
In 1920 the first four Sisters came to Ireland, three Italians and one English of Irish parents, and started their work in Limerick. The sisters run a primary school, Scoil Mhuire Banríon na hÉireann (the "School of Mary, Queen of Ireland") in Caherdavin, a suburb of Limerick city.[5]
They also opened a school in Guwahati, Assam, India called St. Mary's School in the year 1924 which is still the best school in the entire region.
In 2017 the work of Sister Carolin Tahhan Fachakh in Syria was recognised by the United States Secretary of State who awarded her an International Women of Courage Award. Sister Carol runs a nursery in war-torn Aleppo that cares for mothers and children irrespective of faith.[6] The sisters teach mothers to sew. Sister Carol who had been nominated under President Obama spoke out against President Trump and in support of the Syrian president Bashar al-Assad.[7]
Apostolate
The ministry of the Daughters of Mary Help of Christians is youth-centered. The Sisters in Liverpool, England opened Mary, Help of Christians High School in 1965.[4]
- Many Sisters are involved in youth clubs and projects, the present day version of the ‘oratory’ so much a part of Salesian work and belief. Among these is the Follow Your Dream Project, started in 1998 in the Bawnogue area of Clondalkin, Dublin. FYD seeks to promote the growth and development of young people in disadvantaged areas, to increase their confidence and self-esteem and assist them in acquiring new skills and developing their talents. FYD hosts a variety of activities including a bowling night and a trip to a Christmas panto.[8]
As of 2016, they number over 14,000 members in 89 different countries, and on five continents.[1]

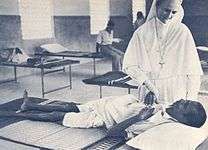 Salesian sister caring for sick and poor in former Madras Presidency, India
Salesian sister caring for sick and poor in former Madras Presidency, India
Controversies
On the 20th of December 2019, Maria Angela Fare, a former Italian nun of the Sisters of Don Bosco, has been sentenced to 3 and a half years facing jail for sexual abuse on a girl she met in the oratory: the girl later committed suicide in 2011 [9]
References
- Daughters of Mary Help of Christians, Western Province, USA Archived 2016-02-08 at the Wayback Machine
- "History and Heritage", Salesian Sisters of St. John Bosco, Eastern Province, USA
- "Significant milestones", Salesian Sisters of Don Bosco, Generalate
- Salesian Sisters of Don Bosco, UK
- Salesian Sisters in Ireland Archived 2016-02-02 at the Wayback Machine
- "Biographies of the Finalists for the 2017 International Women of Courage Awards". www.state.gov. Archived from the original on 2017-03-29. Retrieved 2017-08-25.
- "Syrian nun honored by State Department says U.S. bombing is step back | The Compass". The Compass. 2017-04-11. Retrieved 2017-08-25.
- Follow Your Dream Ltd., Clondalkin
- https://www.en24.news/2019/12/sexual-abuse-a-former-nun-sentenced-to-3-and-a-half-years-she-will-go-to-prison-he-raped-a-girl-he-met-in-the-oratory-who-committed-suicide-in-2011.html