SS Empire Celia
SS Empire Celia was a 7,025 GRT cargo ship built in 1943 by Charles Connell and Company Ltd of Scotstoun, Glasgow for the Ministry of War Transport (MoWT).[1] In 1948 she was sold into merchant service and renamed Putney Hill. Further name changes were Castle Hill in 1949 and London Statesman in 1950. In 1951 she was sold to Panamanian owners and renamed Morella, being sold later that year to Polskie Linie Oceaniczne and renamed Jedność. She served until 1966, when she was scrapped.
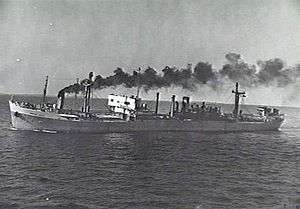 Empire Celia, by then renamed Putney Hill, 3 December 1948 | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: |
|
| Owner: |
|
| Operator: |
|
| Port of registry: | |
| Builder: | Charles Connell & Co Ltd[1] |
| Yard number: | 441 |
| Launched: | |
| Out of service: | 1963–66 |
| Identification: | |
| Fate: | Scrapped |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type: | Cargo ship[1] |
| Tonnage: | |
| Length: | 431.3 ft (131.5 m)[1] |
| Beam: | 56.3 ft (17.2 m)[1] |
| Draught: | 26 ft 9 in (8.15 m)[1] |
| Depth: | 35.2 ft (10.7 m)[1] |
| Installed power: | |
| Propulsion: | 3-cylinder triple-expansion steam engine; screw[1] |
| Speed: | 11 knots (20 km/h)[3] |
| Armament: | 1 x 4" gun (Empire Celia)[4] |
Description
The ship was built by Charles Connell & Co Ltd Glasgow[1] as yard number 441. She was launched in either April[1] or July[2] 1943. She was 431.3 feet (131.5 m) long, with a beam of 56.3 feet (17.2 m). She had a depth of 35.3 feet (10.8 m) and a draught of 26 feet 9 inches (8.15 m).[1] Her tonnages were 7,025 GRT;[1] 6,571 tonnage under deck;[1] 4,856 NRT[1] and 10,821 DWT.[3] She was fitted with direction finding equipment.[1]
She had nine corrugated furnaces with a combined grate surface of 157 square feet (15 m2) that heated three single-ended boilers with a combined heating surface of 7,170 square feet (666 m2). The boilers fed a three-cylinder triple-expansion steam engine rated at 506 NHP or 2,465 brake horsepower (1,838 kW),[3] with cylinders of 24 1⁄2 inches (62 cm), 39 inches (99 cm) and 70 inches (180 cm) diameter by 48 inches (120 cm) stroke. The engine was built by David Rowan & Co Ltd, Glasgow[1] and could propel the ship at 11 knots (20 km/h).[3]
History
Empire Celia was built in 1943 for the MoWT.[5] She was placed under the management of Connell & Grace Ltd. Her port of registry was Glasgow. She was allocated the Code Letters BFGS and United Kingdom Official Number 169757.[1]
Empire Celia was to have been a member of Convoy HX 241, which left New York City on 24 May 1943 and arrived at Liverpool on 10 June. She was due to proceed to Milford Haven, Pembrokeshire for further orders. However, she did not sail with HX 241,[6] but joined Convoy HX 242, which left New York on 31 May and arrived at Liverpool on 15 June. She was carrying a cargo of lumber and steel, destined for either Southampton or Swansea.[7]
Records show that Empire Celia spent the remainder of the war years serving in the Arctic Convoys. She was a member of Convoy JW54A, which departed Loch Ewe on 15 November 1943 and arrived at the Kola Inlet, Soviet Union on 24 November.[8] She returned to the United Kingdom as a member of Convoy RA 55A, which departed the Kola Inlet on 22 December and arrived at Liverpool on 1 January 1944. She was carrying a cargo of magnesite and pit props.[9]
Empire Celia was a member of Convoy JW 57, which departed from Liverpool on 20 February 1944 and arrived at the Kola Inlet on 29 February.[10] She was also a member of Convoy RA58, which departed the Kola Inlet on 7 April 1944 and arrived at Loch Ewe on 14 April. Empire Celia was bound for Hull.[11]
On 2 September three Spitfire LF Mk IX aircraft were loaded aboard Empire Celia. She delivered them to the USSR on 23 September.[12] She was also a member of Convoy RA61, which departed the Kola Inlet on 2 November and arrived at Loch Ewe on 9 November. Empire Celia carried the convoy's Vice Commodore.[13]
Between 23 and 26 December Empire Celia embarked a cargo including thirteen Spitfire LF Mk IX's.[14][15] She then sailed as a member of Convoy JW 63, which departed Loch Ewe on 30 December and arrived at the Kola Inlet on 8 January 1945.[16] The Spitfires were delivered on 9 January.[14][15] On 17 February, Empire Celia departed the Kola Inlet as a member of Convoy RA 64, which arrived at Loch Ewe on 28 February.[16]
A photograph taken in December 1948 shows that Empire Celia was still armed with a 4-inch gun, more than three years after the end of the war.[4]
In 1946, management of Empire Celia was transferred to Counties Ship Management. She was sold to them in 1948 and renamed Putney Hill. In 1949 she was sold to London & Overseas Freighters Ltd and renamed Castle Hill. LOF renamed her again in 1950 as London Statesman. In 1951 she was sold to Far Eastern & Panama Transport Corp, Panama and was renamed Morella.[5] She was placed under the management of Wheelock, Marden & Co Ltd, Hong Kong. She was then sold to Compagnia Istmena de Transportes Maritimos SA.[2]
Later in 1951, Morella was sold to Polskie Linie Oceaniczne, Gdynia,[2] and was renamed Jedność (English: Unity).[5] She served until 1963, when she was withdrawn from service.[3] Jedność arrived at Hong Kong for scrapping on 29 April 1963.[2] In 1966[5] she was scrapped by the Lee Sing Co, Hong Kong.[2]
References
- "Lloyd's Register, Navires à Vapeur et à Moteurs" (PDF). London: Lloyd's Register. Retrieved 31 March 2013.
- "Launched 1943: ss EMPIRE CELIA". Clydesite. Archived from the original on 3 April 2012. Retrieved 31 July 2010.CS1 maint: unfit url (link)
- "Jedność". Polish Ocean Lines. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- "303249". Australian War Memorial. Retrieved 29 July 2010.
- "EMPIRE – C". Mariners. Retrieved 27 July 2010.
- "CONVOY HX 241". Warsailors. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- "CONVOY HX 242". Warsailors. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- "CONVOY JW 54A". Warsailors. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- "Convoy RA.55A". Convoyweb. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- "Navy and Merchant ships on Convoy JW-57". HMS Mahratta (G23) Association. Archived from the original on 29 July 2010. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- "CONVOY RA 58". Warsailors. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- "Spitfire aircraft production page 094". Spitfires. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- "CONVOY RA 61". Warsailors. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- "Spitfire aircraft production page 101". Spitfires. Retrieved 27 July 2010.
- "Spitfire aircraft production page 095". Spitfires. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- "The Arctic Convoy's". Toys out of the Pram. Retrieved 28 July 2010.