SMS Oldenburg (1884)
SMS Oldenburg [lower-alpha 1] was an armored warship of the German Imperial Navy. Laid down at the AG Vulcan shipyard in Stettin in 1883, the ship was launched in December 1884 and commissioned into the Navy in April 1886. Oldenburg was intended to have been a fifth member of the Sachsen class of sortie corvettes, but budgetary limitations and dissatisfaction with the Sachsen class prompted a redesign that bore little resemblance to the earlier vessels. Oldenburg mounted her main battery of eight 24 cm (9.4 in) guns amidships, six in a central casemate on the main deck and two directly above them on the broadside. She was the first German capital ship constructed entirely from German-made steel.
.jpg) A painting of SMS Oldenburg | |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Preceded by: | Sachsen class |
| Succeeded by: | None |
| History | |
| Name: | SMS Oldenburg |
| Namesake: | Oldenburg (German state) |
| Builder: | A.G. Vulcan in Stettin |
| Laid down: | 1883 |
| Launched: | 20 December 1884 |
| Commissioned: | 8 April 1886 |
| Decommissioned: | 1912 |
| Reclassified: | target ship |
| Fate: | scrapped 1919 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type: | Oldenburg class coast defense ship |
| Displacement: |
|
| Length: | 79.8 m (261 ft 10 in) |
| Beam: | 18 m (59 ft 1 in) |
| Draft: | 6.28 m (20 ft 7 in) |
| Installed power: |
|
| Propulsion: |
|
| Speed: | 13.8 kn (25.6 km/h; 15.9 mph) |
| Range: | 1,770 nmi (3,280 km; 2,040 mi) at 9 kn (17 km/h; 10 mph) |
| Complement: |
|
| Armament: |
|
| Armor: |
|
Oldenburg did not see significant service with the German Navy. She participated in fleet training maneuvers in the late-1880s and early 1890s, but she spent the majority of the 1890s in reserve. Her only major deployment came in 1897–1898 when she joined an international naval demonstration to protest the Greek annexation of Crete. In 1900, she was withdrawn from active duty and used as a harbor defense ship. From 1912 to 1919, she was used by the High Seas Fleet as a target ship; she was sold for scrapping in 1919 and broken up that year.
Design
Following the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871, General Albrecht von Stosch became the Chief of the Imperial Admiralty; he immediately set about drafting a new fleet plan, based on the previous program that had been approved in 1867. Stosch saw the role of the navy as primarily defensive; a fleet of ironclad warships would be kept in German waters to defend the coast against the type of blockade the Danish Navy had imposed during the Second Schleswig War and the French Navy had put into place during the Franco-Prussian conflict. Stosch's fleet plan, finalized in 1873, called for a total of eight ocean-going ironclads and six smaller, armored corvettes. The ocean-going component had been completed with the Kaiser class, and of the six corvettes, five had been built: Hansa and the four Sachsens. The last corvette was originally intended to be a fifth Sachsen-type vessel, but dissatisfaction with the design led many senior officers to push for a revised version.[1][2]
The new design was prepared between 1879 and 1881, but budgetary constraints imposed in the aftermath of the accidental sinking of the ironclad Grosser Kurfürst limited the ability of the design staff to produce an effective improvement on the Sachsens. On the available budget, the new ship's displacement would have to be reduced by some 2,000 t (2,000 long tons) compared to the Sachsens.[2][3][4] The limited displacement forced a reversion to the casemate ship arrangement, as well as a reduction in the caliber of guns from 26 cm (10 in) to 24 cm (9.4 in). To somewhat offset the reduction in offensive power, these guns were of a new, longer 30-caliber type that had a higher muzzle velocity than the shorter 22-caliber guns carried by the Sachsen class.[5]
Assessment of the design is mixed; the ship was an anachronism, being the last casemate ship to be laid down by any navy (though the Ottoman ironclad Hamidiye was completed later).[6] The naval historian Erich Gröner states that Oldenburg was an "experimental design, of no real value in combat."[7] Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships concurs, stating that Oldenburg was "considered to be of little fighting value by the time she was completed."[4] The historian Aidan Dodson criticized the ship as being "a poor investment [that] failed to make her designed speed by 0.2 knots (0.37 km/h; 0.23 mph) and had a form that lead to a rapid drop-off of speed in head seas."[6] The 1889 edition of the Brassey's Naval Annual reported a contradictory opinion, however, stating that "The majority of German naval critics are dissatisfied to a greater or less extent with all of these vessels, the König Wilhelm, Kaiser, Deutschland, and Oldenburg excepted."[8]
General characteristics
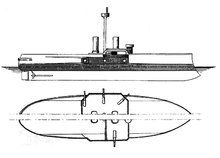
Oldenburg was 78.4 m (257 ft 3 in) long at the waterline and 79.8 m (261 ft 10 in) long overall. She had a beam of 18 m (59 ft 1 in) and a draft of 6.28 m (20 ft 7 in) forward and 6.3 m (20 ft 8 in) aft. As designed, the vessel displaced 5,249 metric tons (5,166 long tons; 5,786 short tons). When the ship was fully loaded, she displaced 5,743 t (5,652 long tons; 6,331 short tons).[7] Her hull was constructed with transverse and longitudinal steel frames; iron was used for the stem and stern. The hull was divided into twelve watertight compartments and incorporated a double bottom that ran for 60 percent of the length of its length.[9] Oldenburg was the first German capital ship built entirely from German-made steel.[10]
The German navy regarded Oldenburg as an adequate sea boat, though she suffered from significant pitching. As a result of her tendency to pitch severely, a 60 t (59 long tons; 66 short tons) ballast was permanently installed in the bow. She also lost a great deal of speed in heavy seas; at conditions above Beaufort sea state 6, this could be up to a 25 percent loss of speed. The ship could not operate under severe weather conditions. Her transverse metacentric height was 0.63 m (2 ft 1 in). Her standard complement consisted of 34 officers and 355 enlisted men, though her crew was later reorganized to 32 officers and 40 enlisted sailors. She carried a number of smaller boats, including one picket boat, one launch, two pinnaces, two cutters, two yawls, and one dinghy.[7]
Machinery

Oldenburg was powered by two horizontal 4-cylinder double-expansion steam engines in separate engine roomes; the two engines each drove a three-bladed screw propeller that was 4.50 m (14.8 ft) in diameter. Steam was provided to the engines by eight transverse, cylindrical fire-tube boilers, divided into two boiler rooms. Each boiler was equipped with three fireboxes, for a total of 24, which operated at up to 5 standard atmospheres (510 kPa) using forced draft. The engines were designed to operate at 3,900 metric horsepower (3,800 ihp) for a top speed of 14 knots (26 km/h; 16 mph). On speed trials, her engines slightly exceeded the designed horsepower, at 3,942 PS (3,888 ihp), though Oldenburg made only 13.8 knots (25.6 km/h; 15.9 mph).[7]
The ship was designed to store 348 t (343 long tons; 384 short tons) of coal normally, though she could accommodate up to 450 t (440 long tons; 500 short tons) under wartime conditions. An additional 120 t (120 long tons; 130 short tons) of coal could be stored on her deck for longer voyages. At a cruising speed of 9 knots (17 km/h; 10 mph), Oldenburg could steam for 1,770 nautical miles (3,280 km; 2,040 mi). Increasing her speed by one knot reduced her range to 1,370 nmi (2,540 km; 1,580 mi), and at 12 knots (22 km/h; 14 mph), she could cruise for only 980 nmi (1,810 km; 1,130 mi). Steering was controlled by a single rudder. She was equipped with three electric generators with a total output of 29 kilowatts at 65 volts.[7]
Armament and armor
Oldenburg carried eight 24 cm (9.4 in) L/30 hooped guns in an unusual configuration: six guns on the main deck, one on each broadside, four in embrasures at each corner of the central battery to give a measure of end-on fire, and two on the upper deck firing broadside.[7][4] These guns were supplied with 494 rounds of ammunition, and could depress to −5° and elevate to 8°. This enabled a maximum range of 5,700 to 8,800 m (6,200 to 9,600 yd).[7] Her secondary battery consisted of four 15 cm (5.9 in) L/22 guns in single mounts. For close-range defense against torpedo boats, she carried a pair of 8.7 cm (3.4 in) L/24 guns in single mounts. Later in her career, she received another six of these guns to strengthen her defensive capabilities. Four 35 cm (14 in) torpedo tubes rounded out her armament. One was mounted in the bow, submerged, two were placed on the broadside above water, and the fourth was located in the stern, also above water. She carried ten torpedoes.[7][4]
Oldenburg's armor consisted of compound steel backed with teak; the steel was fabricated by the Dillinger Works.[10] The main armored belt was composed of two strakes; the steel upper strake was 300 mm (12 in) thick amidships, where it protected the ship's vitals. The belt was reduced on either end of the central portion to 200 mm (7.9 in). The lower strake was 250 mm (9.8 in) thick in the central section and 180 mm (7.1 in) on either end. The entire belt was backed with 250 mm of teak amidships and 300 mm of teak on either end. The sides of the armored casemates for the main battery were 150 mm (5.9 in) thick. The ship's deck was 30 mm (1.2 in) thick. Her forward conning tower had 50 mm (2.0 in) thick sides and a 25 mm (0.98 in) thick roof. The rear conning tower was given only splinter protection, with 15 mm (0.59 in) thick sides and a 12 mm (0.47 in) thick roof.[9]
Service history

Oldenburg was laid down in 1883 at the AG Vulcan shipyard in Stettin, under yard number 132. She was launched on 20 December 1884, after which fitting-out work commenced. She was completed by April 1886 and commissioned into the German Navy on 8 April.[7] She immediately joined I Division of the fleet, alongside Sachsen, Bayern, and Württemberg, for the annual fleet maneuvers. Bayern and Württemberg suffered from engine troubles throughout the exercises, but Oldenburg performed satisfactorily.[11]
In June 1887, Germany dedicated the Kaiser Wilhelm Canal; Oldenburg was among the ships present during the celebrations. Oldenburg was assigned to the training squadron for the maneuvers in August–September 1887, along with König Wilhelm and Kaiser. The majority of the exercises were focused in the Baltic, but the fleet did conduct maneuvers in the North Sea for eight days in September.[12] Oldenburg also participated in the visit to Great Britain in August 1889, where Wilhelm II took part in the Cowes Regatta. The ship was assigned to I Division with Sachsen, Baden, and the new cruiser Irene. Oldenburg and the rest of the fleet joined the Royal Navy in a fleet review for Queen Victoria.[13]
Oldenburg participated in the ceremonial transfer of the island of Helgoland from British to German control in the summer of 1890. She was present during the fleet maneuvers in September, where the entire eight-ship armored squadron simulated a Russian fleet blockading Kiel.[14] She remained with I Division in 1891; the year's maneuvers simulated a two-front war against Russia and either France or Denmark. In 1892, however, Württemberg replaced Oldenburg in I Division, and the latter went into reserve.[15] The ship remained out of service for the next five years. She returned to active duty in 1897 to join an international naval demonstration off the island of Crete, which had been annexed by Greece. The ship remained in the demonstration until March 1898, when Germany and Austria-Hungary withdrew their naval contingents in a show of dissatisfaction over the compromise solution, which left Crete under Ottoman control, but with a Greek prince.[16]
In 1900, Oldenburg was reduced to serve as a harbor guard ship. She was later used as a depot ship before being stricken from the naval register on 13 January 1912. The vessel was then used as a target ship by the High Seas Fleet until after the German defeat in World War I. Oldenburg was sold to Hattinger Company, a ship-breaking firm, on 5 May 1919. The ship was dismantled for scrap in Wilhelmshaven that year.[7]
Notes
- "SMS" stands for "Seiner Majestät Schiff", or "His Majesty's Ship".
References
- Brassey, T. A., ed. (1889). "Germany". Brassey's Annual. Portsmouth: J. Griffin & Co: 74–78.
- Dodson, Aidan (2016). The Kaiser's Battlefleet: German Capital Ships 1871–1918. Barnsley: Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84832-229-5.
- Gardiner, Robert, ed. (1979). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1860–1905. Greenwich: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 978-0-8317-0302-8.
- Gröner, Erich (1990). Jung, Dieter; Maass, Martin (eds.). German Warships: 1815–1945. Vol. I: Major Surface Vessels. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-0-87021-790-6.
- Sondhaus, Lawrence (1997). Preparing for Weltpolitik: German Sea Power Before the Tirpitz Era. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-55750-745-7.