RS Ophiuchi
RS Ophiuchi (RS Oph) is a recurrent nova system approximately 5,000 light-years away in the constellation Ophiuchus. In its quiet phase it has an apparent magnitude of about 12.5. It has been observed to erupt in 1898, 1933, 1958, 1967, 1985, and 2006 and reached about magnitude 5 on average. A further two eruptions, in 1907 and 1945, have been inferred from archival data. The recurrent nova is produced by a white dwarf star and a red giant in a binary system. About every 20 years, enough material from the red giant builds up on the surface of the white dwarf to produce a thermonuclear explosion. The white dwarf orbits close to the red giant, with an accretion disc concentrating the overflowing atmosphere of the red giant onto the white dwarf.
 Recurrent nova RS Ophiuchus in eruption of February 2006 | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Ophiuchus |
| Right ascension | 17h 50m 13.2s |
| Declination | −06° 42′ 28″ |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 9.6 - 13.5 (quiet), < 5 (burst) |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M2III / White Dwarf |
| Variable type | Recurrent nova |
| Astrometry | |
| Distance | 3900 – 6500 ly (1200 – 2000[1] pc) |
| Other designations | |
HD 162214, BD−06° 4661 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Properties
RS Ophiuchi is a system consisting of a white dwarf with a red giant companion. The stars are in a binary system with an orbital period of around 454 days.[2]
Eruptive history
| Date of eruption |
Years since last eruption |
|---|---|
| 1898 | ? |
| 1907 | 9 |
| 1933 | 26 |
| 1945 | 12 |
| 1958 | 13 |
| 1967 | 9 |
| 1985 | 18 |
| 2006 | 21 |
| Present (2018) | >12 |
1898
The 1898 eruption was, in fact, not discovered until several years after it happened. Williamina Fleming discovered a nova-like spectrum in the Henry Draper Memorial photographs and announced it as a potential nova in 1904. This diagnosis was affirmed by Edward Charles Pickering in 1905, after which Annie Jump Cannon determined that RS Ophiuchi had likely reached maximum in 1898.
1907
Though the 1907 eruption was not observed during outburst, measurements of a dip in brightness from archival observations suggests that RS Oph underwent an eruption in early 1907 during a time when it was obscured by the sun.[3][4]
1933
The 1933 outburst was first detected by Eppe Loreta, from Bologna, Italy. Loreta had been observing Y Ophiuchi when he serendipitously noticed a bright object about 50 arcminutes southwest of Y Oph. The detection of this luminous star resulted in the second recorded outburst of RS Oph. An independent discovery of this activity was made several days later by Leslie Peltier (P) while making his routine check of the variable.
1945
The 1945 eruption was also inferred from archival data after the outburst as a result of obscuration from the sun during the peak brightness. This eruption is more certain than that in 1907, as the tail of the eruption was also observed.[5]
1958
The 1958 outburst was detected by Cyrus Fernald, located in Longwood, Florida. Fernald's monthly report for July 1958, containing 345 observations, displays a note in which he comments "Not too good of a month outside of the RS Oph observations (19 in total). It was interesting to watch the change in color as the star faded. It was reddish-yellow the first night, then yellowish-red, and so on. The last observation was the reddest star that I have ever seen." The crimson color of which Fernald speaks is indicative of the strong H-alpha emission displayed in the several days following the outburst.
1967
The 1967 outburst was again detected by Cyrus Fernald (FE), however, Fernald was not given credit for the earliest observation of maximum. For on the same evening, Dr. Max Beyer (BY), located in Hamburg, Germany, observed the variable at 6th magnitude. Due to the 6-hour difference in time zones, Dr. Beyer was credited with the first report.
1985
In January 1985, Warren Morrison of Peterborough, Canada discovered RS Oph to again be in outburst, reaching a maximum brightness of magnitude 5.4.
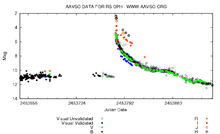
2006
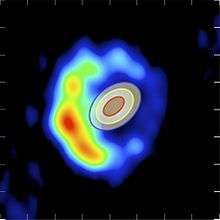
On February 12, 2006 a new outburst occurred, reaching magnitude 4.5. The opportunity was taken to observe it at different wavelengths. It was notably observed with the VLTI by Olivier Chesneau, who discovered an elongated fireball as early as 5.5 days after the explosion (see the figure below).[6][7][8]
References
- Barry, R. K.; Mukai, K.; Sokoloski, J. L. (2008). "On the Distance of RS Ophiuchi". RS Ophiuchi (2006) and the Recurrent Nova Phenomenon. ASP Conference Series. 401: 52. Bibcode:2008ASPC..401...52B.
- Brandi, E.; Quiroga, C.; Mikołajewska, J. (2009). "Spectroscopic orbits and variations of RS Ophiuchi". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 497 (3): 815–825. arXiv:0902.2177. Bibcode:2009A&A...497..815B. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200811417.
- Schaefer, B. E. (August 2004). "RS Ophiuchi". IAU Circular. 8396. Retrieved 24 May 2015.
- Schaefer 2010, p. 312
- Schaefer 2010, p. 313
- Bode; et al. (2006). "Swift Observations of the 2006 Outburst of the Recurrent Nova RS Ophiuchi. I. Early X-Ray Emission from the Shocked Ejecta and Red Giant Wind". The Astrophysical Journal. 652 (1): 629–635. arXiv:astro-ph/0604618. Bibcode:2006ApJ...652..629B. doi:10.1086/507980.
- Monnier; et al. (2006). "No Expanding Fireball: Resolving the Recurrent Nova RS Ophiuchi with Infrared Interferometry". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 647 (2): L127–L130. arXiv:astro-ph/0607399. Bibcode:2006ApJ...647L.127M. doi:10.1086/507584.
- Chesneau (2007). "AMBER/VLTI interferometric observations of the recurrent Nova RS Ophiuchii 5.5 days after outburst". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 464 (1): 119–126. arXiv:astro-ph/0611602. Bibcode:2007A&A...464..119C. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20066609.
Bibliography
- Schaefer, B. E. (2010). "Comprehensive Photometric Histories of All Known Galactic Recurrent Novae". Astrophysical Journal. 187 (2): 275–373. arXiv:0912.4426. Bibcode:2010ApJS..187..275S. doi:10.1088/0067-0049/187/2/275.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to RS Ophiuchi. |
- "V* RS Oph". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg.
- Entry at Astronomy Picture of the Day
- Entry in the Variable Star Index
- AAVSO