Psamathe (moon)
Psamathe /ˈsæməθiː/, also known as Neptune X, is a retrograde irregular satellite of Neptune. It is named after Psamathe, one of the Nereids. Psamathe was discovered by Scott S. Sheppard and David C. Jewitt in 2003 using the 8.2 meter Subaru telescope.[4] Before the announcement of its name on February 3, 2007 (IAUC 8802), it was known by the provisional designation S/2003 N 1.[6]
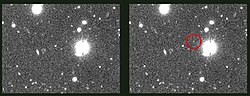 | |
| Discovery[1][2] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | |
| Discovery date | 2003 |
| Designations | |
Designation | Neptune X |
| Pronunciation | /ˈsæməθiː/ |
Named after | Ψαμάθη Psamathē |
| S/2003 N 1 | |
| Adjectives | Psamathean /sæməˈθiːən/ |
| Orbital characteristics[3] | |
| Epoch June 10, 2003 | |
| 46.705 Gm | |
| Eccentricity | 0.4617 |
| −9128.74 d (24.9 a) | |
| Inclination | 137.679° |
| Physical characteristics | |
Mean diameter | 38 km[4][5] |
| Albedo | 0.04 (assumed)[4] |
Psamathe is about 38 kilometers in diameter. It orbits Neptune at a distance of between 25.7 and 67.7 million km (for comparison, the Sun-Mercury distance varies between 46 million and 69.8 million km) and requires almost 25 Earth years to make one orbit. The orbit of this satellite is close to the theoretical stable separation from Neptune for a body in a retrograde orbit. Given the similarity of Psamathe's orbital parameters with Neso (S/2002 N 4), it was suggested that both irregular satellites could have a common origin in the break-up of a larger moon.[4] Both are further from their primary than any other known moon in the Solar System.[7]
See also
- Irregular satellites
References
- JPL (2011-07-21). "Planetary Satellite Discovery Circumstances". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 2011-10-24.
- Green, Daniel W. E. (September 3, 2003). "Satellites of Neptune". IAU Circular. 8193. Retrieved 2011-10-24.
- Jacobson, R. A. (2008). "NEP078 - JPL satellite ephemeris". Planetary Satellite Mean Orbital Parameters. Retrieved 2009-09-23.
- Sheppard, Scott S.; Jewitt, David C.; Kleyna, Jan (2006). "A Survey for "Normal" Irregular Satellites around Neptune: Limits to Completeness". The Astronomical Journal. 132: 171–176. arXiv:astro-ph/0604552. Bibcode:2006AJ....132..171S. doi:10.1086/504799.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Sheppard, Scott S. "Neptune's Known Satellites". Department of Terrestrial Magnetism (Carnegie Institution of Washington). Retrieved 2008-12-13.
- Marsden, Brian G. (2003). "MPEC 2003-R19 : S/2003 N 1". Minor Planet Center, Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. Retrieved 2011-01-08.
- Schmude, Richard, Jr. (2008). Uranus, Neptune, Pluto and How to Observe Them. Springer. p. 106. ISBN 0-387-76601-4.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Psamathe (moon). |


_flatten_crop.jpg)