Politics (Aristotle)
Politics (Greek: Πολιτικά, Politiká) is a work of political philosophy by Aristotle, a 4th-century BC Greek philosopher.
 |
| Part of a series on the |
| Corpus Aristotelicum |
|---|
| Logic (Organon) |
| Natural philosophy (physics) |
|
| Metaphysics |
|
|
|
|
[*]: Generally agreed to be spurious [†]: Authenticity disputed |
The end of the Nicomachean Ethics declared that the inquiry into ethics necessarily follows into politics, and the two works are frequently considered to be parts of a larger treatise--or perhaps connected lectures--dealing with the "philosophy of human affairs". The title of the Politics literally means "the things concerning the polis".
Overview
Structure
Aristotle's Politics is divided into eight books, which are each further divided into chapters. Citations of this work, as with the rest of the works of Aristotle, are often made by referring to the Bekker section numbers. Politics spans the Bekker sections 1252a to 1342b.
Book I
In the first book, Aristotle discusses the city (polis), or as he likes to call it, a "political association" (koinōnia politikē). He states that this city and other cities like it are designed and created with the purpose of achieving happiness or something good. He compares that to the acts of all humans, as he says that all human actions have a positive intention. The highest form of community is the polis (and other cities like it), standing ahead of other political associations such as the household and village. Aristotle comes to this conclusion because he believes the public life is far more virtuous than the private and because people by nature are "political animals". He then goes on to further say that people by nature are worse and more savage than animals.[1] After this Aristotle begins to discus three different types of relationships that can occur in a household which would be the parent to child, husband to wife, and master to slave.
Aristotle discusses the parts of the household (oikos), which includes slaves, leading to a discussion of whether slavery is just and better for the person enslaved or is always unjust and bad. Aristotle defends slavery on the grounds that some people are "natural slaves" by nature and others are naturally leaders or figures of authority. He states that it's better for both parties if one is a slave and the other a master as the master can offer the slave a livelihood. He goes on to further state that slaves aren't rational enough to live and make decisions on their own like the masters so this is the best outcome for them. Aristotle makes an analogy stating that the master to a slave is like a monarch to his people. The monarch serves to help the people by offering them a way of life as long as they stay obedient to the monarch, which he says applies as well to slavery. Only someone as different from other people as the body is from the soul or beasts are from human beings would be a slave by nature, Aristotle concludes, all others being slaves solely by law or convention. Some scholars have therefore concluded that the qualifications for natural slavery preclude the existence of such a being.[2]
Aristotle then moves to the topic of the "Arts of Acquisition", arguing that the acquisition of property does not form a part of household management (oikonomike) and criticizing those who take it too seriously. He defines two words to which he bases his few points off of. These words are natural and unnatural acquisition. Natural acquisition is the ability for one to get basic needs while unnatural acquisition is when one obtains more than they need leading to an overuse of joy, which isn't good or necessary. He claims that the acquisition of property is necessary, but that does not make it a part of household management any more than it makes medicine a part of household management just because health is necessary. He criticizes income based upon trade and upon interest, saying that those who become avaricious do so because they forget that money merely symbolizes wealth without being wealth and "contrary to nature" on interest because it increases by itself not through exchange.
Book I concludes with Aristotle's assertion that the proper object of household rule is the virtuous character of one's wife and children, not the management of slaves or the acquisition of property. Rule over the slaves is despotic, rule over children kingly, and rule over one's wife political (except there is no rotation in office). Aristotle questions whether it is sensible to speak of the "virtue" of a slave and whether the "virtues" of a wife and children are the same as those of a man before saying that because the city must be concerned that its women and children be virtuous, the virtues that the father should instill are dependent upon the regime and so the discussion must turn to what has been said about the best regime. Aristotle also talks about how both the husband and wife are both equal in the sense that they are free in terms of nature but then states that the husband still rules the household over the woman as that is the role to which he is given by nature. He then again compares that to the monarch stating that a king rules while the queen doesn't, though she's free and has power as well.
Book II
Book II examines various views concerning the two different kinds of virtues. These two virtues would be both the intellectual and moral virtues. The difference between these two kinds of virtues would be that a moral virtue is one that is learned by habit and the repetition of it while an intellectual virtue is one that has been taught or instructed to you. For us to be virtuous we must train ourselves and act accordingly as we all are born with the potential to be morally virtuous. Aristotle then discusses the circumstances idea or notion presented by two other philosophers, Phaleas of Chalcedon (2. 7) and Hippodamus of Miletus (2. 8). This talks about the fact that there is no set rule of conducts when it comes to virtue as every person has a different circumstance or situation that engulfs and effects their lives. What this means is that virtue can not be the same for all people as some may have to use or develop it in a different way than another in order to fulfill their circumstances. A specific example discussed in the text would be the idea of courage. Different people would use different amounts of courage in their lives based on how much their lives demand of it. If each person uses the right amount based on their circumstances then they are being equally virtuous though they are using different amounts of courage.
After addressing ideas invented by theorists, Aristotle moves to the examination of three ideas that are commonly held to be well to distinguish people who are actually virtuous versus those who act in a way that makes them look virtuous by accident. These three ideas would be that people who are aware of their correct behavior know they are doing it because they are virtuous, they behave correctly because they want to be virtuous and lastly their behavior becomes a part of their character, not just for the sake of doing it, but because they want to. Aristotle then goes on to compare being virtuous to ones feelings as they both cause people to act in a certain way and make decisions based on that.
Aristotle closes this text by advising three important rules of conduct to ensure one doesn't go too far in the attempt to be virtuous. The first rule would be to avoid extreme action even if it may seem somewhat necessary. The second rule would be to learn the mistakes we make and avoid them so we don't repeat them again. The last rule is to be careful about pleasure and things that are enjoyable as they may hurt your ability to make the correct decisions.
Book III
- Who can be a citizen?
"He who has the power to take part in the deliberative or judicial administration of any state is said by us to be a citizen of that state; and speaking generally, a state is a body of citizens sufficing for the purpose of life. But in practice a citizen is defined to be one of whom both the parents are citizens; others insist on going further back; say two or three or more grandparents." Aristotle asserts that a citizen is anyone who can take part in the governmental process. He finds that most people in the polis are capable of being citizens. This is contrary to the Platonist view, asserting that only very few can take part in the deliberative or judicial administration of the state.[1]
- Classification of constitution and common good.
- Just distribution of political power.
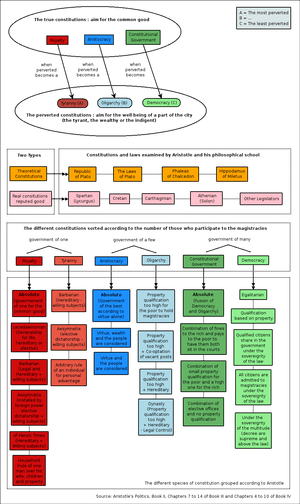
- Types of monarchies:
- Monarchy: exercised over voluntary subjects, but limited to certain functions; the king was a general and a judge, and had control of religion.
- Absolute: government of one for the absolute good
- Barbarian: legal and hereditary + willing subjects
- Dictator: installed by foreign power elective dictatorship + willing subjects (elective tyranny)
Book IV
- Tasks of political theory
- Why are there many types of constitutions?
- Types of democracies
- Types of oligarchies
- Polity (Constitutional Government) – highest form of government
- When perverted, a Polity becomes a Democracy, the least harmful derivative government as regarded by Aristotle.
- Government offices
Book V
- Constitutional change
- Revolutions in different types of constitutions and ways to preserve constitutions
- Instability of tyrannies
Book VI
- Democratic constitutions
- Oligarchic constitutions
Book VII
- Best state and best life
- Ideal state: its population, territory, position, etc.
- Citizens of the ideal state
- Marriage and children
Book VIII
- Education in the ideal state
Classification of constitutions
After studying a number of real and theoretical city-states' constitutions, Aristotle classified them according to various criteria. On one side stand the true (or good) constitutions, which are considered such because they aim for the common good, and on the other side the perverted (or deviant) ones, considered such because they aim for the well being of only a part of the city. The constitutions are then sorted according to the "number" of those who participate to the magistracies: one, a few, or many. Aristotle's sixfold classification is slightly different from the one found in The Statesman by Plato. The diagram above illustrates Aristotle's classification.
Composition
The literary character of the Politics is subject to some dispute, growing out of the textual difficulties that attended the loss of Aristotle's works. Book III ends with a sentence that is repeated almost verbatim at the start of Book VII, while the intervening Books IV–VI seem to have different flavor from the rest; Book IV seems to refer several times back to the discussion of the best regime contained in Books VII–VIII.[3] Some editors have therefore inserted Books VII–VIII after Book III. At the same time, however, references to the "discourses on politics" that occur in the Nicomachean Ethics suggest that the treatise as a whole ought to conclude with the discussion of education that occurs in Book VIII of the Politics, although it is not certain that Aristotle is referring to the Politics here.[4]
Werner Jaeger suggested that the Politics actually represents the conflation of two, distinct treatises.[5] The first (Books I–III, VII–VIII) would represent a less mature work from when Aristotle had not yet fully broken from Plato, and consequently show a greater emphasis on the best regime. The second (Books IV–VI) would be more empirically minded, and thus belong to a later stage of development.
Carnes Lord has argued against the sufficiency of this view, however, noting the numerous cross-references between Jaeger's supposedly separate works and questioning the difference in tone that Jaeger saw between them. For example, Book IV explicitly notes the utility of examining actual regimes (Jaeger's "empirical" focus) in determining the best regime (Jaeger's "Platonic" focus). Instead, Lord suggests that the Politics is indeed a finished treatise, and that Books VII and VIII do belong in between Books III and IV; he attributes their current ordering to a merely mechanical transcription error.[6]
It is uncertain if Politics was translated into Arabic like most of his major works.[7] Its influence and ideas were, however, carried over to Arabic philosophers.[8]
Translations
- Barker, Sir Ernest (1995). The Politics of Aristotle. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-953873-7.
- Jowett, Benjamin (1984). Jonathan Barnes (ed.). Politics. The Complete Works of Aristotle. 2. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-01651-1.
- Lord, Carnes (2013). Aristotle's Politics: Second Edition. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-92183-9.
- Lord, Carnes (1984). The Politics. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-02669-5. (Out of Print)
- Reeve, C. D. C. (1998). Politics. Indianapolis: Hackett. ISBN 978-0-87220-388-4.
- Sachs, Joe (2012). Politics. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Focus. ISBN 978-1585103768.
- Simpson, Peter L. P. (1997). The Politics of Aristotle: Translation, Analysis, and Notes. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 978-0-8078-2327-9.
- Sinclair, T. A. (1981). The Politics. Harmondsworth: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-044421-6.
- Aristotle, Politics
http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Aabo%3Atlg%2C0086%2C035%3A2
- The Internet Classics Archive: Politics By Aristotle
http://classics.mit.edu/Aristotle/politics.2.two.html
- Introduction To Philosophy
Ti Lam - https://courses.lumenlearning.com/sanjacinto-philosophy/chapter/aristotle-politics-book-2/
- The Politics Of Philosophy: A Commentary on Aristotle's Politics
Michael Davis - https://www.questia.com/library/99471794/the-politics-of-philosophy-a-commentary-on-aristotle-s
Notes
- Ebenstein, Alan (2002). Introduction to Political Thinkers. Boston, MA: Wadsworth.
- Nichols, Mary (1992). Citizens and Statesmen. Maryland: Rowman and Little field Publishers, Inc.
- Lord (1982), "Introduction," 15.
- Lord (1982), "Introduction," 19, 246 n. 53.
- Werner Jaeger, Aristoteles: Grundlegung einer Geschichte seiner Entwicklung (1923).
- Lord (1982), "Introduction," 15–16
- Pinès (1986), 47, 56
- Pinès (1986), 56
Works cited
- Lord, Carnes (1982). Education and Culture in the Political Thought of Aristotle. Ithaca: Cornell University Press.
- Pinès, Shlomo (1986). "Aristotle's Politics in Arabic Philosophy". Collected works of Shlomo Pines: Studies in Arabic Versions of Greek texts and in Medieval Science. 2. Jerusalem: The Magnes Press. pp. 146–156. ISBN 965-223-626-8.
- Aristotle, Politics
http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Aabo%3Atlg%2C0086%2C035%3A2
- The Internet Classics Archive: Politics By Aristotle
http://classics.mit.edu/Aristotle/politics.2.two.html
- Introduction To Philosophy
Ti Lam - https://courses.lumenlearning.com/sanjacinto-philosophy/chapter/aristotle-politics-book-2/
- The Politics Of Philosophy: A Commentary on Aristotle's Politics
Michael Davis - https://www.questia.com/library/99471794/the-politics-of-philosophy-a-commentary-on-aristotle-s
- Figure 2f From: Irimia R, Gottschling M (2016) Taxonomic Revision Of Rochefortia Sw. (ehretiaceae, Boraginales). Biodiversity Data Journal 4: E7720. https://doi.org/10.3897/bdj.4.e7720
Further reading
- Aquinas, St. Thomas (2007). Commentary on Aristotle's Politics. Indianapolis: Hackett publishing company, inc.
- Barker, Sir Ernest (1906). The Political Thought of Plato and Aristotle. London: Methuen.
- Davis, Michael (1996). The Politics of Philosophy: A Commentary on Aristotle's Politics. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield.
- Goodman, Lenn E.; Talisse, Robert B. (2007). Aristotle's Politics Today. Albany: State University of New York Press.
- Keyt, David; Miller, Fred D. (1991). A Companion to Aristotle's Politics. Cambridge: Blackwell.
- Kraut, ed., Richard; Skultety, Steven (2005). Aristotle's Politics: Critical Essays. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- Simpson, Peter L. (1998). A Philosophical Commentary on the Politics of Aristotle. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
- Miller, Fred D. (1995). Nature, Justice, and Rights in Aristotle's Politics. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Mayhew, Robert (1997). Aristotle's Criticism of Plato's Republic. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield.
- Strauss, Leo (Ch. 1). The City and Man.
- Salkever, Stephen. Finding the Mean.
- Nussbaum, Martha. The Fragility of Goodness.
- Mara, Gerald. "Political Theory 23 (1995): 280–303". The Near Made Far Away.
- Frank, Jill. A Democracy of Distinction.
- Salkever, Stephen. The Cambridge Companion to Ancient Greek Political Theory.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Politics (Aristotle). |
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
- Aristotle: Politics entry by Edward Clayton in the Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Miller, Fred. "Aristotle's Political Theory". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- Aristotle's Politics on In Our Time at the BBC
Versions
- Politics, full text by Project Gutenberg, trans. by William Ellis
- English translation at Perseus Digital Library, translation by Harris Rackham
- Australian copy, trans. by Benjamin Jowett
- HTML , trans. by Benjamin Jowett
- PDF at McMaster, trans. by Benjamin Jowett

