Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl rhodium dichloride dimer
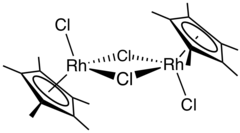
Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl rhodium dichloride is an organometallic compound with the formula [(C5(CH3)5RhCl2)]2, commonly abbreviated [Cp*RhCl2]2 This dark red air-stable diamagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry.[1]
 | |
RhCl2_dimer-2.png) | |
RhCl2_dimer-powder.jpg) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Di-µ-chloro-bis[chloro(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)rhodium(III)] | |
| Other names
Dichloro(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)rhodium(III) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H30Cl4Rh2 | |
| Molar mass | 618.07 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | red solid |
| dichloromethane, chloroform | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H334, H335 |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P285, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P304+341, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P342+311, P362, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Structure and preparation
The compound has idealized C2h symmetry. Each metal centre is pseudo-octahedral.
The compound is prepared by the reaction of rhodium trichloride trihydrate and pentamethylcyclopentadiene in hot methanol, from which the product precipitates:[1]
- 2 Cp*H + 2 RhCl3(H2O)3 [Cp*RhCl2]2 + 2 HCl + 6 H2O
It was first prepared by the reaction of hydrated rhodium trichloride with hexamethyl Dewar benzene[2]
Reactions
Reductive carbonylation gives [Cp*Rh(CO)2].[3]
The Rh-μ-Cl bonds are labile and cleave en route to a variety of adducts of the general formula Cp*RhCl2L. Treatment with silver ions in polar coordinating solvents causes precipitation of silver(I) chloride, leaving a solution containing dications of the form [Cp*RhL3]2+ (L = H2O, MeCN).
The chemistry is similar to that of the analog pentamethylcyclopentadienyl iridium dichloride dimer.
Further reading (early literature)
- Kang, Jung W.; Mosley, K.; Maitlis, Peter M. (1968). "Mechanisms of Reactions of Dewar Hexamethylbenzene with Rhodium and Iridium Chlorides". Chem. Commun. (21): 1304–1305. doi:10.1039/C19680001304.
- Kang, Jung W.; Maitlis, Peter M. (1968). "Conversion of Dewar Hexamethylbenzene to Pentamethylcyclopentadienylrhodium(III) Chloride". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 90 (12): 3259–3261. doi:10.1021/ja01014a063.
- Criegee, Rudolf; Grüner, H. (1968). "Acid-catalyzed Rearrangements of Hexamethyl-prismane and Hexamethyl-Dewar-benzene". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 7 (6): 467–468. doi:10.1002/anie.196804672.
- Kang, Jung W.; Moseley, K.; Maitlis, Peter M. (1969). "Pentamethylcyclopentadienylrhodium and -iridium halides. I. Synthesis and properties". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 91 (22): 5970–5977. doi:10.1021/ja01050a008.
- Herrmann, Wolfgang A.; Zybill, Christian (1996). "Bis{(μ-chloro)[chloro(η-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)rhodium]} — {Rh(μ-Cl)Cl[η-C5(CH3)5]}2". In Herrmann, Wolfgang A.; Salzer, Albrecht (eds.). Synthetic Methods of Organometallic and Inorganic Chemistry – Volume 1: Literature, Laboratory Techniques, and Common Starting Materials. Georg Thieme Verlag. pp. 148–149. ISBN 9783131791610.
- Heck, Richard F. (1974). "Reactions of Dienes Trienes and Tetraenes with Transition Metal Compounds". Organotransition Metal Chemistry: A Mechanistic Approach. Academic Press. pp. 116–117. ISBN 9780323154703.
References
- White, C.; Yates, A.; Maitlis, Peter M. (1992). "(η5-Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)Rhodium and -Iridium Compounds". Inorg. Synth. 29: 228–234. doi:10.1002/9780470132609.ch53.
- Paquette, Leo A.; Krow, Grant R. (1968). "Electrophilic Additions to Hexamethyldewarbenzene". Tetrahedron Lett. 9 (17): 2139–2142. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)89761-0.
- Herrmann, Wolfgang A.; Zybill, Christian (1996). "Dicarbonyl(η-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)rhodium — Rh[η-C5(CH3)5](CO)2". In Herrmann, Wolfgang A.; Salzer, Albrecht (eds.). Synthetic Methods of Organometallic and Inorganic Chemistry – Volume 1: Literature, Laboratory Techniques, and Common Starting Materials. Georg Thieme Verlag. pp. 147–148. ISBN 9783131791610.