Palatoglossus muscle
The palatoglossus, glossopalatinus, or palatoglossal muscle is a small fleshy fasciculus, narrower in the middle than at either end, forming, with the mucous membrane covering its surface, the glossopalatine arch.
| Palatoglossus muscle | |
|---|---|
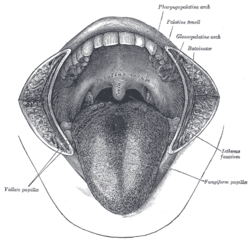 The mouth cavity seen from anterior view. The palatoglossus muscle is beneath the glossopalatine arch (labeled at upper right) | |
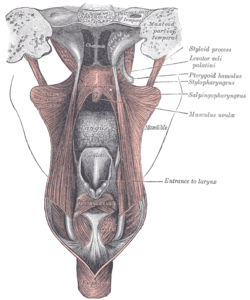 Dissection of the muscles of the palate from behind. (palatoglossus muscle not labeled) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Palatine aponeurosis |
| Insertion | Tongue |
| Nerve | Vagus nerve (via pharyngeal branch to pharyngeal plexus) |
| Actions | Raising the back part of the tongue |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus palatoglossus |
| TA | A05.1.04.110 |
| FMA | 46697 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
Structure
Palatoglossus arises from the palatine aponeurosis of the soft palate,[1] where it is continuous with the muscle of the opposite side, and passing downward, forward, and lateralward in front of the palatine tonsil, is inserted into the side of the tongue, some of its fibers spreading over the dorsum, and others passing deeply into the substance of the organ to intermingle with the transverse muscle of tongue.
Innervation
Palatoglossus is the only muscle of the tongue that is not innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII). It is innervated by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve (CN X).
Controversy
Some sources state that the palatoglossus is innervated by fibers from the cranial part of the accessory nerve (CN XI) that travel via the pharyngeal plexus.[2]
Other sources state that the palatoglossus is not innervated by XI hitchhiking on X, but rather it is innervated by IX via the pharyngeal plexus formed from IX and X.[3]
Function
Elevates posterior tongue, closes the oropharyngeal isthmus, and aids initiation of swallowing. This muscle also prevents the spill of saliva from vestibule into the oropharynx by maintaining the palatoglossal arch.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1139 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Hansen, J.T. (2014) Netter’s Clinical Anatomy. Netter Basic Science. 3rd ed. [online]. Elsevier Health Sciences. Available from: https://books.google.com/books?id=ZL3zAgAAQBAJ
- Section 3, Chapter 35 - Neck and Upper Aerodigestive Tract - Pharynx. In: Standring, S, editors. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, 39th Edition. London: Elsevier; 2008. p628
- Chapter 8 Head and Neck. In: Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AWM, editors. Gray's Anatomy for Students. London: Elsevier; 2005. p991
External links
- "Anatomy diagram: 05287.011-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
.