Levator veli palatini
The levator veli palatini (/lɪˈveɪtər ˈviːlaɪ ˌpæləˈtaɪnaɪ/) is the elevator muscle of the soft palate in the human body. During swallowing, it contracts, elevating the soft palate to help prevent food from entering the nasopharynx. It is innervated via the pharyngeal plexus, primarily by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve (CN X).
| Levator veli palatini | |
|---|---|
 Dissection of the muscles of the palate from behind. (Caption for Levator veli palatini visible at right, second from the top.) | |
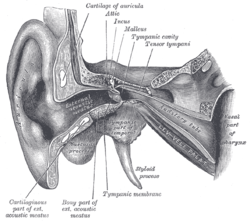 External and middle ear, opened from the front. Right side. (Levator veli palatini visible at bottom right.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | temporal bone, Eustachian tube |
| Insertion | palatine aponeurosis |
| Artery | facial artery |
| Nerve | Pharyngeal Branch of Vagus (CN X) |
| Actions | elevates soft palate |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus levator veli palatini |
| TA | A05.2.01.102 |
| FMA | 46727 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The levator veli palatini (Levator palati) is a thick, rounded muscle situated lateral to the choanæ.
It arises from the under surface of the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone and from the medial lamina of the cartilage of the auditory tube.
After passing above the upper concave margin of the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle it spreads out in the palatine velum, its fibers extending obliquely downward and medially to the middle line, where they blend with those of the opposite side.
Additional images
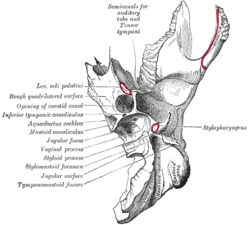 Left temporal bone. Inferior surface.
Left temporal bone. Inferior surface.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1139 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- "Anatomy diagram: 25420.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.