Nurse Licensure Compact
The Nurse Licensure Compact (NLC) is an agreement that allows "mutual recognition" of a nursing license between member states in the United States of America. Enacted into law by the participating states, member states allow a nurse that resides in and possesses a current Compact nursing license in a state that is a member of the NLC, to practice in any of the other member states without obtaining additional licensure in that state. It applies to both registered and practical nurses and is also referred to as a multi-state license.[1]
While a nurse's license may be multi-state, permanent relocation to another Compact state requires obtaining Compact licensure in the new state, as this nurse's residency has changed. Likewise, a license obtained in a Compact state that is not one's primary state of residence is not mutually recognized by the other NLC members.
Participating states
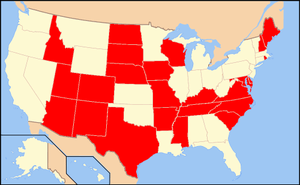
As of July 2020, the NLC states are:
- Alabama
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- Colorado
- Delaware
- Florida
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey (as of 3/24/20-partial implementation)
- New Mexico
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Oklahoma
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Virginia
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
Six other states and Guam, all have active Nurse Licensure Compact bills (Vermont,Pennsylvania,Massachusetts,Michigan,Ohio,and Rhode Island). Connecticut has a "compact study" bill.
References
- "Nurse Licensure Compact (NLC)". National Council of State Boards of Nursing. 2009-11-30. Retrieved 2009-11-30.
External links
- National Council of State Boards of Nursing
- FAQs about the Nursing Licensure Compact at the Texas Board of Nursing
- National Council of State Boards of Nursing. 2009-03-07. Retrieved 2015-03-07