North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways
The North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways (NWNGR) was a railway company that planned to build a number of inter-connected 1 ft 11 1⁄2 in (597 mm) narrow-gauge railways across North Wales. The first two of these lines - jointly known as the "Moel Tryfan Undertaking" - were authorised by Act of Parliament 1872 and were built and opened in the 1870s. The original main line ran from Dinas Junction to Bryngwyn and opened in 1877. The second line was a branch from Tryfan Junction to South Snowdon, though shortly after opening, the company designated the Tryfan Junction to Bryngwyn section as the branch, and the Dinas Junction to South Snowdon section as the main line.
 Map of the NWNGRs | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Locale | Wales |
| Dates of operation | 1877–1916 |
| Successor | Welsh Highland Railway |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 1 ft 11 1⁄2 in (597 mm) |
| Length | 12 1⁄2 miles (20.1 km) |
Routes built
The company completed construction of two lines, The first, opened in 1877, was approximately 3 miles (4.8 km) long, running south-east from a junction with the London and North Western Railway's Caernarfon to Afon Wen branch at Dinas Junction, to Bryngwyn. There were intermediate stations at Tryfan Junction and Rhostryfan. From Bryngwyn, a shallow incline climbed the northern flank of Moel Tryfan. From the top of the incline a number of quarry tramways connected to the Alexandra quarry, Moel Tryfan quarry, Fron quarry, Braich quarry and Cilgwyn quarry.
The second line was opened in stages, and completed in 1881. It connected Tryfan Junction to South Snowdon, a distance of about 5 miles (8.0 km). There were intermediate stations at Waunfawr, Bettws Garmon and Snowdon Ranger. The line from Dinas Junction to South Snowdon was considered the main line from about 1878, with the Tryfan Junction to Bryngwyn section as the branch. South Snowdon station was later renamed Rhyd Ddu.
Routes planned
The line from Dinas Junction to Rhyd Ddu was built and operated, but this was just a small part of the grand scheme for a network of narrow-gauge railways spanning much of north Wales. An Act of Parliament in 1885 authorised an extension northwards to Caernarfon and a Light Railway Order of 1900 authorised an extension southwards to Beddgelert.
A further part of the scheme was the North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways (General Undertaking) which planned a route from Porthmadog to Beddgelert, where it would meet the Rhyd Ddu-Beddgelert extension. From there the line would travel via Capel Curig to Betws-y-Coed. A further branch would have extended the line from Betws y Coed to Cerrig-y-Drudion where the railway would meet the planned Ruthin and Cerrig-y-Drudion Railway.
The General Undertaking was authorised by Act of Parliament in 1872 but officially abandoned in 1876. The section from Porthmadog to Beddgelert was eventually completed by the Welsh Highland Railway as part of its construction, and utilised parts of the Croesor Tramway and the aborted Portmadoc, Beddgelert and South Snowdon Railway (PBSSR) works.
South Snowdon
There are two locations which have been called South Snowdon. One is Rhyd Ddu and the other is the South Snowdon Quarry in the Nant Gwynant Pass and this was the original intended destination of the Portmadoc, Beddgelert and South Snowdon Railway. That company later applied for and received a light railway order to build from Beddgelert to Rhyd Ddu and commenced construction on that section around 1906.
History

The company was formed in 1871, and authorised by the North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways Act of 1872, to build "certain railways in the counties of Carnarvon and Merioneth" and to raise £216,000 in capital. In 1871, the company appointed Charles Easton Spooner, as their chief engineer.[1] Spooner was then the manager of the Festiniog Railway and had been instrumental in the design of their steam locomotives in the 1860s.
By 1876, £66,000 had been raised in capital, the whole amount authorised to pay for the "Moeltryfan Undertaking", but the company needed further capital and applied to Parliament for a second act in April that year. This second Act allowed the company to abandon its "General Undertaking", which would have extended the line to Bettws-y-Coed and beyond.[2] By December of that year, Spooner reported that all but 3 miles (4.8 km) of the line had been built and was "nearly ready to open to traffic" and that mineral traffic would commence immediately.[3]
The line from Dinas Junction to Tryfan Junction and on to Bryngwyn was opened in 1877. In 1878, a branch was built from Tryfan Junction to Snowdon Ranger and this was extended to South Snowdon (later renamed Rhyd Ddu) in 1881. In 1884, the company began the process of relaying the track, upgrading from iron rails weighing 35 lbs per yard, to steel rails weighing 41.5 lbs per yard. At the October 1887 board meeting of the company, a proposal to extend the line from Dinas Junction to Carnarvon was passed unanimously.[4] This extension was never built.
In 1900, the railway company was granted permission for an extension of the main line from South Snowdon to Beddgelert. This was the North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways (Beddgelert Light Railway Extension) Order, which allowed the extension to be built under the Light Railways Act 1896. This extension was not built.
In 1905, the Board of Trade granted permission for the whole railway to convert to a Light Railway under the 1896 Act.[5] In 1906, Sir James Szlumper joined the board of directors, and by 1910 he had been elected Chairman of the board. The 1910 report showed that 6-month net revenues had fallen to £200 amidst a general depression in the country.[6] The difficult financial situation caused the company caused to attempt to find a buyer. In 1910, they approached the London and North Western Railway - who owned the Carnarvon to Afon Wen branch - and negotiations proceeded far enough that the acquisition was announced, but it was not completed.[7]
In 1914, a combined committee of several local authorities applied for a Light Railway Order to combine the NWNGRs with the Portmadoc, Beddgelert & South Snowdon Railway which owned the Croesor Tramway. The accelerating conflict of the First World War stopped this effort. The NWNGRs shut down their passenger services in 1916, and from then on ran a shoestring goods service. In 1918, the application was revived by the owners of the Aluminium Corporation of Dolgarrog which had acquired the Portmadoc, Beddgelert & South Snowdon Railway and was seeking to acquire the NWNGRs. This effort eventually led to the acquisition of the NWNGRs by the Aluminium Corporation and its incorporation into the Welsh Highland Railway in 1922.[8]
Locomotives
| Name | Builder | Type | Date | Works number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snowdon Ranger | Vulcan Foundry | 0-6-4 T | 1875 | 739 | 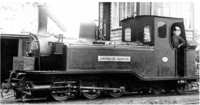 |
| Moel Tryfan | Vulcan Foundry | 0-6-4 T | 1875 | 738 |  |
| Beddgelert | Hunslet | 0-6-4 ST | 1878 | 206 |  Mainly worked the Bryngwyn branch. Scrapped 1906 |
| Russell | Hunslet | 2-6-2 T | 1906 | 901 |  |
| Gowrie | Hunslet | 0-6-4 T | 1908 | 979 | 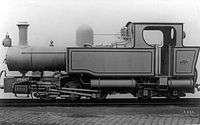 |
| Palmerston | George England | 0-4-0 ST + T | 1867 | unknown |  |
See also
- British narrow-gauge railways
- British narrow-gauge slate railways
- Slate operations on the WHR
References
- "The North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways". North Wales Chronicle. 11 November 1871.
- "North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways". North Wales Chronicle. 15 April 1876.
- "North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways". North Wales Chronicle. 16 December 1876.
- "North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways". North Wales Chronicle. 1 October 1887.
- "General News". Manchester Courier and Lancashire General Advertiser. 19 June 1905.
- "North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways". Cambrian News. 25 March 1910.
- "General News". Sevenoaks Chronicle and Kentish Advertiser. 29 April 1910.
- Johnson, Peter (2017). Festiniog Railway: The Spooner Era and After 1830 - 1920. Pen & Sword Books Limited.
- John Keylock; Michael Bishop (December 2009). "Two into One will go". Welsh Highland Heritage (46).
- "North Wales Narrow Gauge Railway". Locomotive News and Railway Notes. 24 May 1919.
- "The life of "Gowrie"". Welsh Highland Heritage Journal. 38. December 2007.
- Quine, Dan (2013). The George England locomotives of the Ffestiniog Railway. London: Flexiscale.
Further reading
Boyd, James I.C. (1988) [1972]. Narrow Gauge Railways in South Caernarvonshire – Volume 1. Headington: The Oakwood Press. ISBN 978-0-85361-365-7. OCLC 20417464.