Nicotinate dehydrogenase
In enzymology, a nicotinate dehydrogenase (EC 1.17.1.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
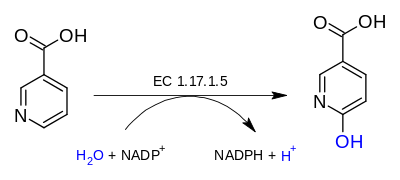
nicotinate + H2O + NADP+ 6-hydroxynicotinate + NADPH + H+
| nicotinate dehydrogenase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 1.17.1.5 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9059-03-4 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The 3 substrates of this enzyme are nicotinate, H2O, and NADP+, whereas its 3 products are 6-hydroxynicotinate, NADPH, and H+.
Classification
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on CH or CH2 groups with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor.
Nomenclature
The systematic name of this enzyme class is nicotinate:NADP+ 6-oxidoreductase (hydroxylating). Other names in common use include nicotinic acid hydroxylase, and nicotinate hydroxylase.
Biological role
This enzyme participates in nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism. It has 2 cofactors: FAD, and Iron.
gollark: Define god first.
gollark: 13.7 billion years.
gollark: http://www.murderousmaths.co.uk/games/ufoattack/dbgoll.gif
gollark: Alternatively,
gollark: Bees. Finite but arbitrarily large quantities of bees.
References
- Holcenberg JS, Stadtman ER (1969). "Nicotinic acid metabolism. 3. Purification and properties of a nicotinic acid hydroxylase". J. Biol. Chem. 244 (5): 1194–203. PMID 4388026.
- Gladyshev VN, Khangulov SV, Stadtman TC (1996). "Properties of the Selenium- and Molybdenum-Containing Nicotinic Acid Hydroxylase from Clostridium barkeri". Biochemistry. 35 (1): 212–23. doi:10.1021/bi951793i. PMID 8555176.
- Gladyshev VN, Khangulov SV, Stadtman TC (1994). "Nicotinic acid hydroxylase from Clostridium barkeri: Electron paramagnetic resonance studies show that selenium is coordinated with molybdenum in the catalytically active selenium-dependent enzyme". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91 (1): 232–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.1.232. PMC 42921. PMID 8278371.
- Dilworth GL (1983). "Occurrence of molybdenum in the nicotinic acid hydroxylase from Clostridium barkeri". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 221 (2): 565–9. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(83)90176-5. PMID 6838209.
- Dilworth GL (1983). "Properties of the selenium-containing moiety of nicotinic-acid hydroxylase from Clostridium barkeri". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 219 (1): 30–38. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(82)90130-8. PMID 7181513.
- Nagel M; Andreesen JR (1990). "Purification and characterization of the molybdoenzymes nicotinate dehydrogenase and 6-hydroxynicotinate dehydrogenase from Bacillus niacini". Arch. Microbiol. 154: 605–613. doi:10.1007/BF00248844.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.