(Methionine synthase) reductase
[Methionine synthase] reductase, or Methionine synthase reductase[1], encoded by the gene MTRR, is an enzyme that is responsible for the reduction of methionine synthase inside human body. This enzyme is crucial for maintaining the one carbon metabolism, specifically the folate cycle. The enzyme employs one coenzyme, flavoprotein.
| [methionine synthase] reductase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 2QTL | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 1.16.1.8 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 207004-87-3 | ||||||||
| Alt. names | MTRR | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Mechanism
MTRR works by catalyzing the following chemical reaction:
- 2 [methionine synthase]-methylcob(I)alamin + 2 S-adenosylhomocysteine + NADP+ 2 [methionine synthase]-cob(II)alamin + NADPH + H+ + 2 S-adenosyl-L-methionine
The 3 products of this enzyme are methionine synthase-methylcob(I)alamin, S-adenosylhomocysteine, and NADP+, whereas its 4 substrates are methionine synthase-cob(II)alamin, NADPH, H+, and S-adenosyl-L-methionine.
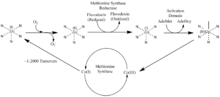
Physiologically speaking, one crucial enzyme participated in the folate cycle is methionine synthase, which incorporated a coenzyme, cobalamin, also known as Vitamin B12. The coenzyme utilizes its cofactor, cobalt to catalyze the transferring function, in which the cobalt will switch between having 1 or 3 valence electrons, dubbed cob(I)alamin, and cob(III)alamin.
Over time, the cob(I)alamin cofactor of methionine synthase becomes oxidized to cob(II)alamin, rendering the enzyme inactive. Therefore, regeneration of the enzyme is necessary. Regeneration requires reductive methylation via a reaction catalyzed by (methionine synthase) reductase in which S-adenosylmethionine is utilized as a methyl donor, reducing cob(II)alamin to cob(I)alamin.[2]
Systematic naming
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, to be specific those oxidizing metal ion with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is [methionine synthase]-methylcob(I)alamin,S-adenosylhomocysteine:NADP+ oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include methionine synthase cob(II)alamin reductase (methylating), methionine synthase reductase, [methionine synthase]-cobalamin methyltransferase (cob(II)alamin, and reducing).
References
- While including parentheses is the correct usage since this denotes the substrate being reduced, it is often omitted as omitting parentheses generally cause no confusion.
- Leclerc, D.; Wilson, A.; Dumas, R.; Gafuik, C.; Song, D.; Watkins, D.; Heng, H. H. Q.; Rommens, J. M.; Scherer, S. W.; Rosenblatt, D. S.; Gravel, R. A. (1998-03-17). "Cloning and mapping of a cDNA for methionine synthase reductase, a flavoprotein defective in patients with homocystinuria". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 95 (6): 3059–3064. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.6.3059. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 19694. PMID 9501215.
- Yamada, Kazuhiro; Roy A. Gravel; Tetsuo Toraya; Rowena G. Matthews (2006-06-20). "Human methionine synthase reductase is a molecular chaperone for human methionine synthase". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 103 (25): 9476–9481. doi:10.1073/pnas.0603694103. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 1480432. PMID 16769880.
- Olteanu H, Banerjee R (2001). "Human methionine synthase reductase, a soluble P-450 reductase-like dual flavoprotein, is sufficient for NADPH-dependent methionine synthase activation". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (38): 35558–63. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103707200. PMID 11466310.
- Olteanu H, Munson T, Banerjee R (2002). "Differences in the efficiency of reductive activation of methionine synthase and exogenous electron acceptors between the common polymorphic variants of human methionine synthase reductase". Biochemistry. 41 (45): 13378–85. doi:10.1021/bi020536s. PMID 12416982.